Abstract
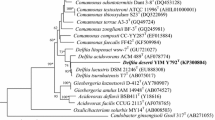
A Gram-stain negative, rod-shaped, aerobic bacterial strain, designated TA-C7eT, was isolated from an agricultural soil obtained from Taean region, Korea. Phylogenetically, the strain was grouped with the genus Massilia and shared 95.33–97.97% 16S rRNA sequence similarity with the type strains of other species of the genus Massilia. The DNA–DNA hybridisation between TA-C7eT and Massilia haematophila KACC 13771T, Massilia suwonesis KACC 12635T, and Massilia yuzhufengensis KACC 16569T revealed a low level of relatedness (<40%). The low levels of DNA–DNA hybridisation values identified strain TA-C7eT as a novel species in the genus Massilia. The major fatty acids of the strain were C16:0 (37.3%) and summed feature 3 (C16:1 ω7c and/or C16:1 ω6c) (40.6%). Q-8 was identified as the only isoprenoid quinone. The polar lipids profile of the strain showed the presence of phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylethanolamine, diphosphatidylglycerol, an unidentified aminophospholipid and three unidentified lipids. The DNA G+C content of the strain was found to be 63.2 mol%. On the basis of the phenotypic, genotypic and chemotaxonomic characteristics, strain TA-C7eT represents a novel species in the genus Massilia, for which the name Massilia chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov. (=KACC 18674T = NBRC 112463T) is proposed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baik KS, Choe HN, Park SC, Hwang YM, Kim EM, Park C, Seong CN (2013) Sphingopyxis rigui sp. nov. and Sphingopyxis wooponensis sp. nov., isolated from wetland freshwater, and emended description of the genus Sphingopyxis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:1297–1303
Breznak JA, Costilow RN (2007) Physicochemical factors in growth. In: Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 309–329
Embley TM, Wait R (1994) Structural lipids of eubacteria. In: Goodfellow M, O’Donnell AG (eds) Modern microbial method: chemical methods in prokaryotic systematics. Wiley, Chichester, pp 121–161
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Gonzalez J, Saiz-Jimenez C (2002) A fluorimetric method for the estimation of G+C mol% content in microorganisms by thermal denaturation temperature. Environ Microbiol 4:770–773
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Monro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic Press, New York, pp 21–132
Kämpfer P, Falsen E, Busse HJ (2008) Naxibacter varians sp. nov. and Naxibacter haematophilus sp. nov., and emended description of the genus Naxibacter. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1680–1684
Kämpfer P, Lodders N, Martin K, Falsen E (2011) Revision of the genus Massilia La Scola et al. 2000, with an emended description of the genus and inclusion of all species of the genus Naxibacter as new combinations, and proposal of Massilia consociata sp nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1528–1533
Kim DU, Ka JO (2014) Roseomonas soli sp. nov., isolated from an agricultural soil cultivated with Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:1024–1029
Kim OS et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Komagata K, Suzuki KI (1987) Lipid and cell-wall analysis in bacterial systematics. Methods Microbiol 19:161–207
La Scola B, Birtles RJ, Mallet MN, Raoult D (1998) Massilia timonae gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from blood of an immunocompromised patient with cerebellar lesions. J Clin Microbiol 36:2847–2852
Luo X, Xie Q, Wang J, Pang H, Fan J, Zhang J (2013) Massilia lurida sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:2118–2123
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Göker M, Spröer C, Klenk HP (2013) When should a DDH experiment be mandatory in microbial taxonomy? Arch Microbiol 195:413–418
Minnikin DE, O’donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Pruesse E, Peplies J, Glockner FO (2012) SINA: accurate high-throughput multiple sequence alignment of ribosomal RNA genes. Bioinformatics 28:1823–1829
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. MIDI technical note 101. Microbial ID, Inc, Newark
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray RGE, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, pp 607–654
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152–155
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE, Stackebrandt E, Starr MP, Truper HG (1987) International Committee on Systematic Bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Weon HY, Yoo SH, Kim SJ, Kim YS, Anandham R, Kwon SW (2010) Massilia jejuensis sp. nov. and Naxibacter suwonensis sp. nov., isolated from air samples. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:1938–1943
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the RDA Genebank Management Program from the Genetic Resources Division, National Institute of Agricultural Biotechnology, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, H., Kim, DU., Park, S. et al. Massilia chloroacetimidivorans sp. nov., a chloroacetamide herbicide-degrading bacterium isolated from soil. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 751–758 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0845-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0845-3