Abstract
Background and aims
Maintaining sustainable high yield and soil fertility is the key to cultivate perennial alfalfa grassland. However, little is known about the effects of rhizosphere microbes on soil fertility and alfalfa yield in different planting years and regimes.
Methods
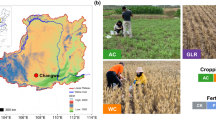
We sampled 10 alfalfa fields to investigate the rhizosphere soil microbial community and yields in monoculture and rotation systems in different planting years.
Results
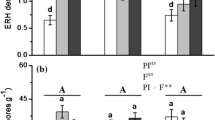
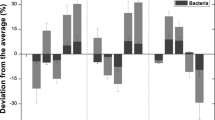
The alfalfa yield in monoculture was significantly declined (P < 0.05) starting in 6 yr. Wheat-corn-alfalfa rotation generated higher (P < 0.05) soil fertility index and alfalfa yield than wheat-alfalfa rotation and 2 yr alfalfa monoculture. The alfalfa yield significantly (R2 = 0.583, P < 0.001) increased with soil fertility. Significant differences were observed for bacteria (RANOSIM = 0.955, P = 0.001) and fungal (RANOSIM = 0.889, P = 0.001) communities in different planting years and regimes. Different ecological processes dominated bacterial and fungal communities assembly. Blastococcus and Massilia were important biomarkers, which had a significant (P < 0.05) positive correlation with alfalfa yield. PLS-PM analysis identified that planting regimes had positive impacts on alfalfa yield through edaphic variables, microbial genera and fungal community composition. Conversely, planting years had negative effects on alfalfa yield by indirectly regulating fungal genera and community composition through fungal community assembly.
Conclusions
This study could help improve our understanding of the role and importance of rhizosphere soil microbial changes in regulating farmland soil processes and crop productivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
All sequences have been deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive database (BioProject accession No. PRJNA787733 for 16S and PRJNA788299 for ITS).
References
Anderson MJ, Crist TO, Chase JM, Vellend M, Inouye BD, Freestone AL, Sanders NJ, Cornell HV, Comita LS, Davies KF (2011) Navigating the multiple meanings of beta diversity: a roadmap for the practicing ecologist. Ecol Lett 14:19–28
Anderson IC, Genney DR, Alexander IJ (2014) Fine-scale diversity and distribution of ectomycorrhizal fungal mycelium in a S cots pine forest. New Phytol 201:1423–1430
Archer E (2018) Estimate permutation p-values for random forest importance metrics. R-project org/package= rfPermute
Ardley JK, Parker MA, De Meyer SE, Trengove RD, Hara GW, Reeve WG, Yates RJ, Dilworth MJ, Willems A, Howieson JG (2018) Microvirga lupini sp. nov., Microvirga lotononidis sp. nov. and Microvirga zambiensis sp. nov. are alphaproteobacterial root-nodule bacteria that specifically nodulate and fix nitrogen with geographically and taxonomically separate legume hosts. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:2579–2588
Bao SD (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. Agriculture Publication, Beijing
Bao Y, Feng Y, Stegen JC, Wu M, Chen R, Liu W, Zhang J, Li Z, Lin X (2020) Straw chemistry links the assembly of bacterial communities to decomposition in paddy soils. Soil Biol Biochem 148:107866
Benitez J, Henseler J, Castillo A, Schuberth F (2020) How to perform and report an impactful analysis using partial least squares: Guidelines for confirmatory and explanatory IS research. Inf Manag 57:103168
Benitez M-S, Ewing PM, Osborne SL, Lehman RM (2021) Rhizosphere microbial communities explain positive effects of diverse crop rotations on maize and soybean performance. Soil Biol Biochem 159:108309
Berti MT, Lukaschewsky J, Samarappuli DP (2021) Intercropping alfalfa into silage maize can be more profitable than maize silage followed by spring-seeded alfalfa. Agronomy 11:1196
Chase JM, Myers JA (2011) Disentangling the importance of ecological niches from stochastic processes across scales. Philos Trans Royal Soc B: Biol Sci 366:2351–2363
Chemists AoOA, Horwitz W (1975) Official methods of analysis. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Chon S, Jennings J, Nelson C (2006) Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) autotoxicity: Current status. Allelopath J 18:57–80
