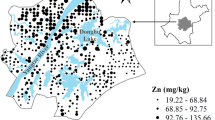
Abstract
Outliers are classified as global outliers and spatial outliers. Up to now, there is little information about the outliers especially the spatial outliers and their influence on the spatial structure modeling of soil properties. A total of 537 soil samples were collected based on a 30 × 30 m grid in a permanent dairy farm in southeast Ireland. Graphic methods of histogram and box plot combined with Moran’s I were applied to detect the outliers of soil phosphorus (P). Sixteen outliers (5 global outliers and 11 spatial outliers) of soil P were found in the study area. Compared to the raw data, the data with global outliers excluded always had the larger global Moran’s I value indicating a stronger spatial autocorrelation. Clear spatial clusters (High–High and Low–Low clusters) were observed based on local Moran’s I. The High–High spatial clusters were located around the main farm yard and near the traffic route due to more intensive management by farmers. The Low–Low spatial clusters were mainly close to the river. For these areas, P fertilizer or slurry should be applied for healthy grass growth. The dataset with outliers excluded had a reliable semi-variogram model with a low nugget/sill ratio (32.4 %), which was closed to its corresponding transformed data (30.5 %). The cross-validation results revealed that the dataset without outliers had the strongest linear regression model (r = 0.768), indicating that the outliers played an important role in the spatial structure modeling.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andronikov, S. V., Davidson, D. A., & Spiers, R. B. (2000). Variability in contamination by heavy metals: sampling implications. Water, Air Soil Pollution, 120, 29–45.
Anselin, L. (1995). Local indicators of spatial association-LISA. Geographical Analysis, 27, 93–115.
Box, G. E. P., & Cox, D. R. (1962). An analysis of transformations. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 26(2), 211–252.
Brody, S. D., Highfield, W. E., & Thornton, S. (2006). Planning at the urban fringe: an examination of the factors influencing nonconforming development patterns in southern Florida. Environment and Planning B-Planning & Design, 33, 75–96.
Cambardella, C. A., Moorman, A. T., Novak, J. M., Parkin, T. B., Karlen, D. L., Turco, R. F., et al. (1994). Field-scale variability of soil properties in central Iowa soils. Soil Science Society of America Journal, 58, 1501–1511.
Clark, I., & Harper, W. V. (2000). Practical geostatistics 2000. Columbus, OH: Ecosse North America Llc.
Cliff, A. D., & Ord, J. K. (1981). Spatial processes: Models and applications. London: Pion Limited.
Coulter, B. S., & Lalor, S. (2008). Nutrient and trace element advice for productive agricultural crops (3rd ed.). Wexford: Teagasc, Johnstown Castle.
Cressie, N. (1993). Statistics for spatial data (revised edition). New York: Wiley.
European Communities (2006) Good agricultural practice for protection of waters) Regulations 2006. S.I. No. 378. Government Publications, Dublin 2. http://www.environ.ie/en/Environment/Water/WaterQuality/NitratesDirective/ Accessed 11 Jan 2014
Everitt, B. S. (2002). The cambridge dictionary of statistics (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
FAO. (1974). Soil map of the world. 1:5,000,000 (Vol. 1–10). Paris: Food and Agriculture Organisation of the United Nations and UNESCO.
Fu, W. J., Tunney, H., & Zhang, C. S. (2010). Spatial variation of soil nutrients in a dairy farm and its implications for site-specific fertilizer application. Soil & Tillage Research, 106, 185–193.
Fu, W. J., Zhao, K. L., Tunney, H., & Zhang, C. S. (2013). Using GIS and geostatistics to optimize soil phosphorus and magnesium sampling in temperate grassland. Soil Science, 178, 240–247.
Fu, W. J., Zhao, K., Zhang, C. S., & Tunney, H. (2011). Using Moran’s I and geostatistics to identify spatial patterns of soil nutrients in two different long termphosphorus application plots. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Soil Science, 174, 785–798.
Gallardo, A., & Paramá, R. (2007). Spatial variability of soil elements in two plant communities of NW Spain. Geoderma, 139, 199–208.
Geary, R. C. (1954). The contiguity ratio and statistical mapping. The Incorporated Statistician, 5, 115–145.
Getis, A., & Ord, J. K. (1992). The analysis of spatial association by use of distance statistics. Geographical Analysis, 24, 189–206.
Goovaerts, P. (1997). Geostatistics for natural resources evaluation. New York: Oxford University Press.
Huo, X. N., Li, H., Sun, D. F., Zhou, L. D., & Li, B. G. (2012). Combining geostatistics with Moran’s I analysis for mapping soil heavy metals in Beijing, China. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 9, 995–1017.
