Abstract
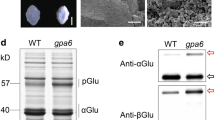
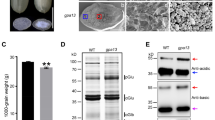
BNM2 is a prototypical member of the enigmatic BURP domain protein family whose members contain the signature FX6–7GX10–28PX25–31CX11–12X2SX45–56CHX10CHX25–29CHX2TX15–16PX5CH in the C-terminus. This protein family occurs only in plants, and the cognate genes vary very widely in their expression contexts in vegetative and reproductive tissues. None of the BURP family members has been assigned any biochemical function. BNM2 was originally discovered as a gene expressed in microspore-derived embryos (MDE) of Brassica napus but we found that MDE do not contain the corresponding protein. We show that BNM2 protein production is confined to the seeds and localized to the protein storage vacuoles (PSV) even though the transcript is found in vegetative parts and floral buds as well. In developing seeds, transcript accumulation precedes protein appearance by more than 18 days. RNA accumulation peaks at ~20 days post anthesis (DPA) whereas protein accumulation reaches its maximum at ~40 DPA. Transgenic expression of BNM2 does not abrogate this regulation to yield ectopic protein production or to alter the temporal aspect of BNM2 accumulation. Overexpression of BNM2 led to spatial distortion of storage protein accumulation within PSV and to some morphological alterations of PSVs. However, the overall storage protein content was not altered.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bassüner R, Bäumlein H, Huth A, Jung R, Wobus U, Rapoport T, Saalbach G, Müntz K (1988) Abundant embryonic mRNA in field bean (Vicia faba L.) codes for a new class of seed proteins: cDNA cloning and characterization of the primary translation product. Plant Mol Biol 11:321–334
Batchelor AK, Boutilier K, Miller SS, Hattori J, Bowman LA, Hu M, Lantin S, Johnson DA, Miki BL (2002) SCB1, a BURP-domain protein gene, from developing soybean seed coats. Planta 215:523–532
Bäumlein H, Boerjan W, Nagy I, Bassuner R, Van Montagu M, Inze D, Wobus U (1991) A novel seed protein gene from Vicia faba is developmentally regulated in transgenic tobacco and Arabidopsis plants. Mol Gen Genet 225:459–467
Bies N, Aspart L, Carles C, Gallois P, Delseny M (1998) Accumulation and degradation of Em proteins in Arabidopsis thaliana; evidence for post-transcriptional controls. J Exp Bot 49:1925–1933
Boothe JG, De Beus MD, Johnson-Flanagan AM (1995) Expression of a low-temperature-induced protein in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 108:795–803
Boutilier KA, Gines MJ, DeMoor JM, Huang B, Baszczynski CL, Iyer VN, Miki BL (1994) Expression of the BnmNAP subfamily of napin genes coincides with the induction of Brassica microspore embryogenesis. Plant Mol Biol 26:1711–1723
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu CM, van Lammeren AA, Miki BL, Custers JB, van Lookeren Campagne MM (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 14:1737–1749
Chen L, Miyazaki C, Kojima A, Saito A, Adachi T (1999) Isolation and characterization of a gene expressed during early embryo sac development in apomictic guinea grass (Panicum maximum). J Plant Physiol 154:55–62
Chen L, Guan L, Seo M, Hoffmann F, Adachi T (2005) Developmental expression of ASG-1 during gametogenesis in apomictic guinea grass (Panicum maximum). J Plant Physiol 162:1141–1148
Chenna R, Sugawara H, Koike T, Lopez R, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG, Thompson JD (2003) Multiple sequence alignment with the clustal series of programs. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3497–3500
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Crouch ML, Sussex IM (1981) Development and storage-protein synthesis in Brassica napus L. embryos in vivo and in vitro. Planta 153:64–74
Datta N, LaFayette PR, Kroner PA, Nagao RT, Key JL (1993) Isolation and characterization of three families of auxin down-regulated cDNA clones. Plant Mol Biol 21:859–869
Delisle AJ, Crouch ML (1989) Seed storage protein transcription and mRNA Levels in Brassica napus during development and in response to exogenous abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 91:617–623
