Abstract
Purpose
To systematically review studies about the quality of life (QOL) of children with various mental disorders relative to healthy controls and to describe limitations in these studies.
Methods
Relevant articles were searched using different databases, by checking reference lists and contacting experts. We included articles that either compared children with mental disorders to healthy controls/norm values or made such a comparison possible.
Results
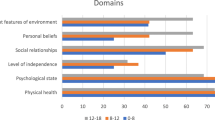
Sixteen out of 4,560 articles met the pre-defined inclusion criteria. These studies revealed that the QOL of children with various mental disorders is compromised across multiple domains. The largest effect sizes were found for psychosocial and family-related domains and for the total QOL score, whereas physical domains generally were less affected. The most important limitations in the existing literature include the lack of study samples drawn from the general population, the failure to use self-ratings, not considering item overlap between measuring QOL and assessing for the presence of a particular mental disorder, and not determining whether the children were receiving medication for their mental disorder.
Conclusions
Children with mental disorders experience a considerable reduction in QOL across various domains. Research studies that avoid previous limitations are crucial to fill existing knowledge gaps.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADHD:
-
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- ASD:
-
Autism spectrum disorders
- CHIP:
-
Child Health and Illness Profile
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CHQ:
-
Child Health Questionnaire
- DSM-IV-TR:
-
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
- DUX-25:
-
Dutch-Child-AZL-TNO-Quality-of-Life
- ES:
-
Effect sizes
- HRQOL:
-
Health-related quality of life
- ICD-10:
-
International Classification of Disease and Related Health Problems
- KINDL-R:
-
Questionnaire for Measuring Health-Related Quality of Life in Children and Adolescent—Revised Version
- PedsQL:
-
Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SpLD:
-
Specific learning disabilities
- TACQOL:
-
TNO-AZL-Child-Quality-of-Life
- QOL:
-
Quality of life
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
World Health Organization (WHO). (2003). Investing in mental health. Geneva: WHO.
World Health Organization (WHO). (1992). The ICD-10 classification of mental and behavioural disorders. Clinical descriptions and diagnostic guidelines. Geneva: WHO.
American Psychological Association (APA). (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th edition text revision). Wahington, DC: APA.
Taylor, R. M., Gibson, F., & Franck, L. S. (2008). A concept analysis of health-related quality of life in young people with chronic illness. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 17(14), 1823–1833.
Coghill, D., Danckaerts, M., Sonuga-Barke, E., & Sergeant, J. (2009). Practitioner review: Quality of life in child mental health—conceptual challenges and practical choices. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 50(5), 544–561.
Bullinger, M. (2009). Wohlbefinden von Kindern und Jugendlichen. Forschungsstand und konzeptueller Hintergrund. Zeitschrift für Gesundheitspsychologie, 17(2), 50–55.
Matza, L. S., Swensen, A. R., Flood, E. M., Secnik, K., & Leidy, N. K. (2004). Assessment of health-related quality of life in children: A review of conceptual, methodological, and regulatory issues. Value in Health, 7(1), 79–92.
Schmeck, K., & Poustka, F. (2006). Quality of life and childhood disorders. In H. Katschnig, H. Freeman, & N. Sartorius (Eds.), Quality of life in mental disorders (2nd ed.). Chichester, NY: Wiley.
Solans, M., Pane, S., Estrada, M. D., Serra-Sutton, V., Berra, S., Herdman, M., et al. (2008). Health-related quality of life measurement in children and adolescents: A systematic review of generic and disease-specific instruments. Value in Health, 11(4), 742–764.
Katschnig, H. (2006). How useful is the concept of quality of life in psychiatry? In H. Katschnig, H. Freeman, & N. Sartorius (Eds.), Quality of life in mental disorders. Chichester: Wiley.
Danckaerts, M., Sonuga-Barke, E. J., Banaschewski, T., Buitelaar, J., Doepfner, M., Hollis, C., et al. (2009). The quality of life of children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A systematic review. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 19(2), 83–105.
Alonso, J., Angermeyer, M. C., Bernert, S., Bruffaerts, R., Brugha, T. S., Bryson, H., et al. (2004). Disability and quality of life impact of mental disorders in Europe: Results from the European Study of the epidemiology of mental disorders (ESEMeD) project. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 420, 38–46.
Mendlowicz, M. V., & Stein, M. B. (2000). Quality of life in individuals with anxiety disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry, 157(5), 669–682.
Ritsner, M., Modai, I., Endicott, J., Rivkin, O., Nechamkin, Y., Barak, P., et al. (2000). Differences in quality of life domains and psychopathologic and psychosocial factors in psychiatric patients. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 61(11), 880–889.
Bullinger, M., & Ravens-Sieberer, U. (1995). General principles, methods and areas of application of quality of life research in children. Praxis der Kinderpsychologie und Kinderpsychiatrie, 44(10), 391–399.
