Abstract
Background
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH)-dependent Cushing’s syndrome, called Cushing disease, is caused by a corticotroph tumor of the pituitary gland. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 (IGFBP6), which regulates insulin-like growth factor (IGF) activity and inhibits several IGF2-dependent cancer growths, plays a pivotal role in the tumorigenesis of malignancy, but its roles in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas remain unclear.
Objective
To investigate IGFBP6 expression in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas, and its involvement in tumor growth.
Methods
Sporadic ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas specimens (n = 41) and adjacent non-tumorous pituitary tissues (n = 9) were collected by transphenoidal surgery. IGFBP6 expression was assessed by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and validated by Western blotting. Associations of IGFBP6 expression with maximum tumor diameter or Ki-67 labeling index were evaluated in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas.
Results
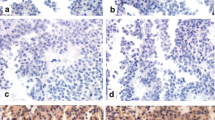
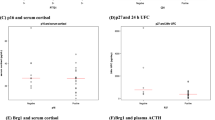
IGFBP6 mRNA and protein expression were both decreased in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas, compared to adjacent non-tumorous pituitary tissues (P < 0.01). IGFBP6 expression was correlated inversely with maximum tumor diameter (Rho = −0.53, P < 0.0001) and Ki-67 levels (Rho = −0.52, P < 0.05). Moreover, IGFBP6 downregulation activated PI3 K-AKT-mTOR pathway in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas.
Conclusions
IGFBP6 attenuation in ACTH-secreting pituitary adenomas is associated with tumor growth, through activation of PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway. The finding underlies IGFBP6 roles in Cushing disease and would potentially provide a novel target of medical therapies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melmed S (2003) Mechanisms for pituitary tumorigenesis: the plastic pituitary. J Clin Invest 112:1603–1618
Meij BP, Lopes MB, Ellegala DB, Alden TD, Laws ER Jr (2002) The long-term significance of microscopic dural invasion in 354 patients with pituitary adenomas treated with transsphenoidal surgery. J Neurosurg 96:195–208
Biller BM, Grossman AB, Stewart PM, Melmed S, Bertagna X, Bertherat J, Buchfelder M, Colao A, Hermus AR, Hofland LJ, Klibanski A, Lacroix A, Lindsay JR, Newell-Price J, Nieman LK, Petersenn S, Sonino N, Stalla GK, Swearingen B, Vance ML, Wass JA, Boscaro M (2008) Treatment of adrenocorticotropin-dependent Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:2454–2462
Kaptain GJ, Vincent DA, Sheehan JP, Laws ER Jr (2008) Transsphenoidal approaches for the extracapsular resection of midline suprasellar and anterior cranial base lesions. Neurosurgery 62:1264–1271
Gadelha M, Neto LV. (2014) Efficacy of medical treatment in Cushing's disease: a systematic review. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 80:1–12
Bach LA (2005) IGFBP-6 five years on; not so ‘forgotten’? Growth Horm IGF Res 15:185–192
Toretsky JA, Helman LJ (1996) Involvement of IGF-II in human cancer. J Endocrinol 149:367–372
Zhang L, Zhou W, Velculescu VE, Kern SE, Hruban RH, Hamilton SR, Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW (1997) Gene expression profiles in normal and cancer cells. Science 276:1268–1272
Gallicchio MA, Kneen M, Hall C, Scott AM, Bach LA (2001) Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 inhibits rhabdomyosarcoma growth in vivo. Int J Cancer 94:645–651
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Gallicchio MA, Kaun C, Wojta J, Binder B, Bach LA (2003) Urokinase type plasminogen activator receptor is involved in insulin-like growth factor-induced migration of rhabdomyosarcoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol 197:131–138
Sueoka N, Lee HY, Wiehle S, Cristiano RJ, Fang B, Ji L, Roth JA, Hong WK, Cohen P, Kurie JM (2000) Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6 activates programmed cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene 19:4432–4436
Vogel T (2013) Insulin/IGF-signalling in embryonic and adult neural proliferation and differentiation in the mammalian central nervous system. doi:10.5772/54946
Werner H, Weinstein D, Bentov I (2008) Similarities and differences between insulin and IGF-I: structures, receptors, and signalling pathways. Arch Physiol Biochem 114:17–22