Emanuelsson O, Brunak S, von Heijne G, Nielsen H (2007) Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat Protoc 2:953–971
Ericson ML, Rodin J, Lenman M, Glimelius K, Josefsson LG, Rask L (1986) Structure of the rapeseed 1.7 S storage protein, napin, and its precursor. J Biol Chem 261:14576–14581
Ferrie AMR, Keller WA (2007) Optimization of methods for using polyethylene glycol as a non-permeating osmoticum for the induction of microspore embryogenesis in the Brassicaceae. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 43:348–355
Gillespie J, Rogers SW, Deery M, Dupree P, Rogers JC (2005) A unique family of proteins associated with internalized membranes in protein storage vacuoles of the Brassicaceae. Plant J 41:429–441
Gutierrez L, Van Wuytswinkel O, Castelain M, Bellini C (2007) Combined networks regulating seed maturation. Trends Plant Sci 12:294–300
Hattori J, Boutilier KA, van Lookeren Campagne MM, Miki BL (1998) A conserved BURP domain defines a novel group of plant proteins with unusual primary structures. Mol Gen Genet 259:424–428
Herman E, Schmidt M (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum to vacuole trafficking of endoplasmic reticulum bodies provides an alternate pathway for protein transfer to the vacuole. Plant Physiol 136:3440–3446
Hills MJ (2004) Control of storage-product synthesis in seeds. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:302–308
Holbrook LA, van Rooijen GJ, Wilen RW, Moloney MM (1991) Oilbody proteins in microspore-derived embryos of Brassica napus: hormonal, osmotic, and developmental regulation of synthesis. Plant Physiol 97:1051–1058
Horton P, Park K-J (2006) Protein subcellular localization prediction with WoLF PSORT. Proceedings of the 4th annual Asia Pacific bioinformatics conference APBC06, Taipei, pp 39–48
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Joosen R, Cordewener J, Supena ED, Vorst O, Lammers M, Maliepaard C, Zeilmaker T, Miki B, America T, Custers J, Boutilier K (2007) Combined transcriptome and proteome analysis identifies pathways and markers associated with the establishment of rapeseed microspore-derived embryo development. Plant Physiol 144:155–172
Kimber DS, McGregor DI (1995) The species and their origin, cultivation and world production. In: Kimber DS, McGregor DI (eds) Brassica oilseeds: production and utilization. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 1–7
Koncz C, Schell J (1986) The promoter of TL-DNA gene 5 controls the tissue-specific expression of chimaeric genes carried by a novel type of Agrobacterium binary vector. Mol Gen Genet 204:383–396
Li CH, Zhu YQ, Meng YL, Wang JW, Xu KX, Zhang TZ, Chen XY (2002) Isolation of genes preferentially expressed in cotton fibers by cDNA filter arrays and RT-PCR. Plant Sci 163:1113–1120
Malik MR, Wang F, Dirpaul JM, Zhou N, Polowick PL, Ferrie AM, Krochko JE (2007) Transcript profiling and identification of molecular markers for early microspore embryogenesis in Brassica napus. Plant Physiol 144:134–154
Moloney MM, Walker JM, Sharma KK (1989) High efficiency transformation of Brassica napus using Agrobacterium vectors. Plant Cell Rep 8:238–242
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Neuhaus JM, Rogers JC (1998) Sorting of proteins to vacuoles in plant cells. Plant Mol Biol 38:127–144
Okita TW, Rogers JC (1996) Compartmentation of proteins in the endomembrane system of plant cells. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:327–350
Otegui MS, Herder R, Schulze J, Jung R, Staehelin LA (2006) The proteolytic processing of seed storage proteins in Arabidopsis embryo cells starts in the multivesicular bodies. Plant Cell 18:2567–2581
Parcy F, Valon C, Raynal M, Gaubier-Comella P, Delseny M, Giraudat J (1994) Regulation of gene expression programs during Arabidopsis seed development: roles of the ABI3 locus and of endogenous abscisic acid. Plant Cell 6:1567–1582
Ragland M, Soliman K (1997) Sali5-4a and Sali3-2, two genes induced by aluminum in soybean roots. Plant Physiol 114:395–396
