Abstract
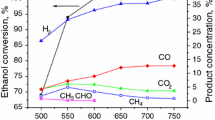
In this paper, we have studied the effect of the synthesis method on the acidity of alumina (Al2O3) support using NH3 chemisorption and impregnated Rh on the Al2O3 support having lower acidity to yield Rh/Al2O3 catalyst. These materials were characterized using different physico-chemical techniques such as BET, XRD, SEM–EDS, TPR, CO pulse chemisorption, and TPO reactions. The performance of the Rh/Al2O3 catalyst was evaluated in catalytic ESR reaction at varying temperatures and space velocities. Our studies revealed that the Rh/Al2O3 catalyst is capable of breaking the C–C bond with a complete elimination of C2 compounds, particularly ethylene in the exit product stream with high H2 yield under the reaction conditions applied. Furthermore, the nature of intermediate species and products formed during catalytic ESR conditions was identified using in situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy (DRIFTS), which revealed that both the acetate driven and formate driven mechanism of ESR prevail over the surface of the prepared catalyst. In view of the absence of ethylene in the product stream as well as in the DRIFT study, it was concluded that due to the inherent lower acidity of the alumina support, ethanol molecules prefer the dehydrogenation route over dehydration. DRIFT studies also brought out the significant role of Rh towards aiding ethanol decomposition. Based on these studies, a plausible mechanism for catalytic ESR reaction over Rh/Al2O3 has been proposed. Time-on-stream studies revealed the good stability of the catalyst over extended periods (~20 h).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schrope M (2001) Which way to energy utopia? Nature 414(6865):682–684
Semelsberger TA, Ott KC, Borup RL, Greene HL (2006) Generating hydrogen-rich fuel-cell feeds from dimethyl ether (DME) using physical mixtures of a commercial Cu/Zn/Al2O3 catalyst and several solid–acid catalysts. Appl Catal B 65(3–4):291–300. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.02.015
Navarro RM, Peña MA, Fierro JLG (2007) Hydrogen production reactions from carbon feedstocks: fossil fuels and biomass. Chem Rev 107(10):3952–3991. doi:10.1021/cr0501994
Xuan J, Leung MKH, Leung DYC, Ni M (2009) A review of biomass-derived fuel processors for fuel cell systems. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 13(6–7):1301–1313. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.09.027
Frusteri F, Freni S (2007) Bio-ethanol, a suitable fuel to produce hydrogen for a molten carbonate fuel cell. J Power Sources 173(1):200–209. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.04.065
Ni M, Leung DYC, Leung MKH (2007) A review on reforming bio-ethanol for hydrogen production. Int J Hydrog Energy 32(15):3238–3247. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2007.04.038
Vaidya PD, Rodrigues AE (2006) Insight into steam reforming of ethanol to produce hydrogen for fuel cells. Chem Eng J 117(1):39–49. doi:10.1016/j.cej.2005.12.008
Mattos LV, Jacobs G, Davis BH, Noronha FB (2012) Production of hydrogen from ethanol: review of reaction mechanism and catalyst deactivation. Chem Rev 112(7):4094–4123. doi:10.1021/cr2000114
Haryanto A, Fernando S, Murali N, Adhikari S (2005) Current status of hydrogen production techniques by steam reforming of ethanol: a review. Energy Fuels 19(5):2098–2106. doi:10.1021/ef0500538
Bshish A, Yaakob Z, Narayanan B, Ramakrishnan R, Ebshish A (2011) Steam-reforming of ethanol for hydrogen production. Chem Pap 65(3):251–266. doi:10.2478/s11696-010-0100-0
Zhang C, Yue H, Huang Z, Li S, Wu G, Ma X, Gong J (2013) Hydrogen production via steam reforming of ethanol on phyllosilicate-derived Ni/SiO2: enhanced metal-support interaction and catalytic stability. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 1(1):161–173. doi:10.1021/sc300081q
Barroso M, Gomez M, Arrúa L, Abello M (2015) Effect of the water–ethanol molar ratio in the ethanol steam reforming reaction over a Co/CeO2/MgAl2O4 catalyst. Reac Kinet Mech Catal. doi:10.1007/s11144-015-0852-1
