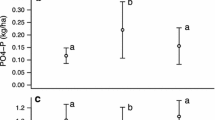
Abstract
Disturbances by fossorial mammals are extremely common in many ecosystems, including the California annual grassland. We compared the impact of juveniles of four common plant colonizers (Aegilops triuncialis, Cerastium glomeratum, Aphanes occidentalis and Lupinus bicolor) on the pools and fluxes of N in mounds created by pocket gophers (Thomomys bottae Mewa). The mechanisms and magnitude of biotic N retention differed among plant species. In mounds colonized by Cerastium, Aphanes and Lupinus, the microbial N pool was significantly larger than the plant N pool, as is typical in California grasslands in the early spring, whereas in mounds colonized by Aegilops, there was a more equal distribution of biotic N between plant and microbial pools. A 1-day 15N pulse field experiment demonstrated that plant species significantly differed in their effects on the distribution of isotopic N, with the N-fixing Lupinus leaving most (82%) 15N as inorganic N in soil, whereas more 15N was immobilized in plants or otherwise removed from the available soil pool in mounds colonized by other species. The impacts of early colonizers on N dynamics suggest that the identity of plant species that initially colonize gopher mounds may have important consequences on the dynamics of the overall grassland community.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R Aerts F S Chapin SuffixIII (2000) ArticleTitleThe mineral nutrition of wild plants revisited: a re-evaluation of processes and patterns Adv. Ecol. Res. 30 1–67 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivVejurw%3D
S Arnthórsdóttir (1994) ArticleTitleColonization of experimental patches in a mown grassland Oikos 70 73–79
R D Bardgett A Shine (1999) ArticleTitleLinkages between plant litter diversity, soil microbial biomass and ecosystem function in temperate grasslands Soil Biol. Biochem. 31 317–321 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhslyhsbo%3D
A Bonis P J Grubb D A Coomes (1997) ArticleTitleRequirements of gap-demanding species in chalk grassland: reduction of root competition versus nutrient enrichment by animals J. Ecol. 85 625–633
P D Brookes A Landman G Pruden D S Jenkinson (1985) ArticleTitleChloroform fumigation and the release of soil nitrogen: a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil Soil Biol.Biochem 17 837–842 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL28XhvFSgug%3D%3D
M Burger L E Jackson (2005) ArticleTitlePlant and microbial nitrogen use and turnover: rapid conversion of nitrate to ammonium in soil with roots Plant Soil 266 289–301 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s11104-005-1362-0
I C Burke W K Lauenroth W J Parton (1997) ArticleTitleRegional and temporal variation in net primary production and nitrogen mineralization in grasslands Ecology 78 1330–1240
R M Canals M T Sebastià (2000) ArticleTitleSoil nutrient fluxes and vegetation changes on molehills J.Veg. Sci. 11 23–30
R M Canals D J Herman M K Firestone (2003) ArticleTitleHow disturbance by fossorial mammals alters N cycling in a California annual grassland Ecology 84 875–881
J D Chase W E Howard J T Roseberry (1982) Pocket gophers J A Chapman G A Feldhammer (Eds) Wild Mammals of North America. Biology, Management and Economics The John Hopkins University Press EUA 239–255
S L Collins S C Barber (1985) ArticleTitleEffects of disturbance on diversity in mixed-grass prairie Vegetatio 64 87–94
C M D’Antonio P M Vitousek (1992) ArticleTitleBiological invasions by exotic grasses, the grass/fire cycle and global change Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 23 63–87
E A Davidson R W Eckert S C Hart M K Firestone (1989) ArticleTitleDirect extraction of microbial biomass nitrogen from forest and grassland soils of California Soil Biol. Biochem. 21 773–778 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(89)90169-7
J S Denslow (1985) Disturbance-mediated coexistence of species S T A Pickett P S White (Eds) : The Ecology of Natural Disturbance and Patch Dynamics Academic Press Inc. San Diego 307–323
J M Di Tomaso (2000) ArticleTitleInvasive weeds in rangelands: species, impacts and management Weed Sci 48 255–265 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsFeqsL4%3D
H E Epstein I C Burke A R Mosier G L Hutchinson (1998) ArticleTitlePlant functional type effects on trace gas fluxes in the shortgrass steppe Biogeochem. 42 145–168 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1005959001235 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXlvVyjsrY%3D
R D Evans R Rimer L Sperry J Belnap (2001) ArticleTitleExotic plant invasion alters nitrogen dynamics in an arid grassland Ecol. Appl. 11 1301–1310
V T Eviner III F S Chapin (2003a) ArticleTitleThe role of species interactions in plant invasions: gopher-plant-fungal interactions affect establishment of an invasive grass Ecology 84 120–128
V T Eviner III F S Chapin (2003b) ArticleTitleFunctional matrix: A conceptual framework for predicting multiple plant effects on ecosystem processes Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 34 455–485
V T Eviner (2004) ArticleTitlePlant species have unique combinations of traits that influence ecosystem processes Ecology 85 2215–2229
V T Eviner III F S Chapin (2005) ArticleTitleSelective gopher disturbance influences plant species effects on nitrogen cycling Oikos 109 154–166 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.12758.x
D R Gordon (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of invasive, non-indigenous plant species on ecosystem processes Ecol. Appl. 8 975–989