Fumagalli L, Campa CC, Germena G, Lowell CA, Hirsch E, Berton G (2013) Class I phosphoinositide-3-kinases and SRC kinases play a nonredundant role in regulation of adhesion-independent and -dependent neutrophil reactive oxygen species generation. J Immunol 190:3648–3660
Gehart H, Kumpf S, Ittner A, Ricci R (2010) MAPK signalling in cellular metabolism: stress or wellness? EMBO Rep 11:834–840
Yamada S, Fukuhara N, Nishioka H, Takeshita A, Inoshita N, Ito J, Takeuchi Y (2012) Surgical management and outcomes in patients with Cushing disease with negative pituitary magnetic resonance imaging. World Neurosurg 77:525–532
Mampalam TJ, Wilson CB (1988) Transsphenoidal microsurgery for cushing disease a report of 216 cases. Ann Intern Med 109(6):487–493
Kiehna EN, Keil M, Lodish M, Stratakis C, Oldfield EH (2010) Pseudotumor cerebri after surgical remission of Cushing’s disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1528–1532
Monteith SJ, Starke RM, Jane JA Jr, Oldfield EH (2012) Use of the histological pseudocapsule in surgery for Cushing disease: rapid postoperative cortisol decline predicting complete tumor resection. J Neurosurg 116:721–727
Xing B, Ren Z, Su C, Wang R, Yang Y, Li Y (2011) Transsphenoidal micrmurgery in 541 patients with Cushing’s disease. Chin J Neurosurg 27:868–871. doi:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2346.2011.09.003
Jagannathan J, Smith R, DeVroom HL, Vortmeyer AO, Stratakis CA, Nieman LK, Oldfield EH (2009) Outcome of using the histological pseudocapsule as a surgical capsule in Cushing disease. J Neurosurg 111:531–539
Vance ML (2003) Perioperative management of patients undergoing pituitary surgery. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 32:355–365
Kato M, Ishizaki A, Hellman U, Wernstedt C, Kyogoku M, Miyazono K, Heldin CH, Funa K (1995) A human keratinocyte cell line produces two autocrine growth inhibitors, transforming growth factor-beta and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-6, in a calcium- and cell density-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 270:12373–12379
Zada G (2013) Diagnosis and multimodality management of cushing’s disease: a practical review. Int J Endocrinol 2013:893781
Nieman LK, Biller BM, Findling JW, Newell-Price J, Savage MO, Stewart PM, Montori VM (2008) The diagnosis of cushing’s syndrome: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1526–1540
Aghi MK (2008) Management of recurrent and refractory Cushing disease. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 4:560–568
Hwa V, Oh Y, Rosenfeld RG (1999) The insulin-like growth factor-binding protein (IGFBP) superfamily. Endocr Rev 20:761–787
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16:3–34
Kelley KM, Oh Y, Gargosky SE, Gucev Z, Matsumoto T, Hwa V, Ng L, Simpson DM, Rosenfeld RG (1996) Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins (IGFBPs) and their regulatory dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 28:619–637
Rajaram S, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1997) Insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in serum and other biological fluids: regulation and functions. Endocr Rev 18:801–831
Djiogue S, Nwabo Kamdje AH, Vecchio L, Kipanyula MJ, Farahna M, Aldebasi Y, Seke Etet PF (2013) Insulin resistance and cancer: the role of insulin and IGFs. Endocr Relat Cancer 20:R1–R17
Koyama N, Zhang J, Huqun, Miyazawa H, Tanaka T, Su X, Hagiwara K (2008) Identification of IGFBP-6 as an effector of the tumor suppressor activity of SEMA3B. Oncogene 27:6581–6589
Kuo YS, Tang YB, Lu TY, Wu HC, Lin CT (2010) IGFBP-6 plays a role as an oncosuppressor gene in NPC pathogenesis through regulating EGR-1 expression. J Pathol 222:299–309
Martins AS, Olmos D, Missiaglia E, Shipley J (2011) Targeting the insulin-like growth factor pathway in rhabdomyosarcomas: rationale and future perspectives. Sarcoma 2011:209736
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Dr. Cuiqi Zhou (Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California) for helpful discussion and editing of this manuscript. This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant 81072084), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2011AA020112 and 2014BAI04B00).
Conflict of interest
The authors do not have conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yakun Yang and Miaomiao Sheng have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Sheng, M., Huang, F. et al. Downregulation of Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 6 is associated with ACTH-secreting pituitary adenoma growth. Pituitary 17, 505–513 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-013-0535-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-013-0535-8