Abstract
Aims
To investigate whether legume-dominated cereal/legume intercropping could facilitate phosphorus acquisition and yield enhancement via changes in root morphology and distribution.
Methods
A field experiment was conducted for two consecutive years in a split-plot design with main plots treated with two phosphorus levels and subplots treated with maize and alfalfa grown alone or intercropped.
Results
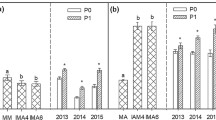
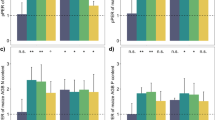
In maize/alfalfa intercropping, alfalfa was 3.0–5.7 times more competitive than maize. Compared to monoculture, soil water balance of intercropped maize was significantly reduced by 115%, while that of alfalfa was dramatically enhanced by 469%. Thus, intercropped maize had pronouncedly reduced root growth by 17–36%, phosphorus uptake by 24%, and yield by 12%, but the associated alfalfa had significantly increased root growth by 26%–175%, phosphorus uptake by 208%, and yield by 137%, leading to significantly improved phosphorus uptake and yield of the composite population. Among root morphological and distribution traits, crown root surface area and lateral root volume were the best predictors of maize and alfalfa phosphorus uptake, respectively.
Conclusions
Legume-dominated maize/alfalfa intercropping can significantly improve phosphorus acquisition and yield production through modifications in soil water balance and root morphology and distribution, and the system overyielding was performed via alfalfa rather than maize.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber SA (1995) Soil nutrient bioavailability: a mechanistic approach, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Bhadoria PBS, Kaselowsky J, Claassen N, Jungk A (1991) Phosphate diffusion coefficients in soil as affected by bulk density and water content. Z Pflanzenernähr Bodenkd 154:53–57
Bhatti IH, Ahmad R, Jabbar A et al (2006) Competitive behaviour of component crops in different sesame-legume intercropping systems. Int J Agric Biol (Pakistan) 8:165–167
Brooker RW, Jones HG, Paterson E et al (2015) Improving intercropping: a synthesis of research in agronomy, plant physiology and ecology. New Phytol 206:107–117
Burnham KP, Anderson DR (2002) Model selection and multimodel inference: a practical information-theoretic approach. Springer Sci Bus Media
Burton AL, Johnson JM, Foerster JM, Hirsch CN, Buell CR, Hanlon MT, Kaeppler SM, Brown KM, Lynch JP (2014) QTL mapping and phenotypic variation for root architectural traits in maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 127:2293–2311
Callaway RM (1995) Positive interactions among plants. Bot Rev 61:306–349
Connell JH (1990) Apparent versus real competition in plants. In: Grace JB, Tilman D (eds) Perspectives on plant competition. Academic Press, Inc., San Diego, pp 9–26
Crawley MJ (2009) Plant ecology, 2nd edn. Blackwell Publishing Ltd, Oxford
Darch T, Giles CD, Blackwell MSA, George TS, Brown LK, Menezes-Blackburn D, Shand CA, Stutter MI, Lumsdon DG, Mezeli MM, Wendler R, Zhang H, Wearing C, Cooper P, Haygarth PM (2018) Inter- and intra-species intercropping of barley cultivars and legume species, as affected by soil phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 427:125–138
Desnos T (2008) Root branching responses to phosphate and nitrate. Curr Opin Plant Biol 11:82–87
Faucon MP, Houben D, Reynoird JP et al (2015) Advances and perspectives to improve the phosphorus availability in cropping systems for agroecological phosphorus management. Adv Agron 134:1–19
Fridley JD (2001) The influence of species diversity on ecosystem productivity: how, where, and why? Oikos 93:514–526
Gao YZ, Lynch JP (2016) Reduced crown root number improves water acquisition under water deficit stress in maize (Zea mays L.). J Exp Bot 67:4545–4557
Gao Y, Duan A, Qiu X, Liu Z, Sun J, Zhang J, Wang H (2010) Distribution of roots and root length density in a maize/soybean strip intercropping system. Agric Water Manag 98:199–212
He Y, Ding N, Shi JC, Wu M, Liao H, Xu J (2013) Profiling of microbial PLFAs: implications for interspecific interactions due to intercropping which increase phosphorus uptake in phosphorus limited acidic soils. Soil Biol Biochem 57:625–634
