Abstract
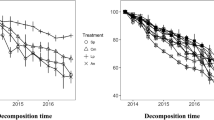
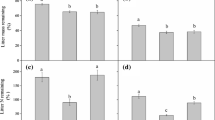
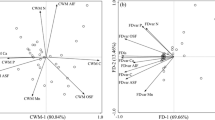
In the last decade a great research effort addressed the effects of litter diversity on ecosystem functions, reporting both synergistic and antagonistic effects for decomposition dynamics. Four coexisting Mediterranean species, representing a range of litter quality, were used to arrange litter mixtures at three diversity levels for a litterbag decomposition experiment. Species identity appeared as the major determinant for litter mass loss (Coronilla emerus∼Hedera helix>Festuca drymeia>Quercus ilex) and nutrient release, with rates for all leaf litter types following the sequence K>N>Mg≥Ca>>Fe. Additive diversity effects were prevalent pooling together all data but also for nutrients separately. Antagonistic interactions were more common than synergistic in the cases of mass loss, N and Ca contents, but not for K, Mg and Fe dynamics. The number of species in the litterbag significantly affected the outcome of non-additive interactions, which were mostly antagonistic for two-species mixtures, and synergistic for the combined 4 species. Litter quality appears to be the most important factor affecting mass loss and nutrient dynamics, while litter diversity, influencing the rates of these processes, plays an important role in reducing their variability, thus suggesting a greater stability of ecosystems properties in presence of mixed litter.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayres E, Steltzer H, Simmons BL, Simpson RT, Steinweg JM, Wallenstein MD, Mellor N, Parton WJ, Moore JC, Wall DH (2009) Home-field advantage accelerates leaf litter decomposition in forests. Soil Biol Biochem 41:606–610
Badre B, Nobelis P, Trémolières M (1998) Quantitative study and modelling of the litter decomposition in a European alluvial forest. Is there an influence of overstorey tree species on the decomposition of ivy litter (Hedera helix L.)? Acta Oecol 19:491–500
Ball BA, Hunter MD, Kominoski JS, Swan CM, Bradford MA (2008) Consequences of non-random species loss for decomposition dynamics: experimental evidence for additive and non-additive effects. J Ecol 96:303–313
Bardgett RD, Freeman C, Ostle NJ (2008) Microbial contribution to climate change through carbon cycle feedbacks. ISME J 2:805–814
Berg B, Staaf H (1981) Leaching, accumulation, and release of nitrogen in decomposing forest litter. Ecol Bull 33:163–178
Berg B, McClaugherty C (2003) Plant litter. Decomposition, humus formation, carbon sequestration. Springer, Berlin
Blondel J, Aronson J (1999) Biology and wildlife of the Mediterranean region. Oxford University, New York
Bonanomi G, Sicurezza M, Caporaso S, Esposito A, Mazzoleni S (2006) Phytotoxicity dynamics of decaying plant materials. New Phytol 169:571–578
Briones MJI, Ineson P (1996) Decomposition of eucalyptus leaves in mixture. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1381–1388
Chapman SK, Koch GW (2007) What type of diversity yields synergy during mixed litter decomposition in a natural forest ecosystem? Plant Soil 299:153–162
Chapman K, Whittaker JB, Heal OW (1988) Metabolic and faunal activity in litters of tree mixtures compared with pure stands. Agric Ecosyst Environ 24:33–40
Conn C, Dighton J (2000) Litter quality influences on decomposition, ectomycorrhizal community structure and mycorrhizal root surface acid phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 32:489–496
Cortez J, Demard JM, Bottner P, Jocteur Monrozier J (1996) Decomposition of Mediterranean leaf litters: a microcosm experiment investigating relationships between decomposition rates and litter quality. Soil Biol Biochem 28:443–452
Cotrufo MF, De Santo AV, Alfani A, Bartoli G, De Cristofaro A (1995) Effects of urban heavy metal pollution on organic matter decomposition in Quercus ilex L. woods. Env Poll 89:81–87
