Abstract
Key message
We curated a reliable dataset of m6A sites in Arabidopsis thaliana, built competitive models for predicting m6A sites, extracted predominant rules from the prediction models and analyzed the most important features.
Abstract
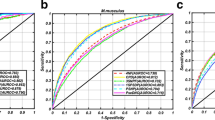
In biological RNA, approximately 150 chemical modifications have been discovered, of which N6-methyladenine (m6A) is the most prevalent and abundant. This modification plays an essential role in a myriad of biological mechanisms and regulates RNA localization, nuclear export, translation, stability, alternative splicing, and other processes. However, m6A-seq and other wet-lab techniques do not easily facilitate accurate and complete determination of m6A sites across the transcriptome. Therefore, the use of computational methods to establish accurate models for predicting m6A sites is essential. In this work, we manually curated a reliable dataset of m6A sites and non-m6A sites and developed a new tool called RFAthM6A for predicting m6A sites in Arabidopsis thaliana. Briefly, RFAthM6A consists of four independent models named RFPSNSP, RFPSDSP, RFKSNPF and RFKNF and strict benchmarks show that the AUC values of the four models reached 0.894, 0.914, 0.920 and 0.926, respectively in a fivefold cross validation and the prediction performance of RFPSDSP, RFKSNPF and RFKNF exceeded that of three previously reported models (AthMethPre, M6ATH and RAM-NPPS). Linear combination of the prediction scores of RFPSDSP, RFKSNPF and RFKNF improved the prediction performance. We also extracted several predominant rules that underlie the m6A site identification from the trained models. Furthermore, the most important features of the predictors for the m6A site identification were also analyzed in depth. To facilitate use of our proposed models by interested researchers, all the source codes and datasets are publicly deposited at https://github.com/nongdaxiaofeng/RFAthM6A.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agris PF, Vendeix FA, Graham WD (2007) tRNA’s wobble decoding of the genome: 40 years of modification. J Mol Biol 366:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2006.11.046
Beemon K, Keith J (1977) Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J Mol Biol 113:165–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(77)90047-X
Bodi Z, Zhong S, Mehra S et al. (2012) Adenosine methylation in Arabidopsis mRNA is associated with the 3′ end and reduced levels cause developmental defects. Front Plant Sci https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2012.00048
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45:5–32. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010933404324
Chang CC, Lin CJ (2011) LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines. ACM Trans Intel Syst Technol 2:27. https://doi.org/10.1145/1961189.1961199
Chen YZ, Tang YR, Sheng ZY, Zhang Z (2008) Prediction of mucin-type O-glycosylation sites in mammalian proteins using the composition of k-spaced amino acid pairs. BMC Bioinform 9:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-101
Chen W, Feng P, Ding H, Lin H, Chou KC (2015) iRNA-methyl: identifying N(6)-methyladenosine sites using pseudo nucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 490:26–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2015.08.021
Chen W, Feng P, Ding H, Lin H (2016) Identifying N6-methyladenosine sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome. Mol Genet Genomics 291:2225–2229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1243-7
Chen W, Tang H, Lin H (2017) MethyRNA: a web server for identification of N6-methyladenosine sites. J Biomol Struct Dyn 35:683–687. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2016.1157761
Clancy MJ, Shambaugh ME, Timpte CS, Bokar JA (2002) Induction of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae leads to the formation of N6-methyladenosine in mRNA: a potential mechanism for the activity of the IME4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res 30:4509–4518. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf573
Desrosiers R, Friderici K, Rottman F (1974) Identification of methylated nucleosides in messenger RNA from Novikoff hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:3971–3975
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S et al (2012) Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-sEq. Nature 485:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11112
Duan H-C, Wei L-H, Zhang C et al (2017) ALKBH10B is An RNA N6-methyladenosine demethylase affecting Arabidopsis floral transition. Plant Cell. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.16.00912
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn Lett 27:861–874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.010
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts565
Fustin JM, Doi M, Yamaguchi Y et al (2013) RNA-methylation-dependent RNA processing controls the speed of the circadian clock. Cell 155:793–806. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.026
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D et al (2015) Stem cells. m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. Science 347:1002–1006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1261417
Geurts P, Ernst D, Wehenkel L (2006) Extremely randomized trees. Mach Learn 63:3–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10994-006-6226-1
Gu J, Patton JR, Shimba S, Reddy R (1996) Localization of modified nucleotides in Schizosaccharomyces pombe spliceosomal small nuclear RNAs: modified nucleotides are clustered in functionally important regions. RNA 2:909–918
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.143.1.7063747
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X et al (2011) N6-Methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 7:885–887. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.687
Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Li D et al (2012) The Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1202–D1210. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkr1090
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14539
Levis R, Penman S (1978) 5′-terminal structures of poly(A) + cytoplasmic messenger RNA and of poly(A) + and poly(A)- heterogeneous nuclear RNA of cells of the dipteran Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol 120:487–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(78)90350-9
