Abstract
Aims
The thiosulphate induced accumulation of mercury by the three plants Brassica juncea var.LDZY, Brassica juncea var.ASKYC and Brassica napus var. ZYYC and the transformation of mercury fractionation in the rhizosphere of each plant was investigated in the field.
Methods
Experimental farmland was divided into control and thiosulphate plots. Each plot was divided into three subplots with each planted with one of the plants. After harvesting, the mercury concentration in plants, mercury fractionation in rhizosphere soil before and after phytoextraction, and the vertical distribution of bioavailable mercury in bulk soil profiles was analyzed.
Results
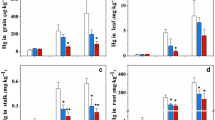
The cultivar B. juncea var.LDZY accumulated a higher amount of mercury in shoots than the other two plants. Thiosulphate treatment promoted an increase in the concentration of metal in plants and a transformation of Fe/Mn oxide-bound and organic-bound mercury (potential bioavailable fractions) into soluble and exchangeable and specifically-sorbed fractions in the rhizosphere. The observed increase in bioavailable rhizosphere mercury concentration was restricted to the root zone; mercury did not move down the soil profile as a function of thiosulphate application to soil.
Conclusions
Thiosulphate-induced phytoextraction has the potential to manage environmental risk of mercury in soil by decreasing the concentration of mercury associated with potential bioavailable fraction that can be accumulated by crop plants.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaylock MJ, David E, Dushenkov S, Zakharova O, Gussman C, Kapulnik Y, Ensley BD, Raskin I (1997) Enhanced accumulation of Pb in Indian mustard by soil-applied chelating agents. Environ Sci Technol 31:860–865
Bishop KH, Lee YH, Munthe J, Dambrine E (1998) Xylem sap as a pathway for total mercury and methylmercury transport from soils to tree canopy in the boreal forest. Biogeochemistry 40:101–113
Chen J, Yang ZM (2012) Mercury toxicity, molecular response and tolerance in higher plants. BioMetals 25:847–857
CNEPA (Chinese National Environment Protect Agency) (1995) Environmental quality standard for soils, GB15618-1995, pp.1–6 (In Chinese)
Dessureault-Rompré J, Nowack B, Schulin R, Tercier-Waeber ML, Luster J (2008) Metal solubility and speciation in the rhizosphere of Lupinus albus cluster roots. Environ Sci Technol 42:7146–7151
Fayiga AO, Ma LQ, Zhou QX (2007) Effects of plant arsenic uptake and heavy metals on arsenic distribution in an arsenic-contaminated soil. Environ Pollut 147:737–742
Feng X, Li P, Qiu G, Wang S, Li G, Shang L, Meng B, Jiang H, Bai W, Li Z (2008) Human exposure to methylmercury through rice intake in mercury mining areas, Guizhou Province, China. Environ Sci Technol 42:326–332
Feng X, Sommar J, Lindqvist O, Hong Y (2002) Occurrence, emissions and deposition of mercury during coal combustion in the province Guizhou, China. Water Air Soil Pollut 139:311–324
Grispen VMJ, Nelissen HJM, Verkleij JAC (2006) Phytoextraction with Brassica napus L.: a tool for sustainable management of heavy metal contaminated soils. Environ Pollut 144:77–83
Haag-Kerwer A, Schäfer HJ, Heiss S, Walter C, Rausch T (1999) Cadmium exposure in Brassica juncea causes a decline in transpiration rate and leaf expansion without effect on photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 50:1827–1835
Hamon RE, McLaughlin MJ (1999) Fifth International Conference on the Biogeochemistry of Trace Elements (ICOBTE), Vienna. pp. 908–909
Han FX, Sridhar B, Monts DL, Su Y (2004) Phytoavailability and toxicity of trivalent and hexavalent chromium to Brassica juncea. New Phytol 162:489–499
