Abstract
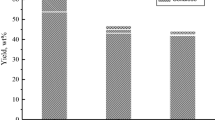
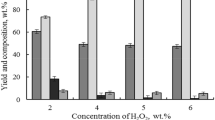
The kinetic study of abies wood delignification by H2O2 in the medium acetic acid–water was first carried out in the presence of TiO2 catalyst under mild conditions: temperatures 70–100 °C, atmospheric pressure. The oxidative delignification process is described satisfactory by the first order equation in all temperature range. The rate constants varied between 0.80 and 12.3 × 10−3 min−1 and the activation energy was near 81 ± 0.21 kJ mol−1. The optimal parameters of the delignification process, providing the effective fractionation of abies wood on microcrystalline cellulose and soluble lignin, were established by experimental and numerical methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Johan G, Fogelbolm CJ (2000) Chemical pulping, papermaking science and technology book 6A. Tappi Press, Finland
Sixta H (2006) Hand book of pulp. Wiley, Weinheim
JiménezL Pérez A, Rodríguez A, de la Torre MJ (2006) New raw materials and pulping processes for production of pulp and paper. Afinidad 63(525):362–369
Rodríguez A, Jiménez L (2008) Pulping with organic solvents other than alcohols. Afinidad 65(535):188–196
Sixta H, Harms H, Dapia S, Parajo JC, Puls J, Saake B, Fink HP, Röder T (2004) Evaluation of new organosolv dissolving pulps. Part I: preparation, analytical characterization and viscose processability. Cellulose 11:73–83
Zhao X, Heide E, Zhang T, Liu D (2010) Delignification of sugarcane bagasse with alkali and peracetic acid and characterization of the pulp. Bioresources 5:1565–1580
López F, Alfaro A, Jiménez L, Rodríguez A (2006) Alcohols as organic solvents for obtainment of cellulose pulp. Afinidad 523:174–182
Villaverde JJ, Ligero P, Vega A (2015) Fractionation of Miscanthus x Giganteus via modification of the Formacell process. Ind Crops Prod 77:275–281
Ligero P, Vega A, Villaverde JJ (2010) Delignification of Miscanthus x Giganteus by the Milox process. Bioresour Technol 101:3188–3193
Suchy M, Argyropoulos D (2001) Catalysis and activation of oxygen and peroxi dedelignification of chemical pulps: a review. ACS Symp Ser 785:2–43
SongYo Wi SG, Kim HM, Bae HJ (2016) Cellulosic bioethanol production from Jerusalem artichoke (Helianthus tuberosus L.) using hydrogen peroxide-acetic acid (HPAC) pretreatment. Bioresour Technol 214:30–36
Dussan K, Girisuta B, Haverty D, Leahy JJ, Hayes MH (2014) The effect of hydrogen peroxide concentration and solid loading on the fractionation of biomass in formic acid. Carbohydr Polym 111:374–384
Das S, Lachenal D, Marlin N (2013) Production of pure cellulose from Kraft pulp by a totally chlorine-free process using catalyzed hydrogen peroxide. Ind Crops Prod 49:844–850
Ramadoss G, Muthukumar K (2015) Influence of dual salt on the pretreatment of sugarcane bagasse with hydrogen peroxide for bioethanol production. Chem Eng J 260:178–187
Gaspar AR, Gamelas JAF, EvtuguinD NetoCP (2007) Alternatives for lignocellulosic pulp delignification using polyoxometalates and oxygen: a review. Green Chem 9:717–730
Popova NR, Tortseva TV, Bogolitsyn KG (2013) Catalytic delignification of cellulose fibers by hydrogen peroxide in presence of polyoxometalates. Russ J Appl Chem 86:1275–1279
Kuznetsov BN, Kuznetsova SA, Danilov VG, Yatsenkova OV, Petrov AV (2011) A green one-step process of obtaining microcrystalline cellulose by catalytic oxidation of wood. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 104:337–343
Kuznetsov BN, Kuznetsova SA, Danilov VG, Yatsenkova OV (2008) Catalytic properties of TiO2 in wood delignification by acetic acid–hydrogen peroxide mixture. React Kinet Catal Lett 94:311–317
Kuznetsov BN, Kuznetsova SA, Danilov VG, Yatsenkova OV (2009) Influence of UV pretreatment on the abies wood catalytic delignification in the medium “acetic acid–hydrogen peroxide–TiO2”. React Kinet Catal Lett 97:295–300
