Abstract
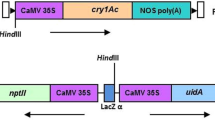
The construct inserted in YieldGard® MON810 maize, produced by Monsanto, contains the CaMV 35S promoter, the hsp70 intron of maize, the cryI(A)b gene for resistance to lepidopterans and the NOS terminator. In a previous work a truncation event at the 3′ end of the cryI(A)b gene leading to the complete loss of the NOS terminator was demonstrated. The 3′ maize genome junction region was isolated in the same experiment not showing any homology with known sequences. The aim of the experiments here reported was therefore to isolate and characterize a larger portion of the 3′ integration junction from genomic DNA of two commercial MON810 maize lines. Specific primers were designed on the 3′ integration junction sequence for the amplification of a 476 bp fragment downstream of the sequence previously detected. In silico analysis identified the whole isolated 3′ genomic region as a gene putatively coding for the HECT E3 ubiquitin ligase. RT-PCR performed in this region produced cDNA variants of different length. In silico translation of these transcripts identified 2 and 18 putative additional aminoacids in different variants, all derived from the adjacent host genomic sequences, added to the truncated CRY1A protein. These putative recombinant proteins did not show homology with any known protein domains. Our data gave new insights on the genomic organization of MON810 in the YieldGard® maize and confirmed the previous suggestion that the integration in the genome of maize caused a complex recombination event without, apparently, interfering with the activity of the partial CRY1A endotoxin and both the vigor and yield of the YieldGard® maize.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301(5633):653–657
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Bogani P, Simoni A, Bettini P, Mugnai M, Pellegrini MG, Buiatti M (1995) Genome flux in tomato auto- and auxotrophic cell clones cultured in different auxin/cytokinin equilibria. I. DNA multiplicity and methylation levels. Genome 38:902–912
Breitler JC, Labeyrie A, Meynard D, Legavre T, Guiderdoni E (2002) Efficient microprojectile bombardment-mediated transformation of rice using gene cassettes. Theor Appl Genet 104:709–719
Brunner S, Pea G, Rafalski A (2005) Origins, genetic organization and transcription of a family of non-autonomous helitron elements in maize. Plant J 43(6):799–810
Chen S, Jin W, Wang M, Zhang F, Zhou J, Jia Q, Wu Y, Liu F, Wu P (2003) Distribution and characterisation of over 1000 T-DNA tags in rice genome. Plant J 36:105–113
Downes BP, Stupar RM, Gingerich DJ, Vierstra RD (2003) The HECT ubiquitin-protein ligase (UPL) family in Arabidopsis: UPL3 has a specific role in trichome development. Plant J 35:729–742
Dunning Hotopp JC, Clark ME, Oliveira DCS, Foster JM, Fischer P, Muñoz Torres MC, Giebel JD, Kumar N, Ishmael N, Wang S, Ingram J, Nene RV, Shepard J, Tomkins J, Richards S, Spiro DJ, Ghedin E, Slatko BE, Tettelin H, Werren JH (2007) Widespread lateral gene transfer from intracellular bacteria to multicellular eukaryotes. Science 317:1753–1756
Fitch MM, Manshardt RM, Gonsalves D, Slightom JL, Sanford JC (1992) Virus resistant papaya plants derived from tissues bombarded with the coat protein gene of papaya ringspot virus. Biotechnology 10:1466–1472
Forsbach A, Schubert D, Lechtenberg B, Gils M, Schmidt R (2003) A comprehensive characterisation of single-copy T-DNA insertions into the Arabidopsis thaliana genome. Plant Mol Biol 52:161–176
Fu X, Duc LT, Fontana S, Bong BB, Tinjuangjun P, Sudhakar D, Twyman RM, Christou P, Kohli A (2000) Linear transgene constructs lacking vector backbone sequences generate low-copy-number transgenic plants with simple integration patterns. Transgenic Res 9:11–19
Hellmann H, Estelle M (2002) Plant development: regulation by protein degradation. Science 297:793–797
