Abstract
Purpose
Children of parents with mental health problems (CPM) have an increased risk for impaired health-related quality of life (HRQoL). This study aims at investigating the age- and gender-specific course of HRQoL and at exploring predictors of HRQoL in CPM based on longitudinal data (baseline, 1-year and 2-year follow-up) of a German population-based sample.
Methods
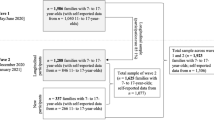
Longitudinal data from the German BELLA study was analyzed (n = 1429; aged 11 to 17 years at baseline). The SCL-S-9 in combination with the cutoff for the General Severity Index (GSI) from the longer SCL-90-R served to identify CPM (n = 312). At first, we compared domain-specific HRQoL according to the KIDSCREEN-27 in CPM versus Non-CPM. Focusing on CPM, we used individual growth modeling to investigate the age and gender-specific course, and to explore effects of risk and (personal, familial and social) resource factors on self-reported HRQoL in CPM.
Results
Self-reported HRQoL was reduced in CPM compared to Non-CPM in all domains, but in social support & peers. However, a minimal important difference was only reached in girls for the domain autonomy & parent relation. Internalizing and externalizing mental health problems were associated with impaired HRQoL in CPM. Self-efficacy, social support and family climate were identified as significant resources, but parental mental health problems over time were not associated with any investigated domain of HRQoL in CPM.
Conclusions
Adolescent female CPM may be especially at risk for reduced HRQoL. When developing support programs for CPM, self-efficacy, social support and family climate should be considered, HRQoL and mental health problems in CPM should be addressed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plass-Christl, A., Haller, A. C., Otto, C., Barkmann, C., Wiegand-Grefe, S., Holling, H., et al. (2017). Parents with mental health problems and their children in a German population based sample: Results of the BELLA study. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180410.
Goodman, S. H., Rouse, M. H., Connell, A. M., Broth, M. R., Hall, C. M., & Heyward, D. (2011). Maternal depression and child psychopathology: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 14(1), 1–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-010-0080-1.
van Santvoort, F., Hosman, C. M. H., Janssens, J., van Doesum, K. T. M., Reupert, A., & van Loon, L. M. A. (2015). The impact of various parental mental disorders on children’s diagnoses: A systematic review. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 18(4), 281–299. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-015-0191-9.
Hagen, K. A., Hilsen, M., Kallander, E. K., & Ruud, T. (2019). Health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in children of ill or substance abusing parents: Examining factor structure and sub-group differences. Quality of Life Research, 28(4), 1063–1073. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-2067-1.
Oltean, I. I., & Ferro, M. A. (2019). Agreement of child and parent-proxy reported health-related quality of life in children with mental disorder. Quality of Life Research, 28(3), 703–712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-018-2026-x.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Erhart, M., Wille, N., Wetzel, R., Nickel, J., & Bullinger, M. (2006). Generic health-related quality-of-life assessment in children and adolescents: Methodological considerations. Pharmacoeconomics, 24(12), 1199–1220.
Ellert, U., Ravens-Sieberer, U., Erhart, M., & Kurth, B. M. (2011). Determinants of agreement between self-reported and parent-assessed quality of life for children in Germany-results of the German Health Interview and Examination Survey for Children and Adolescents (KiGGS). Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 9, 102. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-9-102.
Ellert, U., Brettschneider, A. K., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (2014). Health-related quality of life in children and adolescents in Germany. Results of the KiGGS study: first follow-up (KiGGS Wave 1). Bundesgesundheitsblatt-Gesundheitsforschung-Gesundheitsschutz, 57(7), 798–806. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00103-014-1978-4.
Baumgarten, F., Cohrdes, C., Schienkiewitz, A., Thamm, R., Meyrose, A. K., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (2019). Health-related quality of life and its relation to chronic diseases and mental health problems among children and adolescents. Results from KiGGS Wave 2. Bundesgesundheitsblatt-Gesundheitsforschung-Gesundheitsschutz, 62(10), 1205–1214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00103-019-03006-9.
Giannakopoulos, G., Dimitrakaki, C., Pedeli, X., Kolaitis, G., Rotsika, V., Ravens-Sieberer, U., et al. (2009). Adolescents’ wellbeing and functioning: Relationships with parents’ subjective general physical and mental health. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 7, 100. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7525-7-100.
Barkmann, C., Petermann, F., Schlack, R., Bullinger, M., Schulte-Markwort, M., Klasen, F., et al. (2016). Course of health-related quality of life: Results of the BELLA Cohort Study. Kindheit und Entwicklung, 25(1), 50–59. https://doi.org/10.1026/0942-5403/a000188.
Otto, C., Haller, A. C., Klasen, F., Holing, H., Bullinger, M., Ravens-Sieberer, U., et al. (2017). Risk and protective factors of health-related quality of life in children and adolescents: Results of the longitudinal BELLA study. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0190363.