Cicek H, Entz MH, Martens JRT, Bullock PR (2014) Productivity and nitrogen benefits of late-season legume cover crops in organic wheat production. Can J Plant Sci 94:771–783
Cong L, Sun Y, Wang Z, Kang J, Zhang T, Biligetu B, Yang Q (2018) A rapid screening method for evaluating resistance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) to Fusarium root rot. Can J Plant Path 40:61–69
Cui Q, Xia J, Peng L, Zhao X, Qu F (2022) Positive effects on alfalfa productivity and soil nutrient status in coastal wetlands driven by biochar and microorganisms mixtures. Front Ecol Evol 9:798520
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Oliverio AM, Brewer TE, Benavent-Gonzalez A, Eldridge DJ, Bardgett RD, Maestre FT, Singh BK, Fierer N (2018) A global atlas of the dominant bacteria found in soil. Science 359:320–325
Delgado-Baquerizo M, Reich PB, Trivedi C, Eldridge DJ, Abades S, Alfaro FD, Bastida F, Berhe AA, Cutler NA, Gallardo A (2020) Multiple elements of soil biodiversity drive ecosystem functions across biomes. Nat Ecol Evol 4:210–220
Dini-Andreote F, Stegen JC, Van Elsas JD, Salles JF (2015) Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E1326–E1332
Dong WH, Zhang S, Rao X, Liu CA (2016) Newly-reclaimed alfalfa forage land improved soil properties comparison to farmland in wheat–maize cropping systems at the margins of oases. Ecol Eng 94:57–64
Esmaeilzadeh-Salestani K, Bahram M, Seraj RGM, Gohar D, Tohidfar M, Eremeev V, Talgre L, Khaleghdoust B, Mirmajlessi SM, Luik A (2021) Cropping systems with higher organic carbon promote soil microbial diversity. Agr Ecosyst Environ 319:107521
Fan K, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Guo X, Wang D, Zhu YG, Chu H (2020) Biodiversity of key-stone phylotypes determines crop production in a 4-decade fertilization experiment. ISME J 15:550–561
Fang X, Zhang C, Wang Z, Duan T, Yu B, Jia X, Pang J, Ma L, Wang Y, Nan Z (2021) Co-infection by soil-borne fungal pathogens alters disease responses among diverse alfalfa varieties. Front Microbiol 12:664385
Feng MM, Adams JM, Fan KK, Shi Y, Sun RB, Wang DZ, Guo XS, Chu HY (2018) Long-term fertilization influences community assembly processes of soil diazotrophs. Soil Biol Biochem 126:151–158
Fortmann-Roe S (2015) Consistent and clear reporting of results from diverse modeling techniques: the A3 method. J Stat Softw 66:1–23
Garcia-Tomsig NI, Robledo M, diCenzo GC, Mengoni A, Millan V, Peregrina A, Uceta A, Jimenez-Zurdo JI (2022) Pervasive rna regulation of metabolism enhances the root colonization ability of nitrogen-fixing symbiotic alpha-rhizobia. Mbio 13:e03576–21
Garland G, Edlinger A, Banerjee S, Degrune F, García-Palacios P, Pescador DS, Herzog C, Romdhane S, Saghai A, Spor A (2021) Crop cover is more important than rotational diversity for soil multifunctionality and cereal yields in European cropping systems. Nat Food 2:28–37
German RN, Thompson CE, Benton TG (2017) Relationships among multiple aspects of agriculture’s environmental impact and productivity: a meta-analysis to guide sustainable agriculture. Biol Rev 92:716–738
Ghimire BK, Ghimire B, Yu CY, Chung I-M (2019) Allelopathic and autotoxic effects of Medicago sativa-Derived allelochemicals. Plants 8:233
González-Chávez MdCA, Aitkenhead-Peterson JA, Gentry TJ, Zuberer D, Hons F, Loeppert R (2010) Soil microbial community, C, N, and P responses to long-term tillage and crop rotation. Soil Tillage Res 106:285–293
He F, Xie K, Li X (2018) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer and seeding rate on yield of alfalfa and weeds. Pol J Environ Stud 27:647–653
Hermans SM, Buckley HL, Case BS, Curran-Cournane F, Taylor M, Lear G (2020) Using soil bacterial communities to predict physico-chemical variables and soil quality. Microbiome 8:79
Hierro JL, Callaway RM (2003) Allelopathy and exotic plant invasion. Plant Soil 256:29–39
Hooper DU, Adair EC, Cardinale BJ, Byrnes JE, Hungate BA, Matulich KL, Gonzalez A, Duffy JE, Gamfeldt L, O’Connor MI (2012) A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 486:105–108
Huang Z, Liu Y, Cui Z, Fang Y, He H, Liu B-R, Wu G-L (2018) Soil water storage deficit of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) grasslands along ages in arid area (China). Field Crop Res 221:1–6