Hernandez M, Pla M, Esteve T, Prat S, Puigdomenech P, Ferrando A (2003) A specific real-time quantitative PCR detection system for event MON810 in maize YieldGard® based on the 3′-transgene integration sequence. Transgenic Res 12:179–189
Holck A, Va M, Didierjean L, Rudi K (2002) 5′-nuclease PCR for quantitative event-specific detection of the genetically modified Mon810 MaisGard maize. Eur Food Res Technol 214:449–453
Hulo N, Bairoch A, Bulliard V, Cerutti L, De Castro E, Langendijk-Genevaux PS, Pagni M, Sigrist CJA (2006) The PROSITE database. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D227–D230
Jeong DH, An S, Kang HG, Moon S, Han JJ, Park S, Lee HS, An K, An G (2002) T-DNA insertional mutagenesis for activation tagging in rice. Plant Physiol 130(4):1636–1644
Jeong DH, An S, Kang HG, Park GG, Kim SR, Sim J, Kim YO, Kim MK, Kim SR, Kim J, Shin M, Jung M, An G (2006) Generation of a flanking sequence-tag database for activation-tagging lines in Japonica rice. Plant J 45(1):123–132
Kohli A, Griffiths S, Palacios N, Twyman RM, Vain P, Laurie DA, Christou P (1999) Molecular characterisation of transforming plasmid rearrangements in transgenic rice reveals a recombination hotspot in the CaMV 35S promoter and confirms the predominance of microhomology mediated recombination. Plant J 17(6):591–601
Kohli A, Twyman RM, Abranches R, Wegel E, Stoger E, Christou P (2003) Transgene integration, organization and interaction in plants. Plant Mol Biol 52:247–258
Koncz C, Martini N, Mayerhofer R, Koncz-Kalman Z, Korber H, Redei GP, Schell J (1989) High-frequency T-DNA-mediated gene tagging in plants. PNAS USA 86(21):8467–8471
Korf I, Flicek P, Duan D, Brent MR (2001) Integrating genomic homology into gene structure prediction. Bioinformatics 17(90001):S140–S148
Letunic I, Copley RR, Pils B, Pinkert S, Schultz J, Bork P (2006) SMART 5: domains in the context of genomes and networks. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D257–D260. doi:10.1093/nar/gkj079
Lindsey K, Wei W, Clarke MC, Mcardle HF, Rooke LM, Topping JF (1993) Tagging genomic sequences that direct transgene expression by activation of a promoter trap in plants. Transgenic Res 2(1):33–47
Loc TN, Tinjuangjun P, Gatehouse AMR, Christou P, Gatehouse JA (2002) Linear transgene constructs lacking vector backbone sequences generate transgenic rice plants which accumulate higher levels of proteins conferring insect resistance. Mol Breed 9:231–244
Maqbool SB, Christou P (1999) Multiple traits of agronomic importance in indica rice plants: analysis of transgene integration patterns, expression levels and stability. Mol Breed 5:471–480
Mehlo L, Mazithulela G, Twyman RM, Boulton MI, Davies JW, Christou P (2000) Structural analysis of transgene rearrangements and effects on expression in transgenic maize plants generated by particle bombardment. Maydica 45:277–287
Morgante M, Brunner S, Pea G, Fengler K, Zuccolo A, Rafalski A (2005) Gene duplication and exon shuffling by helitron-like transposons generate intraspecies diversity in maize. Nat Genet 37:997–1002
Pawlowski WP, Somers DA (1996) Transgene inheritance in plants genetically engineered by microprojectile bombardment. Mol Biotechnol 6(1):17–30
Pawlowski WP, Somers DA (1998) Transgenic DNA integrated into the oat genome is frequently interspersed by host DNA. PNAS USA 95(21):12106–12110
Qin G, Kang D, Dong Y, Shen Y, Zhang L, Deng X, Zhang Y, Li S, Chen N, Niu W, Chen C, Liu P, Chen H, Li J, Ren Y, Gu H, Deng X, Qu LJ, Chen Z (2003) Obtaining and analysis of flanking sequences from T-DNA transformants of Arabidopsis. Plant Sci 165:941–949
Rang A, Linke B, Jansen B (2005) Detection of RNA variants transcribed from the transgene in Roundup Ready soybean. Eur Food Res Technol 220:438–443
Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A (2000) EMBOSS: the European molecular biology open software suite. Trends Genet 16(6):276–277
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 365–386