Dey, M., Landolt, M. A., & Mohler-Kuo, M. (2012). Health-related quality of life among children with mental disorders: a systematic review. Quality Life Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-012-0109-7.
Jonsson, U., Alaie, I., Wilteus, A. L., Zander, E., Marschik, P. B., Coghill, D., et al. (2017). Annual research review: Quality of life and childhood mental and behavioural disorders—A critical review of the research. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 58(4), 439–469. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.12645.
Wiegand-Grefe, S., Halverscheid, S., Petermann, F., & Plass, A. (2011). Psychopathology and quality of life in children of mentally ill parents. In L. L’Abate (Ed.), Mental illness. Evaluation, treatments and implications (pp. 21–34). Rijeka: Intech.
Wiegand-Grefe, S., Jeske, J., Bullinger, M., Plass, A., & Petermann, F. (2010). Lebensqualität von Kindern psychisch kranker Eltern Zusammenhänge zwischen Merkmalen elterlicher Erkrankung und gesundheitsbezogener Lebensqualität der Kinder aus Elternsicht. Zeitschrift für Psychiatrie, Psychologie, und Psychotherapie, 58(4), 315–322.
Dittrich, K., Fuchs, A., Bermpohl, F., Meyer, J., Fuhrer, D., Reichl, C., et al. (2018). Effects of maternal history of depression and early life maltreatment on children’s health-related quality of life. Journal of Affective Disorders, 225, 280–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.053.
Kallander, E. K., Weimand, B. M., Hanssen-Bauer, K., Van Roy, B., & Ruud, T. (2020). Factors associated with quality of life for children affected by parental illness or substance abuse. Scandinavian Journal of Caring Sciences. https://doi.org/10.1111/scs.12868.
Plass, A., Haller, A. C., Habermann, K., Barkmann, C., Petermann, F., Schipper, M., et al. (2016). Factors promoting mental health in children of parents with mental health problems: Results of the BELLA Cohort study. Kindheit und Entwicklung, 25(1), 41–49. https://doi.org/10.1026/0942-5403/a000187.
Kurth, B. M., Kamtsiuris, P., Holling, H., Schlaud, M., Dolle, R., Ellert, U., et al. (2008). The challenge of comprehensively mapping children’s health in a nation-wide health survey: Design of the German KiGGS-Study. BMC Public Health, 8(1), 196.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Otto, C., Kriston, L., Rothenberger, A., Dopfner, M., Herpertz-Dahlmann, B., et al. (2015). The longitudinal BELLA study: Design, methods and first results on the course of mental health problems. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 24(6), 651–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-014-0638-4.
Klaghofer, R., & Brahler, E. (2001). Construction and statistical testing of a short version of the SCL-90-R. Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie, 49(2), 115–124.
Derogatis, L. R., Lipman, E. L., Rickels, K., Uhlenhut, E., & Covi, L. (1974). The Hopkins Symptom Checklist (HSCL): A self-report symptom inventory. Behavioral Science, 19, 1–15.
Petrowski, K., Schmalbach, B., Kliem, S., Hinz, A., & Brahler, E. (2019). Symptom-Checklist-K-9: Norm values and factorial structure in a representative German sample. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0213490.
Wustner, A., Otto, C., Schlack, R., Holling, H., Klasen, F., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (2019). Risk and protective factors for the development of ADHD symptoms in children and adolescents: Results of the longitudinal BELLA study. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0214412.
Plass-Christl, A., Otto, C., Klasen, F., Wiegand-Grefe, S., Barkmann, C., Holling, H., et al. (2018). Trajectories of mental health problems in children of parents with mental health problems: Results of the BELLA study. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 27(7), 867–876. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-017-1084-x.
Plass-Christl, A., Klasen, F., Otto, C., Barkmann, C., Hölling, H., Klein, T., et al. (2017). Mental health care use in children of parents with mental health problems. Journal of Child Psychiatry and Human Development. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-017-0721-4.
Klasen, F., Otto, C., Kriston, L., Patalay, P., Schlack, R., Ravens-Sieberer, U., et al. (2015). Risk and protective factors for the development of depressive symptoms in children and adolescents: Results of the longitudinal BELLA study. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 24(6), 695–703. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-014-0637-5.
Franke, G. H. (2002). SCL-90-R: Symptom-Checkliste von L.R. Derogatis—deutsche Version. Göttingen: Beltz Test GmbH.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., & the European KIDSCREEN Group. (2006). The KIDSCREEN Questionnaires—Quality of life questionnaires for children and adolescents—Handbook. Lengerich: Pabst Science Publishers.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., Auquier, P., Erhart, M., Gosch, A., Rajmil, L., Bruil, J., et al. (2007). The KIDSCREEN-27 quality of life measure for children and adolescents: Psychometric results from a cross-cultural survey in 13 European countries. Quality of Life Research, 16(8), 1347–1356. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-007-9240-2.
Goodman, R. (1997). The strengths and difficulties questionnaire: A research note. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 38(5), 581–586.