Lakhapatri SL, Abraham MA (2009) Deactivation due to sulfur poisoning and carbon deposition on Rh-Ni/Al2O3 catalyst during steam reforming of sulfur-doped n-hexadecane. Appl Catal A 364(1–2):113–121. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2009.05.035
Sheng PY, Yee A, Bowmaker GA, Idriss H (2002) H2 production from ethanol over Rh–Pt/CeO2 catalysts: the role of Rh for the efficient dissociation of the carbon-carbon bond. J Catal 208(2):393–403. doi:10.1006/jcat.2002.3576
Diagne C, Idriss H, Kiennemann A (2002) Hydrogen production by ethanol reforming over Rh/CeO2–ZrO2 catalysts. Catal Commun 3(12):565–571. doi:10.1016/S1566-7367(02)00226-1
Sanchez-Sanchez MC, Yerga RMN, Kondarides DI, Verykios XE, Fierro JLG (2010) Mechanistic aspects of the ethanol steam reforming reaction for hydrogen production on Pt, Ni, and PtNi catalysts supported on gamma-Al2O3. J Phys Chem A 114(11):3873–3882
Sheng PY, Bowmaker GA, Idriss H (2004) The reactions of ethanol over Au/CeO2. Appl Catal A 261(2):171–181. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2003.10.046
Raskó J, Hancz A, Erdőhelyi A (2004) Surface species and gas phase products in steam reforming of ethanol on TiO2 and Rh/TiO2. Appl Catal A 269(1–2):13–25. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2004.03.053
Schmal M, Cesar DV, Souza MMVM, Guarido CE (2011) Drifts and TPD analyses of ethanol on Pt catalysts over Al2O3 and ZrO2—partial oxidation of ethanol. Can J Chem Eng 89(5):1166–1175. doi:10.1002/cjce.20597
Erdőhelyi A, Raskó J, Kecskés T, Tóth M, Dömök M, Baán K (2006) Hydrogen formation in ethanol reforming on supported noble metal catalysts. Catal Today 116(3):367–376. doi:10.1016/j.cattod.2006.05.073
Yee A, Morrison SJ, Idriss H (1999) A study of the reactions of ethanol on CeO2 and Pd/CeO2 by steady state reactions, temperature programmed desorption, and in situ FT-IR. J Catal 186(2):279–295. doi:10.1006/jcat.1999.2563
Yee A, Morrison SJ, Idriss H (2000) A study of ethanol reactions over Pt/CeO2 by temperature-programmed desorption and in situ FT-IR spectroscopy: evidence of benzene formation. J Catal 191(1):30–45. doi:10.1006/jcat.1999.2765
Yee A, Morrison SJ, Idriss H (2000) The reactions of ethanol over M/CeO2 catalysts: evidence of carbon–carbon bond dissociation at low temperatures over Rh/CeO2. Catal Today 63(2–4):327–335. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(00)00476-4
da Silva AM, de Souza KR, Jacobs G, Graham UM, Davis BH, Mattos LV, Noronha FB (2011) Steam and CO2 reforming of ethanol over Rh/CeO2 catalyst. Appl Catal B 102(1–2):94–109. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.11.030
de Lima SM, Silva AM, Graham UM, Jacobs G, Davis BH, Mattos LV, Noronha FB (2009) Ethanol decomposition and steam reforming of ethanol over CeZrO2 and Pt/CeZrO2 catalyst: reaction mechanism and deactivation. Appl Catal A 352(1–2):95–113. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2008.09.040
de Lima SM, da Silva AM, da Costa LOO, Assaf JM, Jacobs G, Davis BH, Mattos LV, Noronha FB (2010) Evaluation of the performance of Ni/La2O3 catalyst prepared from LaNiO3 perovskite-type oxides for the production of hydrogen through steam reforming and oxidative steam reforming of ethanol. Appl Catal A 377(1–2):181–190. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2010.01.036
Trueba M, Trasatti SP (2005) γ-Alumina as a support for catalysts: a review of fundamental aspects. Eur J Inorg Chem 17:3393–3403. doi:10.1002/ejic.200500348
Devianto H, Li ZL, Yoon SP, Han J, Nam SW, Lim T-H, Lee H-I (2010) The effect of Al addition on the prevention of Ni sintering in bio-ethanol steam reforming for molten carbonate fuel cells. Int J Hydrog Energy 35(7):2591–2596. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.04.001
Llorca J, Piscina PRdl, Sales J, Homs N (2001) Direct production of hydrogen from ethanolic aqueous solutions over oxide catalysts. Chem Commun 7:641–642. doi:10.1039/b100334h
Morterra C, Zecchina A, Coluccia S, Chiorino A (1977) I.r. spectroscopic study of CO2 adsorption onto [small eta]-Al2O3. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 1 73:1544–1560. doi:10.1039/f19777301544