Ishioka, F., Kurihara, K., Suito, H., Horikawa, Y., & Ono, Y. (2007). Detection of hotspots for three-dimensional spatial data and its application to environmental pollution data. Journal of Environmental Science for Sustainable Society, 1, 15–24.
Jeweel, P. L., Kauferle, D., Gusewell, S., Berry, N. R., Kreuzer, M., & Edwards, P. J. (2007). Redistribution of phosphorus by cattle on a traditional mountain pasture in the Alps. Agriculture, Ecosystem & Environment, 122, 377–386.
Kerry, R., & Oliver, M. A. (2007). Comparing sampling needs for variograms of soil properties computed by the method of moments and residual maximum likelihood. Geoderma, 140, 383–396.
Lalor, G. C., & Zhang, C. S. (2001). Multivariate outlier detection and remediation in geochemical databases. Science of the Total Environment, 281, 99–109.
Li, W. L., Xu, B. B., Song, Q. J., Liu, X. M., Xu, J. M., & Brookes, P. C. (2014). The identification of ‘hotspots’ of heavy metal pollution in soil–rice systems at a regional scale in eastern China. Science of the Total Environment, 472, 407–420.
McCormick, S., Jordan, C., & Bailey, J. S. (2009). Within and between-field spatial variation in soil phosphorus in permanent grassland. Precision Agriculture, 10, 262–276.
McGrath, D., & Zhang, C. S. (2003). Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of Ireland. Applied Geochemistry, 18, 1629–1639.
Moran, P. A. P. (1950). Notes on continuous stochastic phenomena. Biometrika, 37, 17–23.
Norusis, M. (2003). SPSS 12.0 Statistical procedures companion. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Overmars, K. P., de Koning, G. H. J., & Veldkamp, A. (2003). Spatial autocorrelation in multi-scale land use models. Ecological Modeiling, 164, 257–270.
Peech, M., & English, L. (1944). Rapid microchemical tests. Soil Science, 57, 167–193.
Sadeghi, A., Graff, C. D., Starr, J., Mccarty, G., Codling, E., & Sefton, K. (2006). Spatial variability of soil phosphorous levels before and after poultry litter application. Soil Science, 171, 850–857.
Styles, D., Donohue, I., Coxon, C., & Irvine, K. (2006). Linking soil phosphorus to water quality in the Mask catchment of western Ireland through the analysis of moist soil samples. Agriculture Ecosystem & Environment, 112, 300–312.
Tu, J., & Xia, Z. G. (2008). Examining spatially varying relationships between land use and water quality using geographically weighted regression I: Model design and evaluation. Science of the Total Environment, 407, 358–378.
Tunney, H. (2002). Phosphorus needs of grassland soils and loss to water. In E. Walling & A. J. Horowitz (Eds.), Agricultural effects on ground and surface waters: Research at the edge of science and society (Vol. 273, pp. 63–69). Wallingford: IAHS Publ.
Webster, R., & Oliver, M. A. (2001). Geostatistics for environmental scientists. Chichester: Wiley.
Zhang, C. S., Luo, L., Xu, W., & Ledwith, V. (2008). Use of local Moran’s I and GIS to identify pollution hotspots of Pb in urban soils of Galway, Ireland. Science of the Total Environment, 398, 212–221.
Zhang, C. S., Manheim, F. T., Hinde, J., & Grossman, J. N. (2005). Statistical characterization of a large geochemical database and effect of sample size. Applied Geochemistry, 20, 1857–1874.
Zhang, C. S., & McGrath, D. (2004). Geostatistical and GIS analyses on soil organic carbon concentrations in grassland of southeastern Ireland from two different periods. Geoderma, 119, 261–275.
Zhang, C. S., & Selinus, O. (1998). Statistics and GIS in environmental geochemistry-some problems and solutions. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 64, 339–354.
Zhang, C. S., Tang, Y., Luo, L., & Xu, W. L. (2009). Outlier identification and visualization for Pb concentrations in urban soils and its implications for identification of potential contaminated land. Environmental Pollution, 157, 3083–3090.
Zhao, K. L., Fu, W. J., Liu, X. M., Huang, D. L., Zhang, C. S., Ye, Z. Q., et al. (2014). Spatial variations of concentrations of Copper and its speciation in the soil-rice system in Wenling of southeastern China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 21, 7165–7176.
Zhao, K. L., Liu, X. M., Xu, J. M., & Selim, H. M. (2010). Heavy metal contaminations in a soil–rice system: Identification of spatial dependence in relation to soil properties of paddy fields. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 181, 778–787.
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Open Project of Provincial Priority First Level Discipline of Forestry (KF201333), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41201538, 41201323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, W., Zhao, K., Zhang, C. et al. Outlier identification of soil phosphorus and its implication for spatial structure modeling. Precision Agric 17, 121–135 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-015-9411-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-015-9411-z