Heppell J, Talboys P, Payvandi S et al (2015) How changing root system architecture can help tackle a reduction in soil phosphate (P) levels for better plant P acquisition. Plant Cell Environ 38:118–128
Hinsinger P (2001) Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: a review. Plant Soil 237:173–195
Hodge A (2004) The plastic plant: root responses to heterogeneous supplies of nutrients. New Phytol 162:9–24
Jensen JR, Bernhard RH, Hansen S, McDonagh J, Møberg JP, Nielsen NE, Nordbo E (2003) Productivity in maize based cropping systems under various soil-water-nutrient management strategies in a semi-arid, alfisol environment in East Africa. Agric Water Manag 59:217–237
Lambers H, Shane MW, Cramer MD et al (2006) Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits. Ann Bot 98:693–713
Li L, Yang SC, Li XL (1999) Interspecific complementary and competitive interactions between intercropped maize and faba bean. Plant Soil 212:105–114
Li L, Sun J, Zhang F et al (2001) Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping I. Yield advantage and interspeci interactions on nutrients. Field Crop Res 71:123–137
Li L, Tang C, Rengel Z, Zhang F (2003a) Chickpea facilitates phosphorus uptake by intercropped wheat from an organic phosphorus source. Plant Soil 248:297–303
Li L, Zhang F, Li X et al (2003b) Interspecific facilitation of nutrient uptake by intercropped maize and faba bean. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 65:61–71
Li SM, Li L, Zhang FS, Tang C (2004) Acid phosphatase role in chickpea/maize intercropping. Ann Bot 94:297–303
Li L, Sun J, Zhang F, Guo T, Bao X, Smith FA, Smith SE (2006) Root distribution and interactions between intercropped species. Oecologia 147:280–290
Li L, Li SM, Sun JH, Zhou LL, Bao XG, Zhang HG, Zhang FS (2007) Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus-deficient soils. Proc Natl Acad Sci 104:11192–11196
Li C, Dong Y, Li H, Shen J, Zhang F (2016) Shift from complementarity to facilitation on P uptake by intercropped wheat neighboring with faba bean when available soil P is depleted. Sci Rep 6:18663
Loreau M, Hector A (2001) Partitioning selection and complementarity in biodiversity experiments. Nature 412:72–76
Lynch J (1995) Root architecture and plant productivity. Plant Physiol 109:7–13
Lynch JP (2007) Roots of the second green revolution. Aust J Bot 55:493–512
Lynch JP (2011) Root phenes for enhanced soil exploration and phosphorus acquisition: tools for future crops. Plant Physiol 156:1041–1049
Lynch JP (2013) Steep, cheap and deep: an ideotype to optimize water and N acquisition by maize root systems. Ann Bot 112:347–357
Lynch JP, Brown KM (2001) Topsoil foraging - an architectural adaptation of plants to low phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 237:225–237
Lynch JP, Brown KM (2012) New roots for agriculture: exploiting the root phenome. Phil Trans R Soc B 367:1598–1604
Lynch JP, Deikman J (1998) Phosphorus in plant biology: regulatory roles in molecular, cellular, organismic, and ecosystem processes. Volume 19 of Current topics in plant physiology. American Society of Plant Biologists, Rockville, MD, USA
Manske GGB, Ortiz-Monasterio JI, Van Ginkel M et al (2000) Traits associated with improved P-uptake efficiency in CIMMYT’s semidwarf spring bread wheat grown on an acid Andisol in Mexico. Plant Soil 221:189–204
Miguel MA, Widrig A, Vieira RF, Brown KM, Lynch JP (2013) Basal root whorl number: a modulator of phosphorus acquisition in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Ann Bot 112:973–982
Miguel MA, Postma JA, Lynch JP (2015) Phene synergism between root hair length and basal root growth angle for phosphorus acquisition. Plant Physiol 167:1430–1439
Niu YF, Chai RS, Jin GL, Wang H, Tang CX, Zhang YS (2013) Responses of root architecture development to low phosphorus availability: a review. Ann Bot 112:391–408
Richardson AE, Lynch JP, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Smith FA, Smith SE, Harvey PR, Ryan MH, Veneklaas EJ, Lambers H, Oberson A, Culvenor RA, Simpson RJ (2011) Plant and microbial strategies to improve the phosphorus efficiency of agriculture. Plant Soil 349:121–156
Rose TJ, Rengel Z, Ma Q, Bowden JW (2007) Differential accumulation patterns of phosphorus and potassium by canola cultivars compared to wheat. J Plant Nutr Soil Sci 170:404–411