Li GQ, Liu Z, Shen HB, Yu DJ (2016a) TargetM6A: identifying N6-Methyladenosine sites from RNA sequences via position-specific nucleotide propensities and a support vector machine. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 15:674–682. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNB.2016.2599115
Li X, Xiong X, Wang K, Wang L, Shu X, Ma S, Yi C (2016b) Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals reversible and dynamic N(1)-methyladenosine methylome. Nat Chem Biol 12:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2040
Liaw A, Wiener M (2002) Classification and regression by random Forest. R News 2:18–22
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, Meydan C, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2015) Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods 12:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3453
Liu B, Fang L, Wang S, Wang X, Li H, Chou KC (2015a) Identification of microRNA precursor with the degenerate K-tuple or Kmer strategy. J Theor Biol 385:153–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2015.08.025
Liu N, Dai Q, Zheng G, He C, Parisien M, Pan T (2015b) N(6)-methyladenosine-dependent RNA structural switches regulate RNA-protein interactions. Nature 518:560–564. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14234
Liu Z, Xiao X, Yu DJ, Jia J, Qiu WR, Chou KC (2016) pRNAm-PC: Predicting N(6)-methyladenosine sites in RNA sequences via physical-chemical properties. Anal Biochem 497:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2015.12.017
Luo GZ, MacQueen A, Zheng G et al (2014) Unique features of the m6A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun 5:5630. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6630
Machnicka MA, Milanowska K, Osman Oglou O et al (2013) MODOMICS: a database of RNA modification pathways–2013 update. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D262–D267. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1007
Maden BE (1990) The numerous modified nucleotides in eukaryotic ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 39:241–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6603(08)60629-7
Meyer KD, Saletore Y, Zumbo P, Elemento O, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2012) Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3′ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 149:1635–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.05.003
Nichols JL (1979) ‘Cap’ structures in maize poly(A)-containing RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 563:490–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2787(79)90067-4
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez JC, Muller M (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Schmidhuber J (2015) Deep learning in neural networks: an overview. Neural Netw 61:85–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2014.09.003
Schwartz S, Agarwala SD, Mumbach MR et al (2013) High-resolution mapping reveals a conserved, widespread, dynamic mRNA methylation program in yeast meiosis. Cell 155:1409–1421. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.10.047
Walters BJ, Mercaldo V, Gillon CJ et al (2017) The role of The RNA demethylase FTO (fat mass and obesity-associated) and mRNA methylation in hippocampal memory formation. Neuropsychopharmacology 42:1502–1510. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.31
Wan Y, Tang K, Zhang D, Xie S, Zhu X, Wang Z, Lang Z (2015) Transcriptome-wide high-throughput deep m(6)A-seq reveals unique differential m(6)A methylation patterns between three organs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol 16:272. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-015-0839-2
Wang XF, Chen Z, Wang C, Yan RX, Zhang Z, Song J (2011) Predicting residue-residue contacts and helix–helix interactions in transmembrane proteins using an integrative feature-based random forest approach. PLoS ONE 6:e26767. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026767
Wang X, Yan R, Li J, Song J (2016a) SOHPRED: a new bioinformatics tool for the characterization and prediction of human S-sulfenylation sites. Mol Biosyst 12:2849–2858. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00314a
Wang X, Yan R, Song J (2016b) DephosSite: a machine learning approach for discovering phosphotase-specific dephosphorylation sites. Sci Rep 6:23510. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep23510
Xiang S, Yan Z, Liu K, Zhang Y, Sun Z (2016) AthMethPre: a web server for the prediction and query of mRNA m6A sites in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Biosyst 12:3333–3337. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mb00536e
Xing P, Su R, Guo F, Wei L (2017) Identifying N6-methyladenosine sites using multi-interval nucleotide pair position specificity and support vector machine. Sci Rep 7:46757. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46757
Xu Y, Ding J, Wu L-Y, Chou K-C (2013) iSNO-PseAAC: predict cysteine S-nitrosylation sites in proteins by incorporating position specific amino acid propensity into pseudo amino acid composition. PLoS ONE 8:e55844. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0055844
Xu K, Yang Y, Feng GH et al (2017) Mettl3-mediated m6A regulates spermatogonial differentiation and meiosis initiation. Cell Res 27:1100–1114. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.100
Yue Y, Liu J, He C (2015) RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev 29:1343–1355. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.262766.115
Zhong S, Li H, Bodi Z, Button J, Vespa L, Herzog M, Fray RG (2008) MTA Is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 20:1278–1288. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.058883
Zhou Y, Zeng P, Li YH, Zhang Z, Cui Q (2016) SRAMP: prediction of mammalian N6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e91. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw104
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Start-up fund of Shanxi Normal University (83358), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31500673 and 31571300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XW devised the method and drafted the paper. RY revised the paper.
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Yan, R. RFAthM6A: a new tool for predicting m6A sites in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Mol Biol 96, 327–337 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0698-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-018-0698-9