Abstract
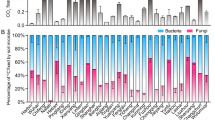
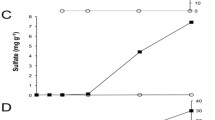
Although soils are generally known to be a net source of CO2 due to microbial respiration, CO2 fixation may also be an important process. The non-phototrophic fixation of CO2 was investigated in a tracer experiment with 14CO2 in order to obtain information about the extent and the mechanisms of this process. Soils were incubated for up to 91 days in the dark. In three independent incubation experiments, a significant transfer of radioactivity from 14CO2 to soil organic matter was observed. The process was related to microbial activity and could be enhanced by the addition of readily available substrates such as acetate. CO2 fixation exhibited biphasic kinetics and was linearly related to respiration during the first phase of incubation (about 20–40 days). The fixation amounted to 3–5% of the net respiration. After this phase, the CO2 fixation decreased to 1–2% of the respiration. The amount of carbon fixed by an agricultural soil corresponded to 0.05% of the organic carbon present in the soil at the beginning of the experiment, and virtually all of the fixed CO2 was converted to organic compounds. Many autotrophic and heterotrophic biochemical processes result in the fixation of CO2. However, the enhancement of the fixation by addition of readily available substrates and the linear correlation with respiration suggested that the process is mainly driven by aerobic heterotrophic microorganisms. We conclude that heterotrophic CO2 fixation represents a significant factor of microbial activity in soils.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FYM:
-
farmyard manure
- LSC:
-
liquid scintillation counting
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RuBisCo:
-
ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
References
Balesdent J., Mariotti A. (1996). Measurement of soil organic matter turnover using 13C natural abundance. In Mass Spectrometry of Soils. Eds. T W Boutton and S-i Yamasaki. pp. 83–111. Marcel Dekker, New York
P. Burauel F. Führ (2000) ArticleTitleFormation and long-term fate of non-extractable residues in outdoor lysimeter studies Environ. Poll. 108 45–52 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00200-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhs1ahsrc%3D
OA Chadwick EF Kelly DM. Merritts RG. Amundson (1994) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide consumption during soil development Biogeochemistry 24 115–127 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00003268 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmtVCgtLw%3D
DD. Clark SA. Ensign (1999) ArticleTitleEvidence for an inducible nucleotide-dependent acetone carboxylase in Rhodococcus rhodochrous B276 J. Bacteriol. 181 2752–2758 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXivFCjsL8%3D Occurrence Handle10217764
Z. Dong DB. Layzell (2001) ArticleTitleH2 oxidation, O2 uptake and CO2 fixation in hydrogen treated soils Plant Soil 229 1–12 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1004810017490 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXitFarsrc%3D
HL Drake S Daniel K Küsel C Matthies C. Kuhner S. Braus-Stromeyer (1997) ArticleTitleAcetogenic bacteria: what are the in situ consequences of their diverse metabolic versatilities? BioFactors 6 13–24 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXksVCksrY%3D Occurrence Handle9233536
SA Ensign FJ Small JR. Allen MK. Sluis (1998) ArticleTitleNew roles for CO2 in the microbial metabolism of aliphatic epoxides and ketones Arch. Microbiol. 169 179–187 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s002030050558 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitVKqs78%3D Occurrence Handle9477250
H Flessa B Ludwig B. Heil W. Merbach (2000) ArticleTitleThe origin of soil organic C, dissolved organic C and respiration in a long-term maize experiment in Halle, Germany, determined by 13C natural abundance J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 163 157–163 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1522-2624(200004)163:2<157::AID-JPLN157>3.0.CO;2-9 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXivVKnsr8%3D
Fuchs G. (1989). Alternative pathways of autotrophic CO2 fixation. In Autotrophic Bacteria. Eds. H G Schlegel and B Bowien. pp. 365–382. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
