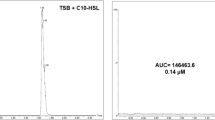
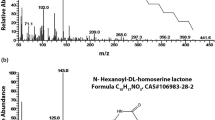
Abstract
Background and aims
Recent basic knowledge on the regulation of virulence in pectinolytic bacteria revealed pathogen communication via quorum sensing signals as a crucial event for the expression of virulence and the onset of disease symptoms. In this paper, we present and discuss advances in a new biocontrol approach based on the interference of microbial communication involved in the cellular density and microenvironment sensoring.
Methods
This emerging strategy consists in the characterization of the signaling molecules used by the target pathogen, then the use of harmless structural analogs to stimulate plant associated-microflora able to degrade both molecule families.
Results
The biocontrol method has been applied for the first time for the control of Pectobacterium atrosepticum. This psychrotrophic bacterium synthesizes N-acyl-homoserine lactones involved in cell-to-cell communication that triggers soft rot and blackleg of potato. The use of the gamma-caprolactone stimulant promotes the emergence and catabolic activity of Rhodococcus erythropolis antagonistic populations in the potato rhizosphere.
Conclusions
Rhodococcus bacteria have the ability to disrupt the quorum sensing-based communication of P. atrosepticum by degrading N-acyl-homoserine lactone signaling molecules and prevent disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alabouvette C, Olivain C, Steinberg C (2006) Biological control of plant diseases: the European situation. Eur J Plant Pathol 114:329–341
Axelrood PE, Rella M, Schroth MN (1988) Role of antibiosis and competition of Erwinia strains in potato infection courts. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:1222–1229
Bainton NJ, Stead P, Chhabra SR, Bycroft BW, Salmond GPC, Stewart GSAB, Williams P (1992) N-(3-oxohexanoyl)-L-homoserine lactone regulates carbapenem antibiotic production in Erwinia carotovora. Biochem J 288:997–1004
Barnard AML, Salmond GPC (2007) Quorum sensing in Erwinia species. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:415–423
Barras F, Van Gijsegem F, Chatterjee AK (1994) Extracellular enzymes and pathogenesis of soft-rot Erwinia. Ann Rev Phytopathol 32:201–234
Bell KS, Sebaihia M, Pritchard L, Holden MTG, Hyman LJ et al (2004) Genome sequence of the enterobacterial phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica and characterization of virulence factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:105–110
Brader G, Sjöblom S, Hyytiäinen H, Sims-Huopaniemi K, Palva ET (2005) Altering substrate chain length specificity of an acylhomoserine lactone synthase in bacterial communication. J Biol Chem 280:10403–10409
Brazelton JN, Pfeufer EE, Sweat TA, MacSpadden Gardener BB, Coenen C (2008) 2,4-Diacetylphloroglucinol alters plant root development. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 21:1349–1358
Brewer MT, Larkin RP (2005) Efficacy of several potential biocontrol organisms against Rhizoctonia solani on potato. Crop Protect 24:939–950
Carlier A, Uroz S, Smadja B, Fray R, Latour X, Dessaux Y, Faure D (2003) The Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens harbors an attM-paralogous gene, aiiB, also encoding N-acyl homoserine lactonase activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:4989–4993
Cha C, Gao P, Chen Y-C, Shaw P, Farrand SK (1998) Production of acyl-homoserine lactone quorum-sensing signals by Gram-negative plant-associated bacteria. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 11:1119–1129
Chatterjee A, Cui Y, Hasegawa H, Leigh N, Dixit V, Chatterjee AK (2005) Comparative analysis of two classes of quorum-sensing signaling systems that control production of extracellular proteins and secondary metabolites in Erwinia carotovora subspecies. J Bacteriol 187:8026–8038
Cirou A, Diallo S, Kurt C, Latour X, Faure D (2007) Growth promotion of quorum-quenching bacteria in the rhizosphere of Solanum tuberosum. Environ Microbiol 9:1511–1522
Cirou A, Raffoux A, Diallo S, Latour X, Dessaux Y, Faure D (2011) Gamma-caprolactone stimulates the growth of quorum-quenching Rhodococcus populations in a large-scale hydroponic system for culturing Solanum tuberosum. Res Microbiol. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2011.01.010