Can F, Le Valant A, Bion N, Epron F, Duprez D (2008) New active and selective Rh–REOx–Al2O3 catalysts for ethanol steam reforming. J Phys Chem C 112(36):14145–14153. doi:10.1021/jp801954s
Freni S (2001) Rh based catalysts for indirect internal reforming ethanol applications in molten carbonate fuel cells. J Power Sources 94(1):14–19. doi:10.1016/S0378-7753(00)00593-0
Cavallaro S, Chiodo V, Freni S, Mondello N, Frusteri F (2003) Performance of Rh/Al2O3 catalyst in the steam reforming of ethanol: H2 production for MCFC. Appl Catal A 249(1):119–128. doi:10.1016/S0926-860X(03)00189-3
Breen JP, Burch R, Coleman HM (2002) Metal-catalysed steam reforming of ethanol in the production of hydrogen for fuel cell applications. Appl Catal B 39(1):65–74. doi:10.1016/S0926-3373(02)00075-9
Idriss H (2004) Ethanol reactions over the surfaces of noble metal/cerium oxide catalysts. Platin Met Rev 48(3):11
Wang J-H, Lee CS, Lin MC (2009) Mechanism of ethanol reforming: theoretical foundations. J Phys Chem C 113(16):6681–6688. doi:10.1021/jp810307h
Kowal A, Li M, Shao M, Sasaki K, Vukmirovic MB, Zhang J, Marinkovic NS, Liu P, Frenkel AI, Adzic RR (2009) Ternary Pt/Rh/SnO2 electrocatalysts for oxidizing ethanol to CO2. Nat Mater 8(4):325–330. doi: http://www.nature.com/nmat/journal/v8/n4/suppinfo/nmat2359_S1.html
Hung C-C, Chen S-L, Liao Y-K, Chen C-H, Wang J-H (2012) Oxidative steam reforming of ethanol for hydrogen production on M/Al2O3. Int J Hydrog Energy 37(6):4955–4966. doi:10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.12.060
Auprêtre F, Descorme C, Duprez D (2002) Bio-ethanol catalytic steam reforming over supported metal catalysts. Catal Commun 3(6):263–267. doi:10.1016/S1566-7367(02)00118-8
Aupretre F, Descorme C, Duprez D, Casanave D, Uzio D (2005) Ethanol steam reforming over MgxNi1−xAl2O3 spinel oxide-supported Rh catalysts. J Catal 233(2):464–477. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2005.05.007
Ferencz Z, Erdőhelyi A, Baán K, Oszkó A, Óvári L, Kónya Z, Papp C, Steinrück HP, Kiss J (2014) Effects of support and Rh additive on co-based catalysts in the ethanol steam reforming reaction. ACS Catal 4(4):1205–1218. doi:10.1021/cs500045z
Varga E, Ferencz Z, Oszkó A, Erdőhelyi A, Kiss J (2015) Oxidation states of active catalytic centers in ethanol steam reforming reaction on ceria based Rh promoted Co catalysts: an XPS study. J Mol Catal A 397:127–133. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2014.11.010
Sharma PK, Saxena N, Bhatt A, Rajagopal C, Roy PK (2013) Synthesis of mesoporous bimetallic Ni-Cu catalysts supported over ZrO2 by a homogenous urea coprecipitation method for catalytic steam reforming of ethanol. Catal Sci Technol 3(4):1017–1026. doi:10.1039/c2cy20563g
Taspinar E, Tas AC (1997) Low-temperature chemical synthesis of lanthanum monoaluminate. J Am Ceram Soc 80(1):133–141. doi:10.1111/j.1151-2916.1997.tb02801.x
Marcelino JEM, Granados-Correa F, Pfeiffer H, Bulbulian S (2012) Synthesis of MgO, ZnO and Al2O3 by solid and solution combustion processes and study of their performances in Co2+ uptake. Ceramics-Silikáty 56(3):254–260
Geyer R, Hunold J, Keck M, Kraak P, Pachulski A, Schödel R (2012) Methods for determining the metal crystallite size of Ni supported catalysts. Chem Ing Tech 84(1–2):160–164. doi:10.1002/cite.201100101
Souza MCP, Lenzi GG, Colpini LMS, Jorge LMM, Santos OAA (2011) Photocatalytic discoloration of reactive blue 5 g dye in the presence of mixed oxides and with the addition of iron and silver. Braz J Chem Eng 28:393–402
Vis JC, van ‘t Blik HFJ, Huizinga T, van Grondelle J, Prins R (1985) The morphology of rhodium supported on TiO2 and Al2O3 as studied by temperature-programmed reduction-oxidation and transmission electron microscopy. J Catal 95(2):333–345. doi:10.1016/0021-9517(85)90111-3
Hwang C-P, Yeh C-T, Zhu Q (1999) Rhodium-oxide species formed on progressive oxidation of rhodium clusters dispersed on alumina. Catal Today 51(1):93–101. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(99)00011-5