Fernández-Rodrígueza C, Dona-Rodrígueza JM, González-Díaza O, Secka I, Zerbani D, Portillob D, Perez-Pena J (2012) Synthesis of highly photoactive TiO2 and Pt/TiO2 nanocatalysts for substrate-specific photocatalytic applications. Appl Catal B 125:383–389
Hu F, Jung S, Radauskas A (2012) Pseudo-lignin formation and its impact on enzymatic hydrolysis. Bioresour Technol 117:7–12
Kuznetsov BN, Sudakova IG, Garyntseva NV, Djakovitch L, Pinel C (2013) Kinetic study of aspen-wood sawdust delignification by H2O2 with sulfuric acid catalyst under mild conditions. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 110:271–280
Sjoöstroöm E, Aleŕn R (1999) Analytical methods in wood chemistry pulping and papermaking, Springer, Berlin
Park S, Baker JO, Himmel ME, Parilla PA, Jonson DK (2010) Cellulose crystallinity index: measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulose performance. Biotechnol Biofuels 3:10
Lente G (2015) Deterministic kinetics in chemistry and systems biology. Springer, New York. ISBN 978-3-319-15481-7
Sudakova IG, Garyntseva NV, Yatsenkova OV, Kuznetsov BN (2013) Optimization of aspen wood delignification by H2O2 with sulfuric acid catalyst. J Sib Fed Univ Chem 6:76–84
Adel AM, El-Wahab ZH, Ibrahim AA, Al-Shemy MT (2011) Characterization of microcrystalline cellulose prepared from lignocellulosic materials part II: physicochemical properties. Carbohydr Polym 83:676–687
Fan M, Dai D, Huang B (2012) Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy for natural fibres. In: SalihSalih (ed) Fourier transform—materials analysis. In Tech, Rijeka. doi:10.5772/35482
Xiang LY, Mohammed MAP, Baharuddin AS (2016) Characterisation of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm fibers for food applications. Carbohydr Polym 148:11–20
Shankar S, Rhim JW (2016) Preparation of nanocellulose from microcrystalline cellulose: the effect on the performance and properties of agar based composite films. Carbohydr Polym 135:18–26
Yuvraj P, Chauhan RS, Sapkal VS, Zamre GS (2009) Microcrystalline cellulose from cotton rags (Waste from garment and hosiery industries. Int J Chem Sci 7:681–688
Moran JI, Alvarez VA, Cyras VP, Vazquez A (2008) Extraction of cellulose and preparation of nanocellulose from sisal fibers. Cellulose 15:149–159
Wikberg H, Maunu SL (2004) Characterization of thermally modified hard- and softwoods by 13C CPMAS NMR. Carbohydr Polym 58:461–466
Zuckerstätter G, Schild G, Wollboldt P, Röder T, Weber HK, Sixta H (2009) The elucidation of cellulose supramolecular structure by 13C CP-MAS NMR. Lenzing Ber 87:38–46
Garyntseva NV, Sudakova IG, Kuznetsov BN (2015) Study of birch wood catalytic delignification by hydrogen peroxide at atmospheric pressure. J Sib Fed Univ. Chem 8:422–429
Ma R, XuYa Zhang X (2015) Catalytic oxidation of biorefinery lignin to value-added chemicals to support sustainable biofuel production. ChemSusChem 8:24–51
Kuznetsov BN, Tarabanko VE, Kuznetsova SA (2008) New catalytic methods for obtaining cellulose and other chemical products from vegetable biomass. Kinet Catal 49:517–526
Acknowledgements
The reported study was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Grant No. 16-13-10326).NMR experiments were conducted on BrukerAvance III spectrometer at Krasnoyarsk Regional Centre of Research Equipment SB RAS. The authors wish to thank Alexander Kondrasenko for the help with NMR experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuznetsov, B.N., Sudakova, I.G., Garyntseva, N.V. et al. Kinetic studies and optimization of abies wood fractionation by hydrogen peroxide under mild conditions with TiO2 catalyst. Reac Kinet Mech Cat 120, 81–94 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-016-1100-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-016-1100-z