Jiao S, Lu YY (2019) Soil pH and temperature regulate assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterial communities in agricultural ecosystems. Environ Microbiol 22:1052–1065
Jiao S, Chen WM, Wang JL, Du NN, Li QP, Wei GH (2018) Soil microbiomes with distinct assemblies through vertical soil profiles drive the cycling of multiple nutrients in reforested ecosystems. Microbiome 6:1–13
Jiao XL, Zhang XS, Lu XH, Qin RJ, Bi YM, Gao WW (2019) Effects of maize rotation on the physicochemical properties and microbial communities of American ginseng cultivated soil. Sci Rep 9:8615
Jolankai R, Csoendes I, Fischl G, Wagner L, Husveth F (2008) Fungi contamination and mycotoxin content of sheep feeds. Cereal Res Commun 36:759–762
Karlen DL, Hurley EG, Andrews SS, Cambardella CA, Meek DW, Duffy MD, Mallarino AP (2006) Crop rotation effects on soil quality at three northern corn/soybean belt locations. Agron J 98:484–495
Knelman JE, Nemergut DR (2014) Changes in community assembly may shift the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem function. Front Microbiol 5:424
Kuerban M, Cong WF, Jing JY, Bezemer TM (2022) Microbial soil legacies of crops under different water and nitrogen levels determine succeeding crop performance. Plant Soil. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05412-6
Lange M, Habekost M, Eisenhauer N, Roscher C, Bessler H, Engels C, Oelmann Y, Scheu S, Wilcke W, Schulze E-D (2014) Biotic and abiotic properties mediating plant diversity effects on soil microbial communities in an experimental grassland. PLoS ONE 9:e96182
Larkin RP, Griffin TS, Honeycutt CW (2010) Rotation and cover crop effects on soilborne potato diseases, tuber yield, and soil microbial communities. Plant Dis 94:1491–1502
Lee H, Kim DU, Park S, Yoon JH, Ka JO (2017) Massilia chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from soil. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1–8
Li YP, Feng YL, Kang ZL, Zheng YL, Zhang JL, Chen YJ (2017) Changes in soil microbial communities due to biological invasions can reduce allelopathic effects. J Appl Ecol 54:1281–1290
Li XP, Zhu HM, Geisen S, Bellard C, Hu F, Li HX, Chen XY, Liu MQ (2020) Agriculture erases climate constraints on soil nematode communities across large spatial scales. Global Change Biology 26:919–930
Li MH, Guo JJ, Ren T, Luo GW, Shen QR, Lu JW, Guo SW, Ling N (2021) Crop rotation history constrains soil biodiversity and multifunctionality relationships. Agric Ecosyst Environ 319:107550
Liu K, Ma B, Luan LM, Li CH (2011) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium nutrient effects on grain filling and yield of high-yielding summer corn. J Plant Nutr 34:1516–1531
Liu W, Graham EB, Zhong L, Zhang J, Li W, Li Z, Lin X, Feng Y (2020a) Dynamic microbial assembly processes correspond to soil fertility in sustainable paddy agroecosystems. Funct Ecol 34:1244–1256
Liu WJ, Graham EB, Zhong LH, Zhang JW, Li WT, Li ZP, Lin XG, Feng YZ, Wang JJ (2020b) Dynamic microbial assembly processes correspond to soil fertility in sustainable paddy agroecosystems. Funct Ecol 34:1244–1256
Liu C, Cui Y, Li X, Yao M (2021) microeco: an R package for data mining in microbial community ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 97:fiaa255
Liu B, Arlotti D, Huyghebaert B, Tebbe CC (2022) Disentangling the impact of contrasting agricultural management practices on soil microbial communities-Importance of rare bacterial community members. Soil Biol Biochem 166:108573
Luo ZZ, Niu YN, Li LL, Cai LQ, Zhang RZ, Xie JH (2015) Soil moisture and alfalfa productivity response from different years of growth on the Loess Plateau of central Gansu. Acta Pratacul Sin 24:31
Ma BL, Ying J, Dwyer LM, Gregorich EG, Morrison MJ (2003) Crop rotation and soil N amendment effects on maize production in eastern Canada. Can J Soil Sci 83:483–495
Meng T, Yang Y, Cai Z, Ma Y (2018) The control of Fusarium oxysporum in soil treated with organic material under anaerobic condition is affected by liming and sulfate content. Biol Fertil Soils 54:295–307
