Abstract
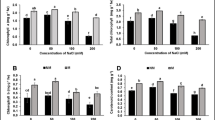
The present greenhouse study was undertaken to evaluate the effects of co-inoculating methylotrophic Methylobacterium oryzae CBMB20 along with nitrogen-fixing Azospirillum brasilense CW903 or a phosphate solubilizing bacterium Burkholderia pyrrocinia CBPB-HOD on the growth and nutrient uptake of tomato, red pepper and rice. Seed inoculation and soil/foliar application of the bacterial strains alone or under dual inoculation increased the plant growth in terms of shoot or root length and increased the nutrient uptake in the plants studied compared to uninoculated control plants. Co-inoculation of M. oryzae CBMB20 with A. brasilense CW903 or B. pyrrocinia CBPB-HOD improved the N and P concentration of plants, while the results varied among the plant species tested. Also, co-inoculation of the bacterial strains increased the activity of nitrogenase, urease and phosphatase enzymes in soil when compared to uninoculated control or individual inoculations. Though the inoculation effects were analyzed at an early stage of plant growth, the results conclusively suggest that M. oryzae being compatible with other microorganisms in the rhizosphere can potentially be used as individual inoculant or co-inoculated with other plant growth promoting bacteria to increase the production in sustainable agricultural systems.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldani VLD, Döbereiner J (1980) Host-plant specificity in the infection of cereals with Azospirillum spp. Soil Biol Biochem 12:433–439. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(80)90021-8
Bano N, Musarat J (2003) Isolation and characterization of phorate degrading soil bacteria of environmental and agronomic significance. Lett Appl Microbiol 36:349–353. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2003.01329.x
Bashan Y, de-Bashan LE (2005) Bacteria/plant growth-promotion. In: Hillel D (ed) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment, vol 1. Elsevier, Oxford, UK, pp 103–115
Bashan Y, Holguin G (1997) Azospirillum-plant relationships: environmental and physiological advances (1990–1996). Can J Microbiol 43:103–121. doi:10.1139/m97-015
Bashan Y, Holguin G, de-Bashan LE (2004) Azospirillum-plant relationships: physiological, molecular, agricultural, and environmental advances (1997–2003). Can J Microbiol 50:521–577. doi:10.1139/W04-035
Compant S, Nowak J, Coenye T, Clement C, Ait Barka E (2008) Diversity and occurrence of Burkholderia spp. in the natural environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:607–626. doi:10.1111/j.1574-6976.2008.00113.x
Cong PT, Dunga TD, Hien TM, Hien NT, Choudhury ATMA, Kecskés ML, Kennedy IR (2009) Inoculant plant growth-promoting microorganisms enhance utilization of urea-N and grain yield of paddy rice in southern Vietnam. Eur J Soil Biol 45:52–61. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2008.06.006
Davies PJ (2004) The plant hormones: their nature, occurrence, and functions. In: Davies PJ (ed) Plant hormones. Biosynthesis, signal transduction, action. Kluwer Academic, The Netherlands, pp 1–15
Felici C, Vettori L, Giraldi E, Forino LMC, Toffanin A, Tagliasacchi AM, Nuti M (2008) Single and co-inoculation of Bacillus subtilis and Azospirillum brasilense on Lycopersicon esculentum: Effects on plant growth and rhizosphere microbial community. Appl Soil Ecol 40:260–270. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2008.05.002
Garland JL, Mills AL (1991) Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community- level sole- carbon-source utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2351–2359. doi:0099-2240/91/082351-09$02.00/0
Hardy RWF, Holsten RD, Jackson EK, Burns RC (1968) The acetylene ethylene assay for nitrogen fixation — Laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol 43:1185–1207. doi:10.1104/pp.43.8.1185
Holland MA, Polacco JC (1992) Urease-null and hydrogenase-null phenotypes of a phylloplane bacterium reveal altered nickel metabolism in two soybean mutants. Plant Physiol 98:942–948. doi:0032-0889/92/98/0942/07/$01.00/0
Idris R, Trifonova R, Puschenreiter M, Wenzel WW, Sessitsch A (2004) Bacterial communities associated with flowering plants of the Ni hyperaccumulator Thlaspi goesingense. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2667–2677. doi:10.1128/AEM.70.5.2667-2677.2004
Jackson ML (1973) Soil Chemical Analysis. Prentice-Hall of India Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, India, pp 54–56
Kim CW, Kecskés ML, Deaker RJ, Gilchrist K, New PB, Kennedy IR, Kim SH, Sa TM (2005) Wheat root colonization and nitrogenase activity by Azospirillum isolates from crop plants in Korea. Can J Microbiol 51:948–956. doi:10.1139/w05-052
Kloepper JW, Lifshitz R, Zablotowicz RM (1989) Free living bacterial inocula for enhancing crop productivity. Trends Biotechnol 7:39–44. doi:10.1016/0167-7799(89)90057-7
Kohler J, Caravaca F, Carrasco L, Roldán A (2007) Interactions between a plant growth-promoting rhizobacterium, an AM fungus and a phosphate-solubilising fungus in the rhizosphere of Lactuca sativa. Appl Soil Ecol 35:480–487. doi:10.1016/j.apsoil.2006.10.006
Lucy M, Reed E, Glick BR (2004) Applications of free living plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 86:1–25. doi:10.1023/B:ANTO.0000024903.10757.6e
