Abstract
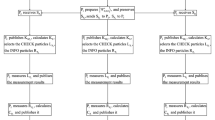
A mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol can authenticate participants’ identities before establishing shared keys fairly. Therefore, it is more in line with the actual demand than the general quantum key agreement protocols. With Bell states and their entanglement exchange relations, a new mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol is proposed. The participants can mutually authenticate each other’s identity by using their secret identity information and the measurement correlation property of Bell states. Moreover, they can negotiate session keys fairly with the entanglement exchange relations of Bell states. The new mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol is proved to be unconditionally secure and has good performance.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability Statement
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Quantum key agreement protocols with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 14, 3483–3498 (2015)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two-party quantum key agreement against collective noise. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 5023–5035 (2016)
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public-key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International conference on computers, systems and signal Processing, Bangalore, India, pp. 175-179. (1984)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: The decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded single-photon source. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 908–917 (2020)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: The enhanced measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded pair coherent state. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 34, 2050063 (2020)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution protocols against collective noise. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 35, 2150195 (2021)
Zhou, N., Zeng, G., Xiong, J.: Quantum key agreement protocol. Electron. Lett. 40, 1149–1150 (2004)
Hsueh, C.C., Chen, C.Y.: Quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. In: Proceedings of the 14th Information security conference (ISC 2004), pp. 236-242. National Taiwan University of Science and Technology, Taipei 10-11 June (2004)
Tsai, C.W., Hwang, T.: On “quantum key agreement protocol.’’. Taiwan. R.O.C, Technical Report, C-S-I-E, NCKU (2009)
Tsai, C.W., Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Comment on quantum key agreement protocol with maximally entangled states. In: Proceedings of the 20th Cryptology and information security conference (CISC 2010), pp. 210-213. National Chiao Tung University, Hsinchu, 27-28 May (2010)
Chong, S.K., Hwang, T.: Quantum key agreement protocol based on BB84. Opt. Commun. 283, 1192–1195 (2010)
Shukla, C., Alam, N., Pathak, A.: Protocols of quantum key agreement solely using Bell states and Bell measurement. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2391–2405 (2014)
Shi, R.H., Zhong, H.: Multi-party quantum key agreement with Bell states and Bell measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 921–932 (2013)
Xu, G.B., Wen, Q.Y., Gao, F., Qin, S.J.: Novel multiparty quantum key agreement protocol with GHZ states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2587–2594 (2014)
Liu, B., Gao, F., Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y.: Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 1797–1805 (2013)
Yin, X.R., Ma, W.P., Liu, W.Y.: Three-party quantum key agreement with two-photon entanglement. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 52, 3915–3921 (2013)
Sun, Z.W., Zhang, C., Wang, B.H., Li, Q., Long, D.Y.: Improvements on “Multiparty quantum key agreement with single particles.’’. Quantum Inf. Process. 12, 3411–3420 (2013)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Su, Q., Gao, F.: Cryptanalysis of a multi-party quantum key agreement protocol with single particles. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 1651–1657 (2014)
Shen, D.S., Ma, W.P., Wang, L.L.: Two-party quantum key agreement with four-qubit cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 2313–2324 (2014)
Sun, Z.W., Yu, J.P., Wang, P.: Efficient multi-party quantum key agreement by cluster states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15, 373–384 (2016)
Huang, W., Wen, Q.Y., Liu, B., Gao, F., Sun, Y.: Quantum key agreement with EPR pairs and single-particle measurements. Quantum Inf. Process. 13, 649–663 (2014)
He, Y.F., Ma, W.P.: Two quantum key agreement protocols immune to collective noise. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 56, 328–338 (2017)
Das, A., Nandi, S., Sazim, S., Agrawal, P.: Resource state structure for controlled quantum key distribution. Eur. Phys. J. D. 74, 91 (2020)
Zhou, N.R., Zhu, K.N., Wang, Y.Q.: Three-party semi-quantum key agreement protocol. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 59, 663–676 (2020)
Zhu, H.F., Wang, C.N., Li, Z.X.: Semi-honest three-party mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ-like state. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 293–303 (2021)
Ma, X.Y., Hur, J.B., Li, Z.X., Zhu, H.F.: Quantum mutual authentication key agreement scheme using five-qubit entanglement towards different realm architecture. Int. J. Theor. Phys. 60, 1933–1948 (2021)
Cai, Q.Y.: Eavesdropping on the two-way quantum communication protocols with invisible photons. Phys. Lett. A 351, 23–25 (2006)
Deng, F.G., Li, X.H., Zhou, H.Y., Zhang, Z.J.: Improving the security of multiparty quantum secret sharing against Trojan horse attack. Phys. Rev. A 72, 044302 (2005)
Gao, F., Qin, S.J., Wen, Q.Y., Zhu, F.C.: Comment on: Three-party quantum secure direct communication based on GHZ states. Phys. Lett. A 372, 3333–3336 (2008)
Xu, G.B., Jiang, D.H.: Novel methods to construct nonlocal sets of orthogonal product states in an arbitrary bipartite high-dimensional system. Quantum Inf. process. 20, 128 (2021)
Wang, T.Y., Wang, X.X., Cai, X.Q., et al.: Analysis of efficient and secure dynamic quantum secret sharing protocol based on Bell states. Quantum Inf. Process. 20, 7 (2021)
Cabello, A.: Quantum key distribution in the Holevo limit. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 5635–5638 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61802302) and the Basic Research Project of Natural Science of Shaanxi Province (Grant No. 2021JM-462).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
He, YF., Pang, Y. & Di, M. Mutual authentication quantum key agreement protocol based on Bell states. Quantum Inf Process 21, 290 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03640-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03640-4