Han FX, Su Y, Monts DL, Waggoner CA, Plodinec MJ (2006) Binding, distribution, and plant uptake of mercury in a soil from Oak Ridge, Tennessee, USA. Sci Total Environ 368:753–768
Hassett DJ, Heebink LV, Pflughoeft-Hassett DF (2009) Potential for mercury vapor release from coal combustion by-products. Fuel Sci Technol 85:613–620
Hauser L, Tandy S, Schulin R, Nowack B (2005) Column extraction of heavy metals from soils using the biodegradable chelating agent EDDS. Environ. Sci Technol 39:6819–6824
Higueras P, Oyarzun R, Biester H, Lillo J, Lorenzo S (2003) A first insight into mercury distribution and speciation in soils from the Almadén mining district, Spain. J Geochem Explor 80:95–104
Huang JW, Chen J, Berti WR, Cunningham SD (1997) Phytoremediation of lead-contaminated soils: role of synthetic chelates in lead phytoextraction. Environ Sci Technol 31:800–805
Israr M, Sahi SV (2006) Antioxidative responses to mercury in the cell cultures of Sesbania Drummondii. Plant Physiol Biochem 44:590–595
Issaro N, Abi-Ghanem C, Bermond A (2009) Fractionation studies of mercury in soils and sediments: a review of the chemical reagents used for mercury extraction. Anal Chim Acta 631:1–12
Järup L (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Br Med Bull 68:167–182
Jing YD, He ZL, Yang XE, Sun CY (2008) Evaluation of soil tests for plant-available mercury in a soil-crop rotation system. Commun Soil Sci Plan 39:3032–3046
Jones DL (1998) Organic acids in the rhizosphere–a critical review. Plant soil 205:25–44
Jones DL, Darah PR, Kochian LV (1996) Critical evaluation of organic acid mediated iron dissolution in the rhizosphere and its potential role in root iron uptake. Plant soil 180:57–66
Lomonte C, Doronila AI, Gregory D, Baker AJM, Kolev SD (2010) Phytotoxicity of biosolids and screening of selected plant species with potential for mercury phytoextraction. J Hazard Mater 173:494–501
Lu R (2000) Chemical analysis method of agricultural soil. China Agricultural Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Luo C, Shen Z, Li X (2005) Enhanced phytoextraction of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cd with EDTA and EDDS. Chemosphere 59:1–11
Moreno F, Anderson C, Stewart R, Robinson B, Nomura, Ghomshei M, Meech JA (2005a) Effect of thioligands on Plant-Hg accumulation and volatilisation from mercury-contaminated mine tailings. Plant Soil 275:233–246
Moreno FN, Anderson CWN, Stewart RB, Robinson BH (2005b) Mercury volatilisation and phytoextraction from base-metal mine tailings. Environ Pollut 136:341–352
Moreno-Jiméneza E, Gamarrab R, Carpena-Ruiza RO, Millánc R, Peñalosaa JM, Esteban E (2006) Mercury bioaccumulation and phytotoxicity in two wild plant species of Almadén area. Chemosphere 63:1969–1973
Mukherjee AB, Zevenhoven R, Brodersen J, Hylander LD, Bhattacharya P (2004) Mercury in waste in the European Union: sources, disposal methods and risks. Resour Conserv Recycl 42:155–182
Patra M, Bhowmik N, Bandopadhyay B, Sharma A (2004) Comparison of mercury, lead and arsenic with respect to genotoxic effects on plant systems and the development of genetic tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 52:199–223
Patra M, Sharma A (2000) Mercury toxicity in plants. Bot Rev 66:379–422
Pedron F, Petruzzell G, Barbafier M, Tassi E (2013) Remediation of a mercury-contaminated industrial soil using bioavailable contaminant stripping. Pedosphere 23:104–110
Qiu G, Feng X, Wang S, Fu X, Shang L (2009) Mercury distribution and speciation in water and fish from abandoned Hg mines in Wanshan, Guizhou province, China. Sci Total Environ 407:5162–5168
Qiu G, Feng X, Wang S, Shang L (2005) Mercury and methylmercury in riparian soil, sediments, mine-waste calcines, and moss from abandoned Hg mines in east Guizhou province, southwestern China. Appl Geochem 20:627–638