Salvo-Garrido H, Travella S, Bilham LJ, Harwood WA, Snape JW (2004) The distribution of transgene insertion sites in barley determined by physical and genetic mapping. Genetics 167(3):1371–1379
Scholte M, D′erfurth I, Rippa S, Mondy S, Cosson V, Durand P, Breda C, Trinh H, Rodriguez-Lorente I, Kondorosi E, Schultze M, Kondorosi A, Ratet P (2002) T-DNA tagging in the model legume Medicago truncatula allows efficient gene discovery. Mol Breed 10:203–215
Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. PNAS 95(11):5857–5864
Sha Y, Li S, Pei Z, Luo L, Tian Y, He C (2004) Generation and flanking sequence analysis of a rice T-DNA tagged population. Theor Appl Genet 108(2):306–314
Siebert PD, Chenchik A, Kellogg DE, Lukyanov KA, Lukyanov SA (1995) An improved method for walking in uncloned genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 23:1087–1088
Somers DA, Makarevitch I (2004) Transgene integration in plants: poking or patching holes in promiscuous genomes? Curr Opin Biotechnol 15(2):126–131
Svitashev SK, Somers DA (2001) Genomic interspersions determine the size and complexity of transgene loci in transgenic plants produced by microprojectile bombardment. Genome 44:691–697
Svitashev SK, Somers DA (2002) Characterization of transgene loci in plants using FISH: a picture is worth a thousand words. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 69:205–214
Svitashev SK, Ananiev E, Pawlowski WP, Somers DA (2000) Association of transgene integration sites with chromosome rearrangements in hexaploid oat. Theor Appl Genet 100:872–880
Szabados L, Kovacs I, Obershall A, Abrahám E, Kerekes I, Zsigmond L, Nagy R, Alvarado M, Krasovskaja I, Gál M, Berente A, Rédei GP, Haim AB, Koncz C (2002) Distribution of 1000 sequenced T-DNA tags in the Arabidopsis genome. Plant J 32:233–242
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22(22):4673–4680
Tinland B (1996) The integration of T-DNA into plant genomes. Trends Plant Sci 1(6):178–184
Tzfira T, Li J, Lacroix B, Citovsky V (2004). Agrobacterium T-DNA integration: molecules and models. Trends Genet 20(8):375–383
Vain P, James VA, Worland B, Snape JW (2002) Transgene behaviour across two generations in a large random population of transgenic rice plants produced by particle bombardment. Theor Appl Genet 105:878–889
Vierstra RD (2003) The ubiquitin/26S proteasome pathway, the complex last chapter in the life of many plant proteins. Trends Plant Sci 8:135–142
Wilson A, Latham J, Steinbrecher R (2006) Transformation-induced mutations in transgenic plants: analysis and biosafety implications. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev 23:209–234
Windels P, Taverniers I, Depicker A, Van Bockstaele E, De Loose M (2001) Characterisation of the roundup ready soybean insert. Eur Food Res Technol 213:107–111
Zhang J, Guo D, Chang Y, You C, Li X, Dai X, Weng Q, Zhang J, Chen G, Li X, Liu H, Han B, Zhang Q, Wu C (2007) Non-random distribution of T-DNA insertions at various levels of the genome hierarchy as revealed by analyzing 13 804 T-DNA flanking sequences from an enhancer-trap mutant library. Plant J 49(5):947–959
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. G. Monastra for providing seeds of MON810 and isogenic control maize. This work was supported by a grant from MIPAF (Ministero delle Politiche Agricole, Alimentari e Forestali), Project: “OGM in Agricoltura”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
EMBL Accession #: AM749995; AM749996; AM749997; AM749998; AM750007.AM749999; AM750000; AM750001; AM750002; AM750003; AM750004; AM750005; AM750006.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosati, A., Bogani, P., Santarlasci, A. et al. Characterisation of 3′ transgene insertion site and derived mRNAs in MON810 YieldGard® maize. Plant Mol Biol 67, 271–281 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9315-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11103-008-9315-7