Abstract
Purpose
The exact quantification of craniofacial characteristics in patients with acromegaly is important because it provides insight in the pathophysiology of the disease and offers a tool to evaluate the effects of treatment on tissue specific endpoints. However, until recently this was not feasible due to limitations of available cephalometric methods. The new technique of three-dimensional (3D) cephalometry enables the accurate quantification of facial anatomical characteristics of both soft tissue and bone. This is the first study that uses 3D cephalometry to analyze craniofacial disproportions in patients in long-term remission of acromegaly.
Methods
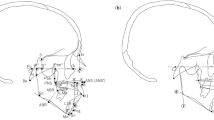
Sixteen patients in remission of acromegaly for over 24 months (50 % male, mean age 56.0 ± 10.7 years, mean body mass index 29.3 ± 5.5 kg/m2) were compared to 16 matched control subjects. A 3D cone beam computed tomography scan and 3D stereophotograph of each individual were acquired and analyzed using 3D cephalometry.
Results
In addition to an accurate quantification of the classical craniofacial characteristics, 3D cephalometry, shows that many typical soft tissue deformities persist, even after long-term remission. Furthermore, we found that, compared to controls, the patients in remission of acromegaly have a wider face at the level of the zygoma and longer maxilla (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
3D cephalometry is an attractive novel imaging modality to accurately investigate craniofacial disproportions of both soft tissue and bony parts of the face in patients with acromegaly, which makes it a promising technique for future research purposes and clinical practice.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melmed S (2006) Medical progress: acromegaly. N Engl J Med 355:2558–2573
Colao A, Ferone D, Marzullo P, Lombardi G (2004) Systemic complications of acromegaly: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. Endocr Rev 25:102–152
Thomson HA (1890) Acromegaly, with the description of a skeleton. J Anat Physiol 24:475–492
Barclay J, Symmers WS (1892) A case of acromegaly. Br Med J 2:1227–1229
Ruttle R (1891) A case of acromegaly. Br Med J 1:697–698
Caton R (1893) Notes of a case of acromegaly treated by operation. Br Med J 2:1421–1423
Matta MP, Couture E, Cazals L, Vezzosi D, Bennet A, Caron P (2008) Impaired quality of life of patients with acromegaly: control of GH/IGF-I excess improves psychological subscale appearance. Eur J Endocrinol 158:305–310
Herrmann BL, Mortsch F, Berg C, Weischer T, Mohr C, Mann K (2011) Acromegaly: a cross-sectional analysis of the oral and maxillofacial pathologies. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes 119:9–14
Ip MS, Tan KC, Peh WC, Lam KS (2001) Effect of Sandostatin LAR on sleep apnoea in acromegaly: correlation with computerized tomographic cephalometry and hormonal activity. Clin Endocrinol 55:477–483
Colao A, Marzullo P, Vallone G, Marino V, Annecchino M, Ferone D et al (1998) Reversibility of joint thickening in acromegalic patients: an ultrasonography study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:2121–2125
Broadbent B (1931) A new X-ray technique and its application to orthodontics. Ang Orthod 1:45–66
Kunzler A, Farmand M (1991) Typical changes in the viscerocranium in acromegaly. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 19:332–340
Dostalova S, Sonka K, Smahel Z, Weiss V, Marek J, Horinek D (2001) Craniofacial abnormalities and their relevance for sleep apnoea syndrome aetiopathogenesis in acromegaly. Eur J Endocrinol 144:491–497
Dostalova S, Sonka K, Smahel Z, Weiss V, Marek J (2003) Cephalometric assessment of cranial abnormalities in patients with acromegaly. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 31:80–87
Ebner FH, Kurschner V, Dietz K, Bultmann E, Nagele T, Honegger J (2010) Craniometric changes in patients with acromegaly from a surgical perspective. Neurosurg Focus 29:E3
Hochban W, Ehlenz K, Conradt R, Brandenburg U (1999) Obstructive sleep apnoea in acromegaly: the role of craniofacial changes. Eur Respir J 14:196–202
Swennen GRJ (2006) Three-dimensional cephalometry. A colour atlas and manual. Springer, Berlin
Heike CL, Upson K, Stuhaug E, Weinberg SM (2010) 3D digital stereophotogrammetry: a practical guide to facial image acquisition. Head Face Med 6:18
Plooij JM, Swennen GR, Rangel FA, Maal TJ, Schutyser FA, Bronkhorst EM et al (2009) Evaluation of reproducibility and reliability of 3D soft tissue analysis using 3D stereophotogrammetry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 38:267–273
Maal TJ, Plooij JM, Rangel FA, Mollemans W, Schutyser FA, Berge SJ (2008) The accuracy of matching three-dimensional photographs with skin surfaces derived from cone-beam computed tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:641–646
Giustina A, Chanson P, Bronstein MD, Klibanski A, Lamberts S, Casanueva FF et al (2010) A consensus on criteria for cure of acromegaly. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:3141–3148
Swennen GR, Mollemans W, Schutyser F (2009) Three-dimensional treatment planning of orthognathic surgery in the era of virtual imaging. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:2080–2092
Zhurov AI, Kau CH, Richmond S (2005) Computer methods for measuring 3D facial morphology. In: Middleton J, Shrive NG, Jones ML (eds) Computer methods in biomechanics and biomedical engineering. Cardiff
Katznelson L (2009) Alterations in body composition in acromegaly. Pituitary 12:136–142
Edler R, Agarwal P, Wertheim D, Greenhill D (2006) The use of anthropometric proportion indices in the measurement of facial attractiveness. Eur J Orthod 28:274–281
Edler R, Rahim MA, Wertheim D, Greenhill D (2010) The use of facial anthropometrics in aesthetic assessment. Cleft Palate-Craniofac J 47:48–57
Algars M, Santtila P, Varjonen M, Witting K, Johansson A, Jern P et al (2009) The adult body: how age, gender, and body mass index are related to body image. J Aging Health 21:1112–1132
Sardella C, Lombardi M, Rossi G, Cosci C, Brogioni S, Scattina I et al (2010) Short- and long-term changes of quality of life in patients with acromegaly: results from a prospective study. J Endocrinol Invest 33:20–25
Swennen GR, Schutyser F, De Barth EL, Groeve P, De Mey A (2006) A new method of 3-D cephalometry part I: the anatomic cartesian 3-D reference system. J Endocrinol Invest 17:314–325
Raisz LG (1999) Physiology and pathophysiology of bone remodeling. Clin Chem 45:1353–1358
Moss ML, Rankow RM (1968) The role of the functional matrix in mandibular growth. Ang Orthod 38:95–103
Miller RE, Learned-Miller EG, Trainer P, Paisley A, Blanz V (2011) Early diagnosis of acromegaly: computers vs clinicians. Clin Endocrinol 75:226–231
Schneider HJ, Kosilek RP, Günther M, Roemmler J, Stalla GK, Sievers C, Reincke M, Schopohl J, Würtz RP (2011) A novel approach to the detection of acromegaly, accuracy of diagnosis by automatic face classification. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:2074–2080
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by IPSEN.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagenmakers, M.A.E.M., Roerink, S.H.P.P., Maal, T.J.J. et al. Three-dimensional facial analysis in acromegaly: a novel tool to quantify craniofacial characteristics after long-term remission. Pituitary 18, 126–134 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-014-0565-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-014-0565-x