Coûteaux M-M, Bottner P, Berg B (1995) Litter decomposition, climate and litter quality. Trends Ecol Evol 10:63–66
Criquet S, Ferre E, Farnet AM, Le Petit J (2004) Annual dynamics of phosphatase activities in an evergreen oak litter: influence of biotic and abiotic factors. Soil Biol Biochem 36:1111–1118
Fioretto A, Papa S, Pellegrino A, Fuggi A (2007) Decomposition dynamics of Myrtus communis and Quercus ilex leaf litter: Mass loss, microbial activity and quality change. Appl Soil Ecol 36:32–40
Fyles JW, Fyles IH (1993) Interaction of Douglas-fir with red alder and salal foliage litter during decomposition. Can J Forest Res 23:358–361
Fukami T, Naeem S, Wardle DA (2001) On similarity among local communities in biodiversity experiments. Oikos 95:340–348
Gartner TB, Cardon ZG (2004) Decomposition dynamics in mixed-species leaf litter. Oikos 104:230–246
Gholz HL, Wedin DA, Smitherman SM, Harmon ME, Parton WJ (2000) Long-term dynamics of pine and hardwood litter in contrasting environments: toward a global model of decomposition. Glob Change Biol 6:751–765
Gustafson FG (1943) Decomposition of the leaves of some forest trees under field conditions. Plant Phys 18:704–707
Hättenschwiler S, Gasser P (2005) Soil animals alter plant litter diversity effects on decomposition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1519–1524
Hättenschwiler S, Tiunov AV, Scheu S (2005) Biodiversity and litter decomposition in terrestrial ecosystems. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 36:191–218
Hector A, Beale AJ, Minns A, Otway SJ, Lawton JH (2000) Consequences of the reduction of plant diversity for litter decomposition: effects through litter quality and microenvironment. Oikos 90:357–371
Hoorens B, Aerts R, Stroetenga M (2003) Does initial litter chemistry explain litter mixture effects on decomposition? Oecologia 442:578–586
Jiang L, Morin PJ (2004) Productivity gradients cause positive diversity-invasibility relationships in microbial communities. Ecol Lett 7:1047–1057
Keith AM, Van Der Wal R, Brooker RW, Osler GHR, Chapman SJ, Burslem DFRP, Elston D (2008) Increasing litter species richness reduces variability in a terrestrial decomposer system. Ecology 89:2657–2664
Kominoski S, Pringle CM, Ball BA, Bradford MA, Coleman DC, Hall DB, Hunter MD (2007) Non additive effects of leaf litter species diversity on breakdown dynamics in a detritus-based stream. Ecology 88:1167–1176
Larsen TH, Williams NM, Kremen C (2005) Extinction order and altered community structure rapidly disrupt ecosystem functioning. Ecol Lett 8:538–547
Laskowski R, Berg B, Johansson MB, McClaugherty C (1995) Release pattern for potassium from decomposing forest needle and leaf litter. Long term decomposition in a Scots pine forest. IX Can J Bot 73:2019–2027
Lecerf A, Risnoveanu G, Popescu C, Gessner MO, Chauvet E (2007) Decomposition of diverse litter mixtures in streams. Ecology 88:219–227
Liu W, Fox JED, Xu Z (2000) Leaf litter decomposition of canopy trees, bamboo and moss in a montane moist evergreen broad-leaved forest on Ailao Mountain, Yunnan, south-west China. Ecol Res 15:435–447
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic, London
McArthur JV, Aho JM, Rader RB et al (1994) Interspecific leaf interactions during decomposition in aquatic and floodplain ecosystems. J N Am Benthol Soc 13:57–67
McCann KS (2000) The diversity-stability debate. Nature 405:228–233
McGrady-Steed J, Harris PM, Morin PJ (1997) Biodiversity regulates ecosystem predictability. Nature 390:162–165
McTiernan KB, Ineson P, Coward PA (1997) Respiration and nutrient release from tree leaf litter mixtures. Oikos 78:527–538
Melillo JM, Aber JD, Steudler PA, Schimel JP (1982) Nitrogen and lignin control of hardwood leaf litter decomposition dynamics. Ecology 63:621–626
