Abstract
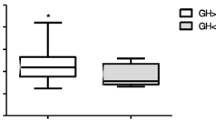
Weight-based (WB: 0.03 mg/kg) and fixed dose (FD: 1–1.5 mg) regimens of the glucagon stimulation test (GST) have been used to evaluate GH and cortisol secretion in children and adults, respectively. However, experience of the WB regimen in assessing GH and cortisol secretion in adults are limited. We describe a multicenter experience using WB and FD regimens in evaluating GH and cortisol secretion in adults suspected of GH deficiency and central adrenal insufficiency. Retrospective case series of GSTs (n = 515) performed at five tertiary centers. Peak and nadir glucose, and peak GH and peak cortisol responses occurred later with WB (mean dose: 2.77 mg) compared to FD (mean dose: 1.20 mg) regimens. Main side-effects were nausea and vomiting, particularly in younger females. Nausea was comparable but vomiting was more frequent in the WB regimen (WB: 10.0 % vs FD: 2.4 %; P < 0.05). Peak and nadir glucose, ΔGH, and peak and Δcortisol were higher in the WB regimen. In both regimens, age correlated negatively with peak cortisol levels, and body mass index (BMI), fasting, peak and nadir glucose correlated negatively with peak GH levels. WB and FD regimens can induce adult GH and cortisol secretion, but peak responses occur later in the WB regimen. Both regimens are relatively safe, and vomiting was more prevalent in the WB regimen. As age, BMI, and glucose tolerance negatively correlated with peak GH and cortisol levels, the WB regimen may be more effective than the FD regimen in older overweight glucose intolerant patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cook DM, Yuen KC, Biller BM, Kemp SF, Vance ML (2009) American Association of clinical endocrinologists medical guidelines for clinical practice for growth hormone use in growth hormone-deficient adults and transition patients—2009 update. Endocr Pract 15(suppl 2):1–29
Ho KK (2007) Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of adults with GH deficiency II: a statement of the GH Research Society in association with the European Society for Pediatric Endocrinology, Lawson Wilkins Society, European Society of Endocrinology, Japan Endocrine Society, and Endocrine Society of Australia. Eur J Endocrinol 157:695–700
Molitch ME, Clemmons DR, Malozowski S, Merriam GR, Vance ML (2011) Evaluation and treatment of adult growth hormone deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1587–1609
Darzy KH, Aimaretti G, Wieringa G, Gattamaneni HR, Ghigo E, Shalet SM (2003) The usefulness of the combined growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone and arginine stimulation test in the diagnosis of radiation-induced GH deficiency is dependent on the post-irradiation time interval. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:95–102
Brabant G, Poll EM, Jonsson P, Polydorou D, Kreitschmann-Andermahr I (2009) Etiology, baseline characteristics, and biochemical diagnosis of GH deficiency in the adult: are there regional variations? Eur J Endocrinol 161(Suppl 1):S25–S31
Yuen KC, Biller BM, Molitch ME, Cook DM (2009) Clinical review: is lack of recombinant growth hormone (GH)-releasing hormone in the United States a setback or time to consider glucagon testing for adult GH deficiency? J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2702–2707
Leong KS, Walker AB, Martin I, Wile D, Wilding J, MacFarlane IA (2001) An audit of 500 subcutaneous glucagon stimulation tests to assess growth hormone and ACTH secretion in patients with hypothalamic-pituitary disease. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 54:463–468
Micmacher E, Assumpcao RP, Redorat RG, Spina LD, Cruz IC, Silva CA, Vaisman M, Conceicao FL (2009) Growth hormone secretion in response to glucagon stimulation test in healthy middle-aged men. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 53:853–858
di Iorgi N, Napoli F, Allegri A, Secco A, Calandra E, Calcagno A, Frassinetti C, Ghezzi M, Ambrosini L, Parodi S, Gastaldi R, Loche S, Maghnie M (2010) The accuracy of the glucagon test compared to the insulin tolerance test in the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency in young children with growth hormone deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:2132–2139
Secco A, di Iorgi N, Napoli F, Calandra E, Ghezzi M, Frassinetti C, Parodi S, Casini MR, Lorini R, Loche S, Maghnie M (2009) The glucagon test in the diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency in children with short stature younger than 6 years. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4251–4257
Conceicao FL, e Silva A, Leal Costa AJ, Vaisman M (2003) Glucagon stimulation test for the diagnosis of GH deficiency in adults. J Endocrinol Invest 26:1065–1070