Cirou A, Uroz S, Chapelle E, Latour X, Orange N, Faure D, Dessaux Y (2009) Quorum sensing as a target for novel biocontrol strategies. In: Gisi U, Chet I, Gullino ML (eds), Recent developments in management of plant diseases Plant Pathology in the 21st Century. Springer, pp 121–132
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka EA (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:4951–4959
Costa JM, Loper JE (1997) EcbI and EcbR: homologs of LuxI and LuxR affecting antibiotic and exoenzyme production by Erwinia carotovora subsp. betavasculorum. Can J Microbiol 43:1164–1171
Coulthurst SJ, Lilley KS, Salmond GPC (2006) Genetic and proteomic analysis of the role of luxS in the enteric phytopathogen, Erwinia carotovora. Mol Plant Pathol 7:31–45
Czajkowski R, Grabe GJ, van der Wolf JM (2009) Distribution of Dickeya spp. and Pectobacterium carotovorum subsp. carotovorum in naturally infected seed potatoes. Eur J Plant Pathol 125:263–275
D’Angelo-Picard C, Faure D, Penot I, Dessaux Y (2005) Diversity of N-acyl homoserine lactone-producing and -degrading bacteria in soil and tobacco rhizosphere. Environ Microbiol 7:1796–1808
de Carvalho CCCR, da Fonseca MMR (2005) The remarkable Rhodococcus erythropolis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:715–726
Delalande L, Faure D, Uroz S, D’Angelo-Picard C, Elasri M, Carlier A, Berruyer R, Petit A, Williams P, Dessaux Y (2005) N-hexanoyl-L-homoserine lactone, a mediator of bacterial quorum-sensing regulation, exhibits plant-dependent stability and may be inactivated by germinating Lotus corniculatus seedlings. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 52:13–20
Diallo S, Crépin A, Barbey C, Orange N, Burini J-F, Latour X (2011) Mechanisms and recent advances in biological control mediated through the potato rhizosphere. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 75:351–364
Diallo S, Latour X, Groboillot A, Copin P, Smadja B, Orange N, Chevalier S (2009) Simultaneous and selective detection of two major soft rot pathogens of potato: Pectobacterium atrosepticum (Erwinia carotovora subsp. atrosepticum) and Dickeya spp. (Erwinia chrysanthemi). Eur J Plant Pathol 125:249–354
Dong YH, Wang LH, Zhang HB, Zhang XF, Zhang LH (2001) Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase. Nature 411:813–817
Dong YH, Xu JL, Li XZ, Zhang LH (2000) AiiA, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of Erwinia carotovora. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:3526–3531
FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) (2008) International year of the potato 2008, New light on a hidden treasure. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, p 144
Faure D, Dessaux Y (2007) Quorum sensing as a target for developing control strategies for the plant pathogen Pectobacterium. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:353–365
Faure D, Cirou A, Dessaux Y (2010) Chemicals promoting the growth of n-acylhomoserine lactone-degrading bacteria. United States Patent Application No.: 20100050719 A1. (WO/2008/090479)
Fravel DR (2005) Commercialization and implementation of biocontrol. Ann Rev Phytopathol 43:337–359
Gebhardt C, Valkonen JPT (2001) Organization of genes controlling disease resistance in the potato genome. Ann Rev Phytopathol 39:79–102
Götz C, Fekete A, Gebefuegi I, Forczek ST, Fuksova K, Li X, Englmann M, Gryndler M, Hartmann A, Matucha M, Schmitt-Kopplin P, Schröder P (2007) Uptake, degradation and chiral discrimination of N-acyl-D/L-homoserine lactones by barley (Hordeum vulgare) and yam bean (Pachyrhizus erosus) plants. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:1447–1457
Gray KM, Garey JR (2001) The evolution of bacterial LuxI and LuxR quorum-sensing regulators. Microbiology 147:2379–2387
Hardie KR, Heurlier K (2008) Establishing bacterial communities by ‘word of mouth’: LuxS and autoinducer 2 in biofilm development. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:635–643
Hélias V, Andrivon D, Jouan B (2000) Internal colonization pathways of potato plants by Erwinia carotovora ssp. atroseptica. Plant Pathol 49:33–42
Jafra S, Przysowa J, Czajkowski R, Michta A, Garbeva P, van der Wolf JM (2006) Detection and characterization of bacteria from the potato rhizosphere degrading N-acyl-homoserine lactone. Can J Microbiol 52:1006–1015
Johansson JF, Paul LR, Finlay RD (2004) Microbial interactions in the mycorrhizosphere and their significance for sustainable agriculture. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 48:1–13