Goodman, A., Lamping, D. L., & Ploubidis, G. B. (2010). When to use broader internalising and externalising subscales instead of the hypothesised five subscales on the Strengths and Difficulties Questionnaire (SDQ): Data from British parents, teachers and children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 38(8), 1179–1191.
Schwarzer, R., & Jerusalem, M. (1995). Generalized Self-Efficacy scale. In J. Weinman, S. Wright, & M. Johnston (Eds.), Measures in health psychology: A user’s portfolio. Causal and control beliefs (pp. 35–37). Windsor: NFER-NELSON.
Schneewind, K., Beckmann, M., & Hecht-Jackl, A. (1985). Familienklima-Skalen. Bericht 8.1 und 8.2. München: Ludwig Maximilians Universität, Institut für Psychologie- Persönlichkeitspsychologie und Psychodiagnostik.
Donald, C. A., & Ware, J. E. (1984). The measurement of social support. Research in Community & Mental Health, 4, 325–370.
Winkler, J., & Stolzenberg, H. (1999). Der Sozialschichtindex im Bundes-Gesundheitssurvey. Gesundheitswesen, 61, S178–S183.
Lange, M., Kamtsiuris, P., Lange, C., Schaffrath Rosario, A., Stolzenberg, H., & Lampert, T. (2007). Messung soziodemographischer Merkmale im Kinder- und Jugendgesundheitssurvey (KiGGS) und ihre Bedeutung am Beispiel der Einschätzung des allgemeinen Gesundheitszustands. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz, 50(5–6), 578–589.
Schenk, L., Bau, A. M., Borde, T., Butler, J., Lampert, T., Neuhauser, H., et al. (2006). Mindestindikatorensatz zur Erfassung des Migrationsstatus. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz, 49(9), 853–860.
Heck, R., Thomas, S., & Tabata, L. (2014). Multilevel and longitudinal modeling with IBM SPSS. New York: Routledge.
McFadden, D. (1974). Conditional logit analysis of qualitative choice behaviour. In P. Zarembka (Ed.), Frontiers in econometrics (pp. 105–142). New York: Academic Press.
Clemens, V., Berthold, O., Witt, A., Sachser, C., Brahler, E., Plener, P. L., et al. (2020). Lifespan risks of growing up in a family with mental illness or substance abuse. Scientific Reports. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72064-w.
Ranoyen, I., Klockner, C., Wallander, J., & Jozefiak, T. (2015). Associations between internalizing problems in adolescent daughters versus sons and mental health problems in mothers versus fathers (the HUNT study). Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24(7), 2008–2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0001-x.
Bastiaansen, D., Ferdinand, R. F., & Koot, H. M. (2020). Predictors of quality of life in children and adolescents with psychiatric disorders. Child Psychiatry & Human Development, 51(1), 104–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-019-00914-4.
Jozefiak, T., Greger, H. K., Koot, H. M., Klockner, C. A., & Wallander, J. L. (2019). The role of family functioning and self-esteem in the quality of life of adolescents referred for psychiatric services: A 3-year follow-up. Quality of Life Research, 28(9), 2443–2452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-019-02197-7.
Ramchandani, P. G., Psychogiou, L., Vlachos, H., Iles, J., Sethna, V., Netsi, E., et al. (2011). Paternal depression: An examination of its links with father, child and family functioning in the postnatal period. Depression and Anxiety, 28(6), 471–477. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20814.
Ramchandani, P., & Psychogiou, L. (2009). Paternal psychiatric disorders and children’s psychosocial development. Lancet, 374(9690), 646–653. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(09)60238-5.
Katschnig, H. (2006). Quality of life in mental disorders: Challenges for research and clinical practice. World Psychiatry, 5(3), 139–145.
McLaughlin, K. A., Gadermann, A. M., Hwang, I., Sampson, N. A., Al-Hamzawi, A., Andrade, L. H., et al. (2012). Parent psychopathology and offspring mental disorders: Results from the WHO World Mental Health Surveys. British Journal of Psychiatry, 200(4), 290–299. https://doi.org/10.1192/bjp.bp.111.101253.
Brent, D., Brunwasser, S. M., Hollon, S. D., Weersing, V. R., Clarke, G. N., Dickerson, J. F., et al. (2015). Effect of a cognitive-behavioral prevention program on depression 6 years after implementation among at-risk adolescents: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2015.1559.
Wiegand-Grefe, S., Alberts, J., Petermann, F., & Plass, A. (2016). Differential perspectives on family functioning and interfamilial relationships: The effect of a manualized intervention program on children of mentally ill parents. Kindheit und Entwicklung, 25(2), 77–88. https://doi.org/10.1026/0942-5403/a000192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plass-Christl, A., Ravens-Sieberer, U., Hölling, H. et al. Trajectories of health-related quality of life in children of parents with mental health problems: results of the BELLA study. Qual Life Res 30, 1841–1852 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-021-02783-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-021-02783-8