Gomez JM, Espadero RM, Escobar-Jimenez F, Hawkins F, Pico A, Herrera-Pombo JL, Vilardell E, Duran A, Mesa J, Faure E, Sanmarti A (2002) Growth hormone release after glucagon as a reliable test of growth hormone assessment in adults. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 56:329–334
Makimura H, Stanley T, Mun D, You SM, Grinspoon S (2008) The effects of central adiposity on growth hormone (GH) response to GH-releasing hormone-arginine stimulation testing in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:4254–4260
Karaca Z, Lale A, Tanriverdi F, Kula M, Unluhizarci K, Kelestimur F (2011) The comparison of low and standard dose ACTH and glucagon stimulation tests in the evaluation of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in healthy adults. Pituitary 14:134–140
Neary N, Nieman L (2010) Adrenal insufficiency: etiology, diagnosis and treatment. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes 17:217–223
Biller BM, Samuels MH, Zagar A, Cook DM, Arafah BM, Bonert V, Stavrou S, Kleinberg DL, Chipman JJ, Hartman ML (2002) Sensitivity and specificity of six tests for the diagnosis of adult GH deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2067–2079
Huypens P, Ling Z, Pipeleers D, Schuit F (2000) Glucagon receptors on human islet cells contribute to glucose competence of insulin release. Diabetologia 43:1012–1019
Orme SM, Price A, Weetman AP, Ross RJ (1998) Comparison of the diagnostic utility of the simplified and standard i.m. glucagon stimulation test (IMGST). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 49:773–778
Rao RH, Spathis GS (1987) Intramuscular glucagon as a provocative stimulus for the assessment of pituitary function: growth hormone and cortisol responses. Metabolism 36:658–663
Giuffrida FM, Berger K, Monte L, Oliveira CH, Hoff AO, Maciel RM, Vieira JG (2009) Relationship between GH response and glycemic fluctuations in the glucagon stimulation test. Growth Horm IGF Res 19:77–81
Waldhausl W, Haydl H, Nowotny P (1976) ACTH and cortisol responses to glucagon stimulation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 43:675–678
Carmichael JD, Danoff A, Milani D, Roubenoff R, Lesser ML, Livote E, Reitz RE, Ferris S, Kleinberg DL (2006) GH peak response to GHRH-arginine: relationship to insulin resistance and other cardiovascular risk factors in a population of adults aged 50–90. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 65:169–177
Colao A, Di Somma C, Savastano S, Rota F, Savanelli MC, Aimaretti G, Lombardi G (2009) A reappraisal of diagnosing GH deficiency in adults: role of gender, age, waist circumference, and body mass index. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4414–4422
Arvat E, Maccagno B, Ramunni J, Maccario M, Giordano R, Broglio F, Camanni F, Ghigo E (2000) Interaction between glucagon and human corticotropin-releasing hormone or vasopressin on ACTH and cortisol secretion in humans. Eur J Endocrinol 143:99–104
Littley MD, Gibson S, White A, Shalet SM (1989) Comparison of the ACTH and cortisol responses to provocative testing with glucagon and insulin hypoglycaemia in normal subjects. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 31:527–533
Cain JP, Williams GH, Dluhy RG (1972) Glucagon-initiated human growth hormone release: a comparative study. Can Med Assoc J 107:617–622
Mitchell ML, Byrne MJ, Sanchez Y, Sawin CT (1970) Detection of growth-hormone deficiency: the glucagon stimulation test. N Engl J Med 282:539–541
Hazem A, Elamin M, Malaga G, Bancos I, Prevost Y, Zeballos-Palacios C, Velasquez ER, Erwin PJ, Natt N, Montori VM, Murad M (2011) The accuracy of diagnostic tests for growth hormone deficiency in adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Endocrinol 165:841–849
Meulenberg PM, Ross HA, Swinkels LM, Benraad TJ (1987) The effect of oral contraceptives on plasma-free and salivary cortisol and cortisone. Clin Chim Acta 165:379–385
Leung KC, Johannsson G, Leong GM, Ho KK (2004) Estrogen regulation of growth hormone action. Endocr Rev 25:693–721
Acknowledgments
KCJY, BMKB and MBG have received research grants and consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk. RS and DMC have received consulting honoraria from Novo Nordisk. This research did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or non-profit sector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuen, K.C.J., Biller, B.M.K., Katznelson, L. et al. Clinical characteristics, timing of peak responses and safety aspects of two dosing regimens of the glucagon stimulation test in evaluating growth hormone and cortisol secretion in adults. Pituitary 16, 220–230 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0407-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11102-012-0407-7