Stein, R. E. (2004). Measurement of children’s health. Ambulatory Pediatrics, 4(4), 365–370.
Steinhausen, H. C. (2006). Psychische Stoerungen bei Kindern und Jugendlichen: Lehrbuch der Kinder- und Jugendpsychiatrie und -psychotherapie (Vol. 6). München: Elsevier.
Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. NJ: Hillsdale.
Norman, G. R., Sloan, J. A., & Wyrwich, K. W. (2003). Interpretation of changes in health-related quality of life. The remarkable universality of half a standard deviation. Medical Care, 41(5), 582–592.
Karande, S., Bhosrekar, K., Kulkarni, M., & Thakker, A. (2009). Health-related quality of life of children with newly diagnosed specific learning disability. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics, 55(3), 160–169.
Sawyer, M. G., Whaites, L., Rey, J. M., Hazell, P. L., Graetz, B. W., & Baghurst, P. (2002). Health-related quality of life of children and adolescents with mental disorders. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 41(5), 530–537.
Kuhlthau, K., Orlich, F., Hall, T. A., Sikora, D., Kovacs, E. A., Delahaye, J., et al. (2010). Health-related quality of life in children with autism spectrum disorders: Results from the autism treatment network. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 40(6), 721–729.
Matza, L. S., Rentz, A. M., Secnik, K., Swensen, A. R., Revicki, D. A., Michelson, D., et al. (2004). The link between health-related quality of life and clinical symptoms among children with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 25(3), 166–174.
Rotsika, V., Coccossis, M., Vlassopoulos, M., Papaeleftheriou, E., Sakellariou, K., Anagnostopoulos, D. C., et al. (2011). Does the subjective quality of life of children with specific learning disabilities (SpLD) agree with their parents’ proxy reports? Quality of Life Research, 20(8), 1271–1278.
Escobar, R., Soutullo, C. A., Hervas, A., Gastaminza, X., Polavieja, P., & Gilaberte, I. (2005). Worse quality of life for children with newly diagnosed attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, compared with asthmatic and healthy children. Pediatrics, 116(3), e364–e369.
Klassen, A. F., Miller, A., & Fine, S. (2006). Agreement between parent and child report of quality of life in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child: Care, Health and Development, 32(4), 397–406.
Rentz, A. M., Matza, L. S., Secnik, K., Swensen, A., & Revicki, D. A. (2005). Psychometric validation of the child health questionnaire (CHQ) in a sample of children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Quality of Life Research, 14(3), 719–734.
Moses, T. (2010). Exploring parents’ self-blame in relation to adolescents’ mental disorders. Family Relations, 59(2), 103–120.
Rosenzweig, J. M., Brennan, E. M., Huffstutter, K., & Bradley, J. R. (2008). Child care and employed parents of children with emotional or behavioral disorders. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 16(2), 78–89.
Jafari, P., Ghanizadeh, A., Akhondzadeh, S., & Mohammadi, M. R. (2011). Health-related quality of life of Iranian children with attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Quality of Life Research, 20(1), 31–36.
Flapper, B. C., & Schoemaker, M. M. (2008). Effects of methylphenidate on quality of life in children with both developmental coordination disorder and ADHD. Developmental Medicine and Child Neurology, 50(4), 294–299.
Shipman, D. L., Sheldrick, C., & Perrin, E. C. (2011). Quality of life in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders: Reliability and validity of self-report. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 32(2), 85–89.
Stewart, M., DelBello, M. P., Versavel, M., & Keller, D. (2009). Psychosocial functioning and health-related quality of life in children and adolescents treated with open-label ziprasidone for bipolar mania, schizophrenia, or schizoaffective disorder. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 19(6), 635–640.
Freeman, A. J., Youngstrom, E. A., Michalak, E., Siegel, R., Meyers, O. I., & Findling, R. L. (2009). Quality of life in pediatric bipolar disorder. Pediatrics, 123(3), e446–e452.
Limbers, C. A., Ripperger-Suhler, J., Heffer, R. W., & Varni, J. W. (2011). Patient-reported pediatric quality of life inventory 4.0 generic core scales in pediatric patients with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and comorbid psychiatric disorders: Feasibility, reliability, and validity. Value in Health, 14(4), 521–530.
Ravens-Sieberer, U., & Bullinger, M. (2000). KINDL-R. Questionnaire for measuring health-related quality of life in children and adolescents, revised version. Manual. Accessed at: http://kindl.org/cms/wp-content/uploads/2009/11/ManEnglish.pdf.