K D Gowans (1958) Soil survey of the Hopland Field Station California Agricultural Experiment Station Berkeley
J P Grime (1977) ArticleTitleEvidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory Amer. Natur. 111 1169–1194 Occurrence Handle10.1086/283244
D J Herman P D Brooks M Ashraf F Azam R L Mulvaney (1995) ArticleTitleEvaluation of methods for nitrogen−15 analysis of inorganic nitrogen in soil extracts. II. Diffusion methods Comm. soil sci. plant anal. 26 1675–1685 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmsVSntL8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1080/00103629509369400
D J Herman L J Halverson M K Firestone (2003) ArticleTitleNitrogen dynamics in a mediterranean annual grassland: effects of oak canopies and tree removal, climatic variables and microbial populations Ecol. Appl. 13 593–604
S E Hobbie (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of plant species on nutrient cycling TREE 7 336–339
R J Hobbs H A Mooney (1985) ArticleTitleCommunity and population dynamics of serpentine grassland annuals in relation to gopher disturbance Oecologia 67 342–351
A Hodge E Paterson S J Grayston C D Campbell B G Ord K Killham (1998) ArticleTitleCharacterisation and microbial utilisation of exudate material from the rhizosphere of Lolium perenne grown under CO2 enrichment Soil Biol. Biochem. 30 1033–1043 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0038-0717(97)00269-1 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktlKgtLw%3D
P B Hook I C Burke W K Lauenroth (1991) ArticleTitleHeterogeneity of soil and plant N and C associated with individual plants and openings in North American shortgrass steppe Plant Soil 138 247–256 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00012252 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XktVentQ%3D%3D
B A Hungate J Canadell III F S Chapin (1996) ArticleTitlePlant species mediate changes in soil microbial N in response to elevated CO2 Ecology 77 2505–2515
N J Huntly R S Inouye (1988) ArticleTitlePocket gophers in ecosystems. patterns and mechanisms Bioscience 38 786–793
L E Jackson R B Strauss M K Firestone J W Bartolome (1988) ArticleTitlePlant and soil nitrogen dynamics in California annual grassland Plant Soil 110 9–17 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02143533
L E Jackson J P Schimel M K Firestone (1989) ArticleTitleShort-term partitioning of ammonium and nitrate between plants and microbes in an annual grassland Soil Biol. Biochem. 21 409–415 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0038-0717(89)90152-1
C H Jaeger R K Monson M C Fisk S K Schmidt (1999a) ArticleTitleSeasonal partitioning of nitrogen by plants and soil microorganisms in an alpine ecosystem Ecology 80 1883–1891
C H Jaeger S E Lindow W Miller E Clark M K Firestone (1999b) ArticleTitleMapping of sugar and amino acid availability in soil around roots with bacterial sensors of sucrose and tryptophan Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65 2685–2690 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXjs12gtLw%3D
W Jingguo L R Bakken (1997) ArticleTitleCompetition for nitrogen during decomposition of plant residues in soil: effect of spatial placement of N-rich and N-poor plant residues Soil Biol. Biochem. 29 153–162 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXjsl2lt70%3D
M I Litaor R Mancinelli J C Halfpenny (1996) ArticleTitleThe influence of pocket gophers on the status of nutrients in Alpine soils Geoderma 70 37–48 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjsVaktb4%3D
R N Mack D Simberloff W M Lonsdale H Evans M Clout F A Bazzaz (2000) ArticleTitleBiotic invasions: causes, epidemiology, global consequences, and control Ecol. Appl. 10 689–710
M Redente J E Friedlander T Mc Lendon (1992) ArticleTitleResponse of early and later semiarid seral species to nitrogen and phosphorous gradients Plant Soil 140 127–135 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00012814 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XitFemtrs%3D
O J Reichman J U M Jarvis (1989) ArticleTitleThe influence of three sympatric species of fossorial mole-rats (Bathyergidae) on vegetation J. Mamm. 70 763–771
O J Reichman E W Seabloom (2002) ArticleTitleThe role of pocket gophers as subterranean ecosystem engineers TREE 17 44–49
O E Sala W J Parton L A Joyce W K Lauenroth (1988) ArticleTitlePrimary production of the central grasslands region of the United States Ecology 69 40–45
J M Stark S C Hart (1997) ArticleTitleHigh rates of nitrification and nitrate turnover in undisturbed coniferous forests Nature 385 61–64 Occurrence Handle10.1038/385061a0 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXisl2qsg%3D%3D
Torre, I 2004 Distribution, population dynamics and habitat selection of small mammals in Mediterranean environments: the role of climate, vegetation structure and predation risk. Ph.D. Dissertation. Facultat de Biologia, Universitat de Barcelona, Barcelona
M A Vinton I C Burke (1995) ArticleTitleInteractions between individual plant species and soil nutrient status in shortgrass steppe Ecology 76 1116–1133
P M Vitousek C M D’Antonio L L Loope R Westbrooks (1996) ArticleTitleBiological invasions as global environmental change Am. Sci. 84 468–478
D A Wedin D Tilman (1990) ArticleTitleSpecies effects on nitrogen cycling: a test with perennial grasses Oecologia 84 433–441
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Canals, R.M., Eviner, V.T., Herman, D.J. et al. Plant Colonizers Shape Early N-dynamics in Gopher-mounds. Plant Soil 276, 327–334 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-5086-y
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-005-5086-y