Jones S, Yu B, Bainton NJ, Birdsall M, Bycroft BW, Chhabra SR, Cox AJR, Golby P, Reeves PJ, Stephens S, Wilson MK, Salmond GPC, Stewart GSAB, Williams P (1993) The Lux autoinducer regulates the production of exoenzyme virulence determinants in Erwinia carotovora and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. EMBO J 12:2477–2482
Keller L, Surette MG (2006) Communication in bacteria: an ecological and evolutionary perspective. Nat Rev Microbiol 4:249–258
Laasik E, Andresen L, Maë A (2006) Type II quorum sensing regulates virulence in Erwinia carotovora ssp. carotovora. FEMS Microbiol Lett 258:227–234
Latour X, Delorme S, Mirleau P, Lemanceau P (2009) Identification of traits implicated in the rhizosphere competence of fluorescent pseudomonads: description of a strategy based on population and model strain studies. In: Lichtfouse E, Navarrete M, Debaeke P, Véronique S, Alberola C (eds), Sustainable Agriculture, vol. 1. Springer, pp 285–296
Latour X, Diallo S, Chevalier S, Morin D, Smadja B, Burini J-F, Haras D, Orange N (2007) Thermoregulation of N-acyl homoserine lactones-based quorum sensing in the soft rot bacterium Pectobacterium atrosepticum. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4078–4081
Latour X, Faure D, Diallo S, Cirou A, Smadja B, Dessaux Y, Orange N (2008) Control of bacterial diseases of potato caused by Pectobacterium spp. (Erwinia carotovora). Cah Agric 17:355–359
Liao C-H (1989) Analysis of pectate lyases produced by soft rot bacteria associated with spoilage of vegetables. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:1677–1683
Liu H, Coulthurst SJ, Pritchard L, Hedley PE, Ravensdale M, Humphris S, Burr T, Takle G, Brurberg MB, Birch PR, Salmond GPC, Toth IK (2008) Quorum sensing coordinates brute force and stealth modes of infection in the plant pathogen Pectobacterium atrosepticum. PLoS Pathogens 20:e1000093
Maë A, Montesano M, Koiv V, Palva ET (2001) Transgenic plants producing the bacterial pheromone N-acylhomoserine lactone exhibit enhanced resistance to the bacterial phytopathogen Erwinia carotovora. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:1035–1042
Margesin R, Fonteyne P-A, Redl B (2005) Low-temperature biodegradation of high amounts of phenol by Rhodococcus spp. and basidiomycetous yeasts. Res Microbiol 156:68–75
Molina L, Constantinescu F, Michel L, Reimmann C, Duffy B, Défago G (2003) Degradation of pathogen quorum-sensing molecules by soil bacteria: a preventive and curative biological control mechanism. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45:71–81
Montesinos E (2003) Development, registration and commercialization of microbial pesticides for plant protection. Int Microbiol 6:245–252
Myskja BK (2006) The moral difference between intragenic and transgenic modification of plants. J Agric Environ Ethics 19:225–238
Park SY, Hwang BJ, Shin MH, Kim JA, Kim HK, Lee JK (2006) N-acylhomoserine lactonase-producing Rhodococcus spp. with different AHL-degrading activities. FEMS Microbiol Lett 261:102–108
Pérombelon MCM (2002) Potato diseases caused by soft rot erwinias: an overview of pathogenesis. Plant Pathol 51:1–12
Pérombelon MCM, Kelman A (1980) Ecology of the soft rot erwinias. Ann Rev Phytopathol 18:361–387
Pérombelon MCM, Kelman A (1987) Blackleg and other diseases caused by soft rot erwinias. Plant Dis 71:283–285
Pérombelon MCM, Salmond GPC (1995) Bacterial soft rots. In: Singh IUS, Singh RP, Kohmoto K (eds) Pathogenesis and host specifity in plant disease. Pergamon Press, Oxford, UK, pp 1–20
Pirhonen M, Flego D, Heikinheimo R, Palva ET (1993) A small diffusible signal molecule is responsible for the global control of virulence and exoenzyme production in plant pathogen Erwinia carotovora. EMBO J 12:2467–2476
Pritchard L, Liu H, Booth C, Douglas, E, François P, Schrenzel J, Hedley PE, Birch PR, Toth IK (2009) Microarray comparative genomic hybridisation analysis incorporating genomic organisation, and application to enterobacterial plant pathogens. PLoS Comput Biol, e1000473
Reading NC, Sperandio V (2006) Quorum sensing: the many languages of bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 254:1–11
Reimmann C, Ginet N, Michel L, Keel C, Michaix P, Krishnapillai V, Zala M, Heurlier K, Triandafillu K, Harms H, Défago G, Haas D (2002) Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Microbiology 148:923–932
Ryan RP, Dow JM (2008) Diffusible signals and interspecies communication in bacteria. Microbiology 154:1845–1858