Nilsson M-C, Gallet C, Wallstedt A (1998) Temporal variability of phenolics and batatasin-III in Empetrum hermaphroditum leaves over an eight-year period: interpretation of ecological function. Oikos 81:6–16
Nilsson M-C, Wardle DA, DeLuca TH (2008) Belowground and aboveground consequences of interactions between live plant species mixtures and dead organic substrate mixtures. Oikos 117:439–449
Palviainen M, Finér L, Kurka A, Mannerkoski H, Piirainen S, Starr M (2004) Release of potassium, calcium, iron and aluminium from Norway spruce, Scots pine and silver birch logging residues. Plant Soil 259:123–136
Papa S, Pellegrino A, Fioretto A (2008) Microbial activity and quality changes during decomposition of Quercus ilex leaf litter in three Mediterranean woods. Appl Soil Ecol 40:401–410
Parton W, Silver WL, Burke IC, Grassens L, Harmon ME, Currie WS, King JY, Adair EC, Brandt LA, Hart SC, Fasth B (2007) Global-scale similarities in nitrogen release patterns during long-term decomposition. Science 315:361–364
Rustad LE (1994) Element dynamics along a decay continuum in a red spruce ecosystem in Maine, USA. Ecology 75:867–879
Salamanca EF, Kaneko N, Katagiri S (1998) Effects of leaf litter mixtures on the decomposition of Quercus serrata and Pinus densiflora using field and laboratory microcosm methods. Ecol Eng 10:53–73
Salisbury FB, Ross CW (1985) Plant physiology. Wadsworth, California, p 540
Schädler M, Brandl R (2005) Do invertebrate decomposers affect the disappearance rate of litter mixtures? Soil Biol Biochem 37:329–337
Schimel JP, Cates RG, Ruess R (1998) The role of balsam poplar secondary chemicals in controlling soil nutrient dynamics through succession in the Alaskan taiga. Biogeochemistry 42:221–34
Seastedt TR (1984) The role of arthropods in decomposition and mineralization processes. Annu Rev Entomol 29:25–46
Silver WL, Miya RK (2001) Global patterns in root decomposition: comparisons of climate and litter quality effects. Oecologia 129:407–419
Suding KN, Miller AE, Bechtold H, Bowman WD (2006) The consequence of species loss on ecosystem nitrogen cycling depends on community compensation. Oecologia 149:141–149
Swan CM, Palmer MA (2004) Leaf diversity alters litter breakdown in a Piedmont stream. J North Am Benthol Soc 23:15–28
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops J, Wedin D, Mielke T, Lehman C (2001) Diversity and productivity in a long-term grassland experiment. Science 294:843–845
Tilman D, Reich PB, Knops JMH (2006) Biodiversity and ecosystem stability in a decade-long grassland experiment. Nature 441:629–632
Tukey HB Jr (1970) The leaching of substances from plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 21:305–332
Vivanco L, Austin AT (2008) Tree species identity alters forest litter decomposition through long-term plant and soil interactions in Patagonia, Argentina. J Ecol 96:727–736
Wardle DA, Bonner KI, Nicholson KS (1997) Biodiversity and plant litter: experimental evidence which does not support the view that enhanced species richness improves ecosystem function. Oikos 79:247–258
Wardle DA, Nilsson M-C, Zackrisson O, Gallet C (2003) Determinants of litter mixing effects in a Swedish boreal forest. Soil Biol Biochem 35:827–835
Wardle DA, Yeates GW, Barker GM, Bonner KI (2006) The influence of plant litter diversity on decomposer abundance and diversity. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1052–1062
Acknowledgements
The work has been supported with grants by MIUR (PRIN 2005-050197 and FISR MESCOSAGR). We thank two anonymous reviewers whose comments have been useful to improve early version of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Alfonso Escudero.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonanomi, G., Incerti, G., Antignani, V. et al. Decomposition and nutrient dynamics in mixed litter of Mediterranean species. Plant Soil 331, 481–496 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0269-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0269-6