Ravichandran M (2004) Interactions between mercury and dissolved organic matter––a review. Chemosphere 55:319–331
Ravichandran M, Aiken GR, Reddy MM, Ryan JN (1998) Enhanced dissolution of cinnabar (mercuric sulfide) by dissolved organic matter isolated from the Florida Everglades. Environ Sci Technol 32:3305–3311
Rio M, Font R, Fernandez-Martinez J, Domínguez J, Haro A (2000) Field trials of Brassica carinata and Brassica juncea in polluted soils of the Guadiamar river area. Fresen Environ Bull 9:328–332
Rodriguez L, López-Bellido F, Carnicer A, Alcalde-Morano V (2003) Phytoremediation of mercury-polluted soils using crop plants. Fresen Environ Bull 12:967–971
Rodriguez L, Rincon J, Asencio I, Rodriguez-Castellanos L (2007) Capability of selected crop plants for shoot mercury accumulation from polluted soils: phytoremediation perspectives. Int J Phytoremediat 9:1–13
Sholupov S, Pogarevb S, Ryzhovb S, Mashyanovb V, Stroganova A (2004) Zeeman atomic absorption spectrometer RA-915+ for direct determination of mercury in air and complex matrix samples. Fuel Process Technol 85:473–485
Smolińska B, Cedzyńska K (2007) EDTA and urease effects on Hg accumulation by Lepidium sativum. Chemosphere 69:1388–1395
Ullah MB (2008) Mercury Stabilization using Thiosulphate and Thioselenate. Dissertation, University of British Columbia
Wang J, Feng X, Anderson CWN, Qiu GL, Ping L, Bao ZD (2011a) Ammonium thiosulphate enhanced phytoextraction from mercury contaminated soil-results from a greenhouse study. J Hazard Mater 186:119–127
Wang J, Feng X, Anderson CWN, Zhu W, Yin R, Wang H (2011b) Mercury distribution in the soil–plant–air system at the Wanshan mercury mining district in Guizhou, Southwest China. Environ Toxicol Chem 30:2725–2731
Wang J, Feng X, Anderson CWN, Xing Y, Shang L (2012a) Remediation of mercury contaminated sites-a review. J Hazard Mater 221-222:1–18
Wang J, Feng X, Anderson CWN, Wang H, Zheng L, Hu T (2012b) Implications of mercury speciation in thiosulphate treated plants. Environ Sci Technol 46:5361–5368
Wang SF, Feng XB, Qiu GL, Fu XW, Wei ZQ (2007) Characteristics of mercury exchange flux between soil and air in the heavily air-polluted area, eastern Guizhou, China. Atmos Environ 41:5584–5594
Wang YD, Greger M (2006) Use of iodide to enhance the phytoextraction of mercury-contaminated soil. Sci Total Environ 368:30–39
Wu Y, Wang S, Streets DG, Hao J, Chan M, Jiang J (2006) Trends in anthropogenic mercury emissions in China from 1995 to 2003. Environ Sci Technol 40:5312–5318
Yang Y, Fang J, Tang Y, Ji C, Zheng CY, He JS, Zhu B (2008) Storage, patterns and controls of soil organic carbon in the Tibetan grasslands. Global Change Biol 14:1592–1599
Yang Y, Ratte D, Smets B, Pignatello J, Grasso D (2001) Mobilization of soil organic matter by complexing agents and implications for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon desorption. Chemosphere 43:1013–1021
Zhang H, Feng X, Larssen T, Qiu G, Vogt R (2010) In inland China, rice, rather than fish is the major pathway for methylmercury exposure. Environ Health Perspect 118:1183–1188
Acknowledgments
This research was financed by the Natural Science Foundation of China (41030752, 41021062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Henk Schat.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Feng, X., Anderson, C.W.N. et al. Thiosulphate-induced mercury accumulation by plants: metal uptake and transformation of mercury fractionation in soil - results from a field study. Plant Soil 375, 21–33 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1940-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-013-1940-5