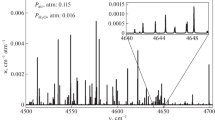
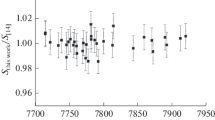
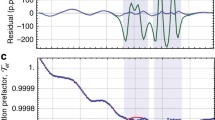
An important physical problem of supplying the Earth's atmosphere satellite monitoring with precise laboratory measurements of the line constants of atmospheric gases has been resolved. We developed a complex of spectrometers and techniques which improves the accuracy of line-constant measurements by about an order of magnitude. Systematic errors of measurements do not exceed the statistical ones. Agreement of the results obtained by two different spectrometers improves reliability of the measured constants. Examples of measurements of collisional constants (broadening, shift, and collisional coupling) for the most important diagnostic atmospheric lines of water and oxygen molecules are presented. A number of collisional constants of the molecules are obtained for the first time and some errors of the previous researchers are corrected. The measured parameters have been used for the international projects. Prospects for supplying planned satellite terahertz projects with precise laboratory data are pointed out.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. C. Pumphrey and S. Buehler, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 64, 421 (2000).
A. F. Krupnov, G. Yu. Golubiatnikov, V. N. Markov, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 215, 309 (2002).
H. M. Pickett, E. A. Cohen, and D. E. Brinza, Astrophys. J., 248, L49 (1981).
J. Urban, N. Lautie, D. Murtagh, et al., Proc. Int. Workshop on Critical Evaluation of mm/sub-mm-Wave Spectroscopic Data for Atmospheric Observations, Ibaraki, Japan (2004), p. 69.
A. F. Krupnov, Vestnik Akad. Nauk SSSR, 7, 18 (1978).
A. F. Krupnov, M. Yu. Tretyakov, V. V. Parshin, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 202, 107 (2000).
J. B. Rusk, J. Chem. Phys., 42, 493 (1965).
Yu. A. Dryagin, A. G. Kislyakov, L. M. Kukin, et al., Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 9, No. 6, 624 (1966).
L. Frenkel and D. Woods. Proc. IEEE, 54, 498 (1966).
C. O. Hemmi and A. W. Straiton, Radio Sci., 4, 9 (1969).
V. Ya. Ryadov and N. I. Furashov, Radiophys. Quantum Electron., 18, No. 3, 256 (1975).
A. Bauer, M. Godon, and B. Duterage, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 33, 167 (1985).
A. Bauer, M. Godon, M. Kheddar, and J. M. Hartmann, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 41, 49 (1989).
T. M. Goyette and F. C. De Lucia, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 143, 346 (1990).
M. Yu. Tretyakov, V. V. Parshin, M. A. Koshelev, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 218, 239 (2003).
G. Yu. Golubiatnikov, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 230, 196 (2005).
G. Yu. Golubiatnikov, M. A. Koshelev, and A. F. Krupnov, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 222, 191 (2003).
M. Yu. Tretyakov, M. A. Koshelev, V. V. Dorovskikh, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 231, 1 (2005).
G. Yu. Golubiatnikov and A. F. Krupnov, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 217, 282 (2003).
M. Yu. Tretyakov, G. Yu. Golubiatnikov, V. V. Parshin, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 223, 31 (2004).
M. A. Koshelev, M. Yu. Tretyakov, G. Yu. Golubiatnikov, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 241, 101 (2007).
A. E. Schulze and C. W. Tolbert, Nature, 200, 747 (1963).
H. Liebe, R. W. Rosenkranz, and G. A. Hufford, J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transfer, 48, 629 (1992).
E. W. Smith, J. Chem. Phys., 74, 6658 (1981).
A. Perrin, C. Puzzarini, J. M. Colmont, et al., J. Atm. Chem., 51, 161 (2005).
L. S. Rothman, N. Jacquinet-Husson, C. Boulet, et al., C. R. Physique, 6, 897 (2005).
http://eospso.gsfc.nasa.gov/ftp_docs/validation/Cohen_Report_04.pdf.
M. Yu. Tretyakov, V. V. Parshin, M. A. Koshelev, et al., J. Mol. Spectrosc., 238, 91 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Izvestiya Vysshikh Uchebnykh Zavedenii, Radiofizika, Vol. 51, No. 9, pp. 789–794, September 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tretyakov, M.Y., Golubiatnikov, G.Y., Parshin, V.V. et al. Obtaining precise constants of atmospheric lines in the millimeter and submillimeter wavelength ranges. Radiophys Quantum El 51, 713–717 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-008-9074-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11141-008-9074-y