Meriles JM, Gil SV, Conforto C, Figoni G, Lovera E, March GJ, Guzman CA (2009) Soil microbial communities under different soybean cropping systems: Characterization of microbial population dynamics, soil microbial activity, microbial biomass, and fatty acid profiles. Soil Tillage Res 103:271–281
Mori AS, Isbell F, Seidl R (2018) β-diversity, community assembly, and ecosystem functioning. Trends Ecol Evol 33:549–564
Ning DL, Yuan MT, Wu LW, Zhang Y, Guo X, Zhou XS, Yang YF, Arkin AP, Firestone MK, Zhou JZ (2020) A quantitative framework reveals ecological drivers of grassland microbial community assembly in response to warming. Nat Commun 11:1–12
Ofiţeru ID, Lunn M, Curtis TP, Wells GF, Criddle CS, Francis CA, Sloan WT (2010) Combined niche and neutral effects in a microbial wastewater treatment community. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15345–15350
Ohtsubo Y, Nonoyama S, Ogawa N, Kato H, Nagata Y, Tsuda M (2016) Complete genome sequence of Burkholderia caribensis Bcrs1W (NBRC110739), a strain co-residing with phenanthrene degrader Mycobacterium sp. EPa45. J Biotechnol 228:67–68
Orwin KH, Buckland SM, Johnson D, Turner BL, Smart S, Oakley S, Bardgett RD (2010) Linkages of plant traits to soil properties and the functioning of temperate grassland. J Ecol 98:1074–1083
Osterholz WR, Ruark MD, Renz MJ, Grabber JH (2021) Interseeding alfalfa into corn silage increases corn N fertilizer demand and increases system yield. Agron Sustain Dev 41:1–13
Pérez-Montaño F, Alías-Villegas C, Bellogín R, Del Cerro P, Espuny M, Jiménez-Guerrero I, López-Baena FJ, Ollero F, Cubo T (2014) Plant growth promotion in cereal and leguminous agricultural important plants: from microorganism capacities to crop production. Microbiol Res 169:325–336
Powell JR, Karunaratne S, Campbell CD, Yao H, Robinson L, Singh BK (2015) Deterministic processes vary during community assembly for ecologically dissimilar taxa. Nat Commun 6:1–10
Pullens JWM, Sørensen P, Melander B, Olesen JE (2021) Legacy effects of soil fertility management on cereal dry matter and nitrogen grain yield of organic arable cropping systems. Eur J Agron 122:126169
Qi Y, Darilek JL, Huang B, Zhao Y, Sun W, Gu Z (2009) Evaluating soil quality indices in an agricultural region of Jiangsu Province, China. Geoderma 149:325–334
Qu Q, Zhang ZY, Peijnenburg W, Liu WY, Lu T, Hu BL, Chen JM, Chen J, Lin ZF, Qian HF (2020) Rhizosphere microbiome assembly and its impact on plant growth. J Agric Food Chem 68:5024–5038
Sanchez G, Trinchera L, Russolillo G (2013) plspm: tools for partial least squares path modeling (PLS-PM). R package version 04 1
Smith MB, Rocha AM, Smillie CS, Olesen SW, Paradis C, Wu L, Campbell JH, Fortney JL, Mehlhorn TL, Lowe KA (2015) Natural bacterial communities serve as quantitative geochemical biosensors. Mbio 6:e00326-e315
Stegen JC, Fredrickson JK, Wilkins MJ, Konopka AE, Nelson WC, Arntzen EV, Chrisler WB, Chu RK, Danczak RE, Fansler SJ (2016) Groundwater-surface water mixing shifts ecological assembly processes and stimulates organic carbon turnover. Nat Commun 7:1–12
Song J, Li SX, Wei W, Xu YL, Yao Q (2017) Assessment of parasitic fungi for reducing soybean cyst nematode with suppressive soil in soybean fields of northeast China. Acta Agriculturae Scandinavica Section B-Soil And Plant Science 67:730–736
Su Y, Hu Y, Zi H, Chen Y, Deng X, Hu B, Jiang Y (2022) Contrasting assembly mechanisms and drivers of soil rare and abundant bacterial communities in 22-year continuous and non-continuous cropping systems. Sci Rep 12:1–13
Tang H, Xiao CH, Ma JZ, Yu M, Li YM, Wang GL, Zhang LP (2009) Prokaryotic diversity in continuous cropping and rotational cropping soybean soil. FEMS Microbiol Lett 298:267–273
Tiemann L, Grandy A, Atkinson E, Marin-Spiotta E, McDaniel M (2015) Crop rotational diversity enhances belowground communities and functions in an agroecosystem. Ecol Lett 18:761–771
Tripathi BM, Stegen JC, Kim M, Dong K, Adams JM, Lee YK (2018) Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J 12:1072–1083
Venter ZS, Jacobs K, Hawkins HJ (2016) The impact of crop rotation on soil microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Pedobiologia 59:215–223
Wang X, Ding T, Li Y, Guo Y, Li Y, Duan T (2020) Dual inoculation of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) with Funnelliformis mosseae and Sinorhizobium medicae can reduce Fusarium wilt. J Appl Microbiol 129:665–679