Basile F, Fornasari G, Gazzano M, Kiennemann A, Vaccari A (2003) Preparation and characterisation of a stable Rh catalyst for the partial oxidation of methane. J Catal 217(2):245–252. doi:10.1016/S0021-9517(03)00021-6
Patel M, Jindal TK, Pant KK (2013) Kinetic study of steam reforming of ethanol on Ni-based Ceria-Zirconia catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 52(45):15763–15771. doi:10.1021/ie401570s
Fajardo HV, Probst LFD (2006) Production of hydrogen by steam reforming of ethanol over Ni/Al2O3 spherical catalysts. Appl Catal A 306:134–141. doi:10.1016/j.apcata.2006.03.043
Hussein GAM, Sheppard N, Zaki MI, Fahim RB (1991) Infrared spectroscopic studies of the reactions of alcohols over group IVB metal oxide catalysts. Part 3. Ethanol over TiO2, ZrO2 and HfO2, and general conclusions from parts 1 to 3. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 87(16):2661–2668. doi:10.1039/ft9918702661
Binet C, Daturi M, Lavalley J-C (1999) IR study of polycrystalline ceria properties in oxidised and reduced states. Catal Today 50(2):207–225. doi:10.1016/S0920-5861(98)00504-5
Mattos LV, Noronha FB (2005) Partial oxidation of ethanol on supported Pt catalysts. J Power Sources 145(1):10–15. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.12.034
Mattos LV, Noronha FB (2005) The influence of the nature of the metal on the performance of cerium oxide supported catalysts in the partial oxidation of ethanol. J Power Sources 152:50–59. doi:10.1016/j.jpowsour.2004.12.052
Knoezinger H, Stuebner B (1978) Adsorption of alcohols on alumina. 1. Gravimetric and infrared spectroscopic investigation. J Phys Chem 82(13):1526–1532. doi:10.1021/j100502a013
Benítez JJ, Carrizosa I, Odriozola JA (1995) In situ diffuse reflectance infrared (DRIFTS) identification of active sites in the CO + H2 reaction over lanthanide-modified Rh/Al2O3 catalysts. Appl Surf Sci 84(4):391–399. doi:10.1016/0169-4332(94)00568-0
Greenler RG (1962) Infrared study of the adsorption of methanol and ethanol on aluminum oxide. J Chem Phys 37(9):2094–2100. doi:10.1063/1.1733430
Kagel RO (1967) Infrared investigation of the adsorption and surface reactions of the C1 through C4 normal alcohols on γ -alumina. J Phys Chem 71(4):844–850. doi:10.1021/j100863a010
Sanchez-Sanchez MC, Navarro Yerga RM, Kondarides DI, Verykios XE, Fierro JLG (2010) Mechanistic aspects of the ethanol steam reforming reaction for hydrogen production on Pt, Ni, and PtNi catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3. J Phys Chem A 114(11):3873–3882. doi:10.1021/jp906531x
Knözinger H, Ratnasamy P (1978) Catalytic aluminas: surface models and characterization of surface sites. Catal Rev 17(1):31–70. doi:10.1080/03602457808080878
Harrison B, Diwell AF, Hallett C (1988) Promoting platinum metals by ceria metal -support interactions in autocatalysts. Platin Met Rev 32(2):73–83
Chen L, Choong CKS, Zhong Z, Huang L, Ang TP, Hong L, Lin J (2010) Carbon monoxide-free hydrogen production via low-temperature steam reforming of ethanol over iron-promoted Rh catalyst. J Catal 276(2):197–200. doi:10.1016/j.jcat.2010.08.018
Laosiripojana N, Assabumrungrat S (2006) Catalytic steam reforming of ethanol over high surface area CeO2: the role of CeO2 as an internal pre-reforming catalyst. Appl Catal B 66(1–2):29–39. doi:10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.01.011
Duprez D, Hadj-Aissa M, Barbier J (1989) Effect of steam on the coking of platinum catalysts: I. Inhibiting effect of steam at low partial pressure for the dehydrogenation of cyclopentane and the coking reaction. Appl Catal 49(1):67–74. doi:10.1016/S0166-9834(00)81422-0
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Director, CFEES for providing the laboratory facilities. The authors are also thankful to SSPL, Delhi for carrying out XRD analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, P.K., Saxena, N., Roy, P.K. et al. Hydrogen generation from ethanol by steam reforming using a Rh catalyst supported over low acidic Al2O3 . Reac Kinet Mech Cat 117, 655–674 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-015-0959-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-015-0959-4