Saengwilai P, Tian X, Lynch JP (2014) Low crown root number enhances nitrogen acquisition from low-nitrogen soils in maize. Plant Physiol 166:581–589
Shen J, Yuan L, Zhang J, Li H, Bai Z, Chen X, Zhang W, Zhang F (2011) Phosphorus dynamics: from soil to plant. Plant Physiol 156:997–1005
Sun B, Peng Y, Yang H, Li Z, Gao Y, Wang C, Yan Y, Liu Y (2014) Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)/maize (Zea mays L.) intercropping provides a feasible way to improve yield and economic incomes in farming and pastoral areas of Northeast China. PLoS One 9:e110556
Tilman D, Fargione J, Wolff B, D'Antonio C, Dobson A, Howarth R, Schindler D, Schlesinger WH, Simberloff D, Swackhamer D (2001) Forecasting agriculturally driven global environmental change. Science 292:281–284
Tilman D, Reich PB, Isbell F (2012) Biodiversity impacts ecosystem productivity as much as resources, disturbance, or herbivory. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109:10394–10397
Trachsel S, Kaeppler SM, Brown KM, Lynch JP (2011) Shovelomics: high throughput phenotyping of maize (Zea mays L.) root architecture in the field. Plant Soil 341:75–87
Trachsel S, Kaeppler SM, Brown KM, Lynch JP (2013) Maize root growth angles become steeper under low N conditions. Field Crop Res 140:18–31
Turner FT, Gilliam JW (1976) Increased P diffusion as an explanation of increased P availability in flooded rice soil. Plant Soil 45:365–377
Vance CP, Uhde-Stone C, Allan DL (2003) Phosphorus acquisition and use: critical adaptations by plants for securing a nonrenewable resource. New Phytol 157:423–447
Xia HY, Wang ZG, Zhao JH, Sun JH, Bao XG, Christie P, Zhang FS, Li L (2013) Contribution of interspecific interactions and phosphorus application to sustainable and productive intercropping systems. Field Crop Res 154:53–64
Xue Y, Xia H, Christie P, Zhang Z, Li L, Tang C (2016) Crop acquisition of phosphorus, iron and zinc from soil in cereal/legume intercropping systems: a critical review. Ann Bot 117:363–377
Zhang G, Yang Z, Dong S (2011) Interspecific competitiveness affects the total biomass yield in an alfalfa and corn intercropping system. Field Crop Res 124:66–73
Zhang YK, Chen FJ, Li L, Chen YH, Liu BR, Zhou YL, Yuan LX, Zhang FS, Mi GH (2012) The role of maize root size in phosphorus uptake and productivity of maize/faba bean and maize/wheat intercropping systems. Sci China Life Sci 55:993–1001
Zhang G, Zhang C, Yang Z, Dong S (2013) Root distribution and N acquisition in an alfalfa and corn intercropping system. J Agric Sci 5:128–142
Zhang CC, Postma JA, York LM, Lynch JP (2014) Root foraging elicits niche complementarity-dependent yield advantage in the ancient “three sisters” (maize/bean/squash) polyculture. Ann Bot 114:1719–1733
Zhang DB, Yao PM, Na Z et al (2016) Soil water balance and water use efficiency of dryland wheat in different precipitation years in response to green manure approach. Sci Rep 6:26856
Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2005a) Topsoil foraging and phosphorus acquisition efficiency in maize (Zea mays). Funct Plant Biol 32:749–762
Zhu J, Kaeppler SM, Lynch JP (2005b) Mapping of QTL controlling root hair length in maize (Zea mays L.) under phosphorus deficiency. Plant Soil 270:299–310
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Key Basic Research Program of China (2016YFC0500703), Human Resources and Social Security Department of Jilin Province (2016-28), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670446, 31270444), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Y821RE1001), and the Major State Basic Research Development Program of China (2015CB150801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Yinglong Chen.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 1529 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, B., Gao, Y., Yang, H. et al. Performance of alfalfa rather than maize stimulates system phosphorus uptake and overyielding of maize/alfalfa intercropping via changes in soil water balance and root morphology and distribution in a light chernozemic soil. Plant Soil 439, 145–161 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3888-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3888-y