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Senthilkumar M, Seshadri S, Chung HY, Yang JC, Sundaram SP, Sa TM (2004) Growth promotion and induction of systemic resistance in rice cultivar Co-47 (Oryza sativa L.) by Methylobacterium spp. Bot Bull Acad Sin 45:315–324
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Ryu JH, Sa TM (2006a) Regulation of ethylene levels in canola (Brassica campestris) by 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase-containing Methylobacterium fujisawaense. Planta 224:268–278. doi:10.1007/s00425-005-0211-y
Madhaiyan M, Suresh Reddy BV, Anandham R, Senthilkumar M, Poonguzhali S, Sundaram SP, Sa TM (2006b) Plant growth promoting Methylobacterium induces defense responses in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) compared to rot pathogens. Curr Microbiol 53:270–276. doi:10.1007/s00284-005-0452-9
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Sa TM (2007a) Characterization of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate (ACC) deaminase containing Methylobacterium spp. and interactions with auxins and ACC regulation of ethylene in canola. Planta 226:867–876. doi:10.1007/s00425-007-0532-0
Madhaiyan M, Kim BY, Poonguzhali S, Kwon SW, Song MH, Ryu JH, Go SJ, Koo BS, Sa TM (2007b) Methylobacterium oryzae sp. nov., a novel aerobic, pink-pigmented, facultatively methylotrophic, 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase producing bacterium isolated from rice. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:326–331. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64603-0
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Sa TM (2007c) Metal tolerating methylotrophic bacteria reduces nickel and cadmium toxicity and promotes plant growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Chemosphere 69:220–228. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.04.017
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Kwon SW, Song MH, Sa TM (2008) Molecular characterization of Burkholderia strains isolated from rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.) for species identification and phylogenetic grouping. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1005–1010
Naiman AD, Latrónico A, de Salamone IEG (2009) Inoculation of wheat with Azospirillum brasilense and Pseudomonas fluorescens: Impact on the production and culturable rhizosphere microflora. Eur J Soil Biol 45:44–51. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2008.11.001
Naseby DC, Lynch JM (1997) Rhizosphere soil enzymes as indicators of perturbation caused by a genetically modified strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens on wheat seed. Soil Biol Biochem 29:1353–1362. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00061-8
Okon Y, Itzigsohn R, Burdman S, Hampel M (1995) Advances in agronomy and ecology of the Azospirillum/plant association. In: Tikhonovich IA, Provarov NA, Romanov VI, Newton WE (eds) Nitrogen fixation: fundamentals and applications. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp 635–640
Omer ZS, Tombolini R, Broberg A, Gerhardson B (2004) Indole-3-acetic acid production by pink-pigmented facultative methylotrophic bacteria. Plant Growth Regul 43:93–96. doi:10.1023/B:GROW.0000038360.09079.ad
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Microbiologiya 17:362–370 (in Russian language)
Poonguzhali S, Madhaiyan M, Sa TM (2007) Quorum-sensing signals produced by plant-growth promoting Burkholderia strains under in vitro and in planta conditions. Res Microbiol 158:287–294. doi:10.1016/j.resmic.2006.11.013
Ryu JH, Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Yim WJ, Indiragandhi P, Kim KA, Anandham R, Yun JC, Sa TM (2006) Plant growth substances produced by Methylobacterium spp. and their effect on the growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) and red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:1622–1628
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969) Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for the assay of phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 1:301–307. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(69)90012-1
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1972) Assay of urease activity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 4:479–487. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(72)90064-8
Turner GL, Gibson AH (1980) In: Methods for evaluating biological nitrogen fixation. (ed.) Bergerson FJ, John Wiley and Sons, New York. pp.111
Whittenbury R, Davies SL, Wilkinson JF (1970) Enrichment, isolation and some properties of methane-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol 61:205–218
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the support of “Cooperative Research Program for Agricultural Science and Technology Development” Rural Development Administration (RDA), Republic of Korea. The authors also thank Soo-Jae Park and Sook-Jin Kim for their help and assistance in conducting the pot culture experiments and for analyzing the samples by ICP-OES.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Jesus Mercado-Blanco.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhaiyan, M., Poonguzhali, S., Kang, BG. et al. Effect of co-inoculation of methylotrophic Methylobacterium oryzae with Azospirillum brasilense and Burkholderia pyrrocinia on the growth and nutrient uptake of tomato, red pepper and rice. Plant Soil 328, 71–82 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0083-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-009-0083-1