Schippers B, Bakker AW, Bakker PAHM (1987) Interactions of deleterious and beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms and the effect of cropping practice. Ann Rev Phytopathol 25:339–358
Smadja B, Latour X, Faure D, Chevalier S, Dessaux Y, Orange N (2004a) Involvement of N-acylhomoserine lactones throughout the plant infection by Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica (Pectobacterium atrosepticum). Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 17:1269–1278
Smadja B, Latour X, Trigui S, Burini J-F, Chevalier S, Orange N (2004b) Thermodependence of growth and enzymatic activities implicated in pathogenicity of two Erwinia carotovora subspecies (Pectobacterium spp.). Can J Microbiol 50:19–27
Swift S, Winson MK, Chan PF, Bainton NJ, Birdsall M, Reeves PJ, Rees CED, Chhabra SR, Hill PJ, Throup JP, Bycroft BW, Salmond GPC, Williams P, Stewart GSAB (1993) A novel strategy for the isolation of luxI homologues: evidence for the widespread distribution of a LuxR:LuxI superfamily in enteric bacteria. Mol Microbiol 10:511–520
Toth IK, Pritchard L, Birch PRJ (2006) Comparative genomics reveals what makes an enterobacterial plant pathogen. Ann Rev Phytopathol 44:305–336
Toth IK, van der Wolf JM, Saddler G, Lojkowska E, Hélias V, Pirhonen M, Tsor L, Elphinstone JG (2011) Dickeya species: an emerging problem for potato production in Europe. Plant Pathol 60:385–399
Uroz S, Chhabra SR, Camara M, Williams P, Oger P, Dessaux Y (2005) N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing molecules are modified and degraded by Rhodococcus erythropolis W2 by both amidolytic and novel oxidoreductase activities. Microbiology 151:3313–3322
Uroz S, Dessaux Y, Oger P (2009) Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: the yin and yang of bacterial communication. ChemBioChem 10:205–216
Uroz S, Heinonsalo J (2008) Degradation of N-acyl homoserine lactone quorum sensing signal molecules by forest root-associated fungi. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 65:271–278
Uroz S, Oger PM, Chapelle E, Adeline MT, Faure D, Dessaux Y (2008) A Rhodococcus qsdA-encoded enzyme defines a novel class of large-spectrum quorum-quenching lactonases. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1357–1366
van Peer R, Schippers B (1989) Plant growth responses to bacterization with selected Pseudomonas spp. strains and rhizosphere microbial development in hydroponic cultures. Can J Microbiol 35:456–463
Varzakas TH, Arvanitoyannis IS, Baltas H (2007) The politics and science behind GMO acceptance. Crit Rev Food Sci Nut 47:335–361
Waters CM, Bassler BL (2005) Quorum sensing: cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 21:319–346
Welch M, Dutton JM, Glansdorp FG, Thomas GL, Smith DS, Coulthurst SJ, Barnard AML, Salmond GPC, Spring DR (2005) Structure-activity relationships of Erwinia carotovora quorum sensing signaling molecules. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 15:4235–4238
Whitehead NA, Barnard AML, Slater H, Simpson NJL, Salmond GPC (2001) Quorum-sensing in Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 25:365–404
Whyte LG, Hawari J, Zhou E, Bourbonnière L, Inniss WE, Greer CW (1998) Biodegradation of variable-chain-length alkanes at low temperatures by a psychrotrophic Rhodococcus sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2578–2584
Acknowledgments
ACr and ACi are supported by Comité Nord Plants de Pommes de terre (CNPPT, France) and ANRT (CIFRE) ; CB, NO, JFB, and XL are funded by grants from Conseil Régional de Haute-Normandie & Ministère délégué à l’Enseignement Supérieur et à la Recherche, GRR VATA & FEDER, and by the national grant CAS-DAR AAP N°7124; MT, YD, and DF are funded by CNRS, CNRS program Ingénierie Ecologique, National program PESTICIDES, and Région Ile-de-France (DIM R2DS). Works are related to COST631 action-Understanding and Modelling Plant-Soil Interactions in the Rhizosphere Environment. We also thank Christine Farmer for linguistic support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Bernard Glick.
Alexandre Crépin and Corinne Barbey contributed equally to this paper.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crépin, A., Barbey, C., Cirou, A. et al. Biological control of pathogen communication in the rhizosphere: A novel approach applied to potato soft rot due to Pectobacterium atrosepticum . Plant Soil 358, 27–37 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1030-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-011-1030-5