RE Hartman NT. Keen M. Long (1972) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide fixation by Verticillium albo-atrum. J. Gen Microbiol. 73 29–34 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXis1alsw%3D%3D
M Kästner S Lotter J Heerenklage M Breuer-Jammali R. Stegmann B. Mahro (1995) ArticleTitleFate of 14C-labeled anthracene and hexadecane in compost-manured soil Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43 1128–1135 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00166937 Occurrence Handle8590663
M Kästner S Streibich M Beyrer HH. Richnow W. Fritsche (1999) ArticleTitleFormation of bound residues during microbial degradation of [14C]anthracene in soil Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65 1834–1842 Occurrence Handle10223966
HA. Krebs (1941) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide assimilation in heterotrophic organisms Nature (London) 147 560–563 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaH3MXjtVCnug%3D%3D
K. Küsel HL. Drake (1995) ArticleTitleEffects of environmental parameters on the formation and turnover of acetate by forest soils Appl. Environ. Microbiol 61 3667–3675
K. Küsel HL. Drake (1999) ArticleTitleMicrobial turnover of low molecular weight organic acids during leaf litter decomposition Soil Biol. Biochem. 31 107–118
C Menendez Z Bauer H Huber N Gad’on K-O. Stetter G. Fuchs (1999) ArticleTitlePresence of acetyl coenzyme A (CoA) carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase in autotrophic Crenarchaeota and indication for operation of a 3-hydroxypropionate cycle in autotrophic carbon fixation J. Bacteriol. 181 1088–1098 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXhsV2ru7w%3D Occurrence Handle9973333
Merbach W, Schmidt L., Wittenmeyer L 1999 Die Dauerdüngungsversuche in Halle (Saale). Teubner, Stuttgart. 150 pp.
G Michal (1999) Biochemical Pathways Spektrum Akademischer Verlag Heidelberg 276
SM Parkinson R Jones AA Meharg M. Wainwright K. Killham (1991) ArticleTitleThe quantity and fate of carbon assimilated from 14CO2 by Fusarium oxysporum grown under oligotrophic and near oligotrophic conditions Mycol. Res. 95 1345–1349 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XisFWrsbg%3D
EA. Paul FE. Clark (1996) Soil Microbiology and Biochemistry Academic Press San Diego 340
RC. Perez A. Matin (1982) ArticleTitleCarbon dioxide assimilation by Thiobacillus novellus under nutrient-limited mixotrophic conditions J. Bacteriol. 150 46–51 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38XhslOktr4%3D Occurrence Handle6801026
JW. Raich CS. Potter (1995) ArticleTitleGlobal patterns of carbon dioxide emissions from soils Global Biogeochem. Cycles 9 23–36 Occurrence Handle10.1029/94GB02723 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXktFGitL0%3D
JW. Raich WH. Schlesinger (1992) ArticleTitleThe global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate Tellus 44B 81–99 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XksVOgsLY%3D
HH Richnow E Annweiler M Koning J-C. Lüth R Stegmann C Garms W. Francke W. Michaelis (2000) ArticleTitleTracing the transformation of labeled [1-13C]phenanthrene in a soil bioreactor Environ. Poll. 108 91–101 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0269-7491(99)00205-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhs1ahs7o%3D
HG. Schlegel (1985) Allgemeine Mikrobiologie Thieme Verlag Stuttgart 571
Selesi D E, Schmid M., Hartmann A 2004 Diversity of ‘green-like’ and ‘red-like’ ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase large subunit genes (cbbL) in differently managed agricultural soils. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. (In press)
K Sonntag J Schwinde AA Graaf Particlede A Marx BJ Eikmanns W. Wiechert H. Sahm (1995) ArticleTitle 13C NMR studies of the fluxes in the central metabolism of Corynebacterium glutamicum during growth and overproduction of amino acids in barch cultures Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 44 489–495 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XitVert78%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miltner, A., Kopinke, FD., Kindler, R. et al. Non-phototrophic CO 2 fixation by soil microorganisms. Plant Soil 269, 193–203 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0483-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-004-0483-1