Abstract
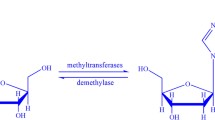
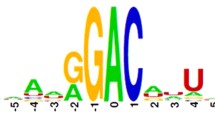
N 6-Methyladenosine (m6A) plays important roles in many biological processes. The knowledge of the distribution of m6A is helpful for understanding its regulatory roles. Although the experimental methods have been proposed to detect m6A, the resolutions of these methods are still unsatisfying especially for Arabidopsis thaliana. Benefitting from the experimental data, in the current work, a support vector machine-based method was proposed to identify m6A sites in A. thaliana transcriptome. The proposed method was validated on a benchmark dataset using jackknife test and was also validated by identifying strain-specific m6A sites in A. thaliana. The obtained predictive results indicate that the proposed method is quite promising. For the convenience of experimental biologists, an online webserver for the proposed method was built, which is freely available at http://lin.uestc.edu.cn/server/M6ATH. These results indicate that the proposed method holds a potential to become an elegant tool in identifying m6A site in A. thaliana.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantara WA, Crain PF, Rozenski J, McCloskey JA, Harris KA, Zhang X, Vendeix FA, Fabris D, Agris PF (2011) The RNA modification database, RNAMDB: 2011 update. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D195–D201
Cao R, Wang Z, Cheng J (2014a) Designing and evaluating the MULTICOM protein local and global model quality prediction methods in the CASP10 experiment. BMC Struct Biol 14:13
Cao R, Wang Z, Wang Y, Cheng J (2014b) SMOQ: a tool for predicting the absolute residue-specific quality of a single protein model with support vector machines. BMC Bioinform 15:120
Chen W, Feng P, Lin H (2012) Prediction of replication origins by calculating DNA structural properties. FEBS Lett 586:934–938
Chen W, Feng PM, Lin H, Chou KC (2013) iRSpot-PseDNC: identify recombination spots with pseudo dinucleotide composition. Nucleic Acids Res 41:e68
Chen W, Feng PM, Deng EZ, Lin H, Chou KC (2014a) iTIS-PseTNC: a sequence-based predictor for identifying translation initiation site in human genes using pseudo trinucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 462:76–83
Chen W, Feng PM, Lin H, Chou KC (2014b) iSS-PseDNC: identifying splicing sites using pseudo dinucleotide composition. Biomed Res Int 2014:623149
Chen T, Hao YJ, Zhang Y, Li MM, Wang M, Han W, Wu Y, Lv Y, Hao J, Wang L, Li A, Yang Y, Jin KX, Zhao X, Li Y, Ping XL, Lai WY, Wu LG, Jiang G, Wang HL, Sang L, Wang XJ, Yang YG, Zhou Q (2015a) m(6)A RNA methylation is regulated by microRNAs and promotes reprogramming to pluripotency. Cell Stem Cell 16:289–301
Chen W, Feng P, Ding H, Lin H, Chou KC (2015b) iRNA-Methyl: identifying N(6)-methyladenosine sites using pseudo nucleotide composition. Anal Biochem 490:26–33
Chen W, Tran H, Liang Z, Lin H, Zhang L (2015c) Identification and analysis of the N(6)-methyladenosine in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcriptome. Sci Rep 5:13859
Chen W, Feng P, Tang H, Ding H, Lin H (2016a) Identifying 2′-O-methylationation sites by integrating nucleotide chemical properties and nucleotide compositions. Genomics 107:255–258
Chen W, Tang H, Ye J, Lin H, Chou KC (2016b) iRNA-PseU: identifying RNA pseudouridine sites. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 5:e332
Chen W, Tang H, Lin H (2016) MethyRNA: a web server for identification of N6-methyladenosine sites. J Biomol Struct Dyn. doi:10.1080/07391102.2016.1157761
Chou KC (2011) Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J Theor Biol 273:236–247
Dominissini D, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Schwartz S, Salmon-Divon M, Ungar L, Osenberg S, Cesarkas K, Jacob-Hirsch J, Amariglio N, Kupiec M, Sorek R, Rechavi G (2012) Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 485:201–206
Feng P, Jiang N, Liu N (2014a) Prediction of DNase I hypersensitive sites by using pseudo nucleotide compositions. Sci World J 2014:740506
Feng P, Lin H, Chen W, Zuo Y (2014b) Predicting the types of J-proteins using clustered amino acids. Biomed Res Int 2014:935719
Frank E, Hall M, Trigg L, Holmes G, Witten IH (2004) Data mining in bioinformatics using Weka. Bioinformatics 20:2479–2481
Fu L, Niu B, Zhu Z, Wu S, Li W (2012) CD-HIT: accelerated for clustering the next-generation sequencing data. Bioinformatics 28:3150–3152
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon-Divon M, Hershkovitz V, Peer E, Mor N, Manor YS, Ben-Haim MS, Eyal E, Yunger S, Pinto Y, Jaitin DA, Viukov S, Rais Y, Krupalnik V, Chomsky E, Zerbib M, Maza I, Rechavi Y, Massarwa R, Hanna S, Amit I, Levanon EY, Amariglio N, Stern-Ginossar N, Novershtern N, Rechavi G, Hanna JH (2015) Stem cells. m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. Science 347:1002–1006
Jia G, Fu Y, Zhao X, Dai Q, Zheng G, Yang Y, Yi C, Lindahl T, Pan T, Yang YG, He C (2011) N 6-methyladenosine in nuclear RNA is a major substrate of the obesity-associated FTO. Nat Chem Biol 7:885–887
Lin H, Chen W, Ding H (2013) AcalPred: a sequence-based tool for discriminating between acidic and alkaline enzymes. PLoS One 8:e75726
Linder B, Grozhik AV, Olarerin-George AO, Meydan C, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR (2015) Single-nucleotide-resolution mapping of m6A and m6Am throughout the transcriptome. Nat Methods 12:767–772
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, Dai Q, Chen W, He C (2014) A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N 6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol 10:93–95
Luo GZ, MacQueen A, Zheng G, Duan H, Dore LC, Lu Z, Liu J, Chen K, Jia G, Bergelson J, He C (2014) Unique features of the m6A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Commun 5:5630
Meyer KD, Jaffrey SR (2014) The dynamic epitranscriptome: N 6-methyladenosine and gene expression control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:313–326
Nilsen TW (2014) Molecular biology. Internal mRNA methylation finally finds functions. Science 343:1207–1208
Schwartz S, Agarwala SD, Mumbach MR, Jovanovic M, Mertins P, Shishkin A, Tabach Y, Mikkelsen TS, Satija R, Ruvkun G, Carr SA, Lander ES, Fink GR, Regev A (2013) High-resolution mapping reveals a conserved, widespread, dynamic mRNA methylation program in yeast meiosis. Cell 155:1409–1421
Zhou Y, Zeng P, Li YH, Zhang Z, Cui Q (2016) SRAMP: prediction of mammalian N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) sites based on sequence-derived features. Nucleic Acids Res 44:e91
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Program for the Top Young Innovative Talents of Higher Learning Institutions of Hebei Province (No. BJ2014028), the Outstanding Youth Foundation of North China University of Science and Technology (No. JP201502), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2015M582533), the Scientific Research Foundation of the Education Department of Sichuan Province (No. 2015JY0100), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, China (Nos. ZYGX2015J144, ZYGX2015Z006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, W., Feng, P., Ding, H. et al. Identifying N 6-methyladenosine sites in the Arabidopsis thaliana transcriptome. Mol Genet Genomics 291, 2225–2229 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1243-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-016-1243-7