Schwenke KD, Raab B, Linow KJ, Pahtz W, Uhlig J (1981) Isolation of the 12 S globulin from rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) and characterization as a “neutral” protein. On seed proteins. Nahrung 25:271–280
Sjodahl S, Gustavsson HO, Rodin J, Lenman M, Hoglund AS, Rask L (1993) Cruciferin gene families are expressed coordinately but with tissue-specific differences during Brassica napus seed development. Plant Mol Biol 23:1165–1176
Taylor D, Weber N, Underhill E, Pomeroy M, Keller W, Scowcroft W, Wilen R, Moloney M, Holbrook L (1990) Storage-protein regulation and lipid accumulation in microspore embryos of Brassica napus L. Planta 181:18–26
Treacy BK, Hattori J, Prud’homme I, Barbour E, Boutilier K, Baszczynski CL, Huang B, Johnson DA, Miki BL (1997) Bnm1, a Brassica pollen-specific gene. Plant Mol Biol 34:603–611
Tsuwamoto R, Fukuoka H, Takahata Y (2007) Identification and characterization of genes expressed in early embryogenesis from microspores of Brassica napus. Planta 225:641–652
Vicente-Carbajosa J, Carbonero P (2005) Seed maturation: developing an intrusive phase to accomplish a quiescent state. Int J Dev Biol 49:645–651
Vicient CM, Hull G, Guilleminot J, Devic M, Delseny M (2000) Differential expression of the Arabidopsis genes coding for Em-like proteins. J Exp Bot 51:1211–1220
Vicient CM, Gruber V, Delseny M (2001) The Arabidopsis AtEm1 promoter is active in Brassica napus L. and is temporally and spatially regulated. J Exp Bot 52:1587–1591
Vitale A, Hinz G (2005) Sorting of proteins to storage vacuoles: how many mechanisms? Trends Plant Sci 10:316–323
Wang A, Xia Q, Xie W, Datla R, Selvaraj G (2003) The classical Ubisch bodies carry a sporophytically produced structural protein (RAFTIN) that is essential for pollen development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14487–14492
Watson CF, Zheng L, DellaPenna D (1994) Reduction of tomato polygalacturonase β subunit expression affects pectin solubilization and degradation during fruit ripening. Plant Cell 6:1623–1634
West M, Harada JJ (1993) Embryogenesis in higher plants: an overview. Plant Cell 5:1361–1369
Yamada K, Tomoo S, Mikio N, Ikuko H (2005) A VPE family supporting various vacuolar functions in plants. Physiol Plant 123:369–375
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Shinozaki K (1993) The plant hormone abscisic acid mediates the drought-induced expression but not the seed-specific expression of rd22, a gene responsive to dehydration stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet 238:17–25
Yeung EC, Rahman MH, Thorpe TA (1996) Comparative development of zygotic and microspore-derived embryos in Brassica napus L. cv. Topas. I. histodifferentiation. Int J Plant Sci 157:27
Yu S, Zhang L, Zuo K, Li Z, Tang K (2004) Isolation and characterization of a BURP domain-containing gene BnBDC1 from Brassica napus involved in abiotic and biotic stress. Physiol Plant 122:210–218
Zakharov A, Giersberg M, Hosein F, Melzer M, Muntz K, Saalbach I (2004) Seed-specific promoters direct gene expression in non-seed tissue. J Exp Bot 55:1463–1471
Zheng L, Heupel RC, DellaPenna D (1992) The β-subunit of tomato fruit polygalacturonase isoenzyme 1: isolation, characterization, and identification of unique structural features. Plant Cell 4:1147–1156
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Dwayne Hegedus for cruciferin and napin antibodies and Dr. Alison Ferrie for microspore embryos, Dr. John Kelly for LC-MS/MS of peptides. PT is grateful for Devin Polichuk for valuable discussions. We thank the PBI DNA Technology Unit for DNA synthesis and sequencing. This work is supported by National Research Council of Canada (NRC) and Natural Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC). This is NRCC publication 50148. GS dedicates this paper to the memory of his professor Dr. V. N. Iyer.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teerawanichpan, P., Xia, Q., Caldwell, S.J. et al. Protein storage vacuoles of Brassica napus zygotic embryos accumulate a BURP domain protein and perturbation of its production distorts the PSV. Plant Mol Biol 71, 331 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9541-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-009-9541-7