Wang LL, Xie JH, Luo ZZ, Niu YN, Coulter JA, Zhang RZ, Ling Ling L (2021) Forage yield, water use efficiency, and soil fertility response to alfalfa growing age in the semiarid Loess Plateau of China. Agric Water Manag 243:106415
Wang J, Liao LR, Ye ZC, Liu HF, Zhang C, Zhang L, Liu GB, Wang GL (2022a) Different bacterial co-occurrence patterns and community assembly between rhizosphere and bulk soils under N addition in the plant-soil system. Plant Soil 471:697–713
Wang YT, Zhang JG, Yu LQ, Xu ZY, Samac DA (2022b) Overwintering and yield responses of two late-summer seeded alfalfa cultivars to phosphate supply. Agronomy-Basel 12:327
Xuan DT, Guong VT, Rosling A, Alström S, Chai BL, Högberg N (2011) Different crop rotation systems as drivers of change in soil bacterial community structure and yield of rice, Oryza sativa. Biol Fertil Soils 48:217–225
Yao HY, Jiao XD, Wu FZ (2006) Effects of continuous cucumber cropping and alternative rotations under protected cultivation on soil microbial community diversity. Plant Soil 284:195–203
Yao Q, Xu YX, Liu XF, Liu JJ, Huang XY, Yang W, Yang Z, Lan L, Zhou J, Wang G (2019) Dynamics of soil properties and fungal community structure in continuous-cropped alfalfa fields in Northeast China. PeerJ 7:e7127
Yatsunenko T, Rey FE, Manary MJ, Trehan I, Dominguez-Bello MG, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Baldassano RN, Anokhin AP (2012) Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 486:222–227
Zeng XY, Li SW, Leng Y, Kang XH (2020) Structural and functional responses of bacterial and fungal communities to multiple heavy metal exposure in arid loess. Sci Total Environ 723:138081
Zhang KP, Adams JM, Shi Y, Yang T, Sun RB, He D, Ni YY, Chu HY (2017) Environment and geographic distance differ in relative importance for determining fungal community of rhizosphere and bulk soil. Environ Microbiol 19:3649–3659
Zhang F, Xu X, Huo Y, Xiao Y (2018a) Trichoderma-inoculation and mowing synergistically altered soil available nutrients, rhizosphere chemical compounds and soil microbial community, potentially driving alfalfa growth. Front Microbiol 9:3241
Zhang FG, Huo YQ, Xu XX, Hu J, Sun X, Xiao Y, Zhang YJ (2018b) Trichoderma improves the growth of Leymus chinensis. Biol Fertil Soils 54:685–696
Zhang F, Xu X, Wang G, Wu B, Xiao Y (2020) Medicago sativa and soil microbiome responses to Trichoderma as a biofertilizer in alkaline-saline soils. Appl Soil Ecol 153:103573
Zhang F, Zhou Z, Xiao Y (2022) Trichoderma biofertilizer facilitating Leymus chinensis production in different growth stages is strongly linked to dynamically altered soil microbiomes. Agr Ecosyst Environ 324:107706
Zhao J, Li Y, Wang B, Huang X, Yang L, Lan T, Zhang J, Cai Z (2017) Comparative soil microbial communities and activities in adjacent Sanqi ginseng monoculture and maize-Sanqi ginseng systems. Appl Soil Ecol 120:89–96
Zhao J, Yang YD, Zhang K, Jeong J, Zeng ZH, Zang HD (2020) Does crop rotation yield more in China? A Meta-Analysis. Field Crops Res 245:107659
Zheng BX, Bi QF, Hao XL, Zhou GW, Yang XR (2017) Massilia phosphatilytica sp. nov., a phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from a long-term fertilized soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2514–2519
Zheng Y, Xiang J, Liu Y, Zhang K, Liu G, Zhang Z (2021) Effects of continuous cropping on Panax notoginseng growth, yield and saponins content. Allelopathy J 54:95-+
Acknowledgements
We thank the assistants who helped to collect soil samples. This work was financially supported by the research start-up fee for high-level talents introduction of Nanjing Agricultural University (720804004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Sven Marhan.
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Z., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, F. Community assembly correlates with alfalfa production by mediating rhizosphere soil microbial community composition in different planting years and regimes. Plant Soil 479, 355–370 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05525-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-022-05525-y