Rajmil, L., Herdman, M., Ferandez de Sanmamed, M.-J., Detmar, S., Bruil, J., Ravens-Sieberer, U., et al. (2004). Generic health-related quality of life instruments in children and adolescents: A qualitative analysis of content. Journal of Adolescent Health, 34(1), 37–45.
Eiser, C., & Morse, R. (2001). A review of measures of quality of life for children with chronic illness. Archives of Disease in Childhood, 84(3), 205–211.
Bastiaansen, D., Koot, H. M., Ferdinand, R. F., & Verhulst, F. C. (2004). Quality of life in children with psychiatric disorders: Self-, parent, and clinician report. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 43(2), 221–230.
Davis, E., Mackinnon, A., & Waters, E. (2011). Parent proxy-reported quality of life for children with cerebral palsy: Is it related to parental psychosocial distress? Child Care Health Dev. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2214.2011.01267.x.
Jozefiak, T., Larsson, B., Wichstrom, L., Wallander, J., & Mattejat, F. (2010). Quality of life as reported by children and parents: A comparison between students and child psychiatric outpatients. Health and Quality of Life Outcomes, 8, 136–145.
Huebner, E. S., Valois, R. F., Suldo, S. M., Smith, L. C., McKnight, C. G., Seligson, J. L., et al. (2004). Perceived quality of life: A neglected component of adolescent health assessment and intervention. Journal of Adolescent Health, 34(4), 270–278.
Varni, J. W., & Burwinkle, T. M. (2006). The PedsQL as a patient-reported outcome in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: A population-based study. Health Quality of Life Outcomes, 21(4), 26–36.
Pongwilairat, K., Louthrenoo, O., Charnsil, C., & Witoonchart, C. (2005). Quality of life of children with attention-deficit/hyper activity disorder. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand, 88(8), 1062–1066.
Preuss, U., Ralston, S. J., Baldursson, G., Falissard, B., Lorenzo, M. J., Rodrigues Pereira, R., et al. (2006). Study design, baseline patient characteristics and intervention in a cross-cultural framework: Results from the ADORE study. European Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 15(1), 4–14.
Wehmeier, P. M., Schacht, A., Dittmann, R. W., Helsberg, K., Schneider-Fresenius, C., Lehmann, M., et al. (2010). Effect of atomoxetine on quality of life and family burden: Results from a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study in children and adolescents with ADHD and comorbid oppositional defiant or conduct disorder. Quality of Life Research, 20(5), 691–702.
Riley, A. W., Robertson, J. A., Forrest, C. B., Green, B. F., Rebok, G., & Starfield, B. (2001). Technical manual for the child health and illness profile—child edition (CHIP-CE™) parent and child report forms (1.0th ed.). Baltimore: John Hopkins University.
Landgraf, J. M., Abetz, L., & Ware, J. E. (1999). The CHQ: A user’s manual. Boston, MA: The Health Institute.
Kolsteren, M. M. P., Koopman, H. M., Schalekamp, G., & Mearin, M. L. (2001). Health-related quality of life in children with celiac disease. Journal of Pediatrics, 138(4), 593–595.
Varni, J. W., Seid, M., & Kurtin, P. S. (2001). PedsQLtm 4.0: Reliability and validity of the pediatric quality of life inventory tm version 4.0 generic core scales in healthy and patient populations. Medical Care, 39(8), 800–812.
Varni, J. W., Seid, M., & Rode, C. A. (1999). The PedsQL (TM): Measurement model for the pediatric quality of life inventory. Medical Care, 37(2), 126–139.
Theunissen, N., Vogels, T., Koopman, H., Verrips, G., Zwinderman, K., Verloove-Vanhorick, S., et al. (1998). The proxy problem: Child report versus parent report in health-related quality of life research. Quality of Life Research, 7(5), 387–397.
Verrips, E. G. H., Vogels, T. G. C., Koopman, H. M., Theunissen, N. C. M., Kamphuis, R. P., Fekkes, M., et al. (1999). Measuring health-related quality of life in a child population. European Journal of Public Health, 9(3), 188–193.
Vogels, T., Verrips, G. H. W., Verloove-Vanhorick, S. P., Fekkes, M., Kamphuis, R. P., Koopman, H. M., et al. (1998). Measuring health-related quality of life in children: The development of the TACQOL parent form. Quality of Life Research, 7(5), 457–465.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all authors who provided additional data we needed to complete the evaluation of papers and the data extraction. Furthermore, we would like to thank Didier Kramer for providing practical hints on conducting a systematic review, Alois Tschopp for his statistical consulting and Rahel Schümperli for her assistance in obtaining relevant articles. This work is supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (325130_125486) and the Swiss School of Public Health plus.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dey, M., Landolt, M.A. & Mohler-Kuo, M. Health-related quality of life among children with mental disorders: a systematic review. Qual Life Res 21, 1797–1814 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-012-0109-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11136-012-0109-7