Abstract
Purpose
Is to characterize the drug release from the ß-cyclodextrin (ß-CD) cavity and the drug transfer into model membranes by affinity capillary electrophoresis. Phospholipid liposomes with and without cholesterol were used to mimic the natural biological membrane.
Methods
The interaction of cationic and anionic drugs with ß-CD and the interaction of the drugs with liposomes were detected separately by measuring the drug mobility in ß-CD containing buffer and liposome containing buffer; respectively. Moreover, the kinetics of drug release from ß-CD and its transfer into liposomes with or without cholesterol was studied by investigation of changes in the migration behaviours of the drugs in samples, contained drug, ß-CD and liposome, at 1:1:1 molar ratio at different time intervals; zero time, 30 min, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 and 24 h. Lipophilic drugs such as propranolol and ibuprofen were chosen for this study, because they form complexes with ß-CD.
Results
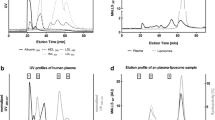
The mobility of the both drug liposome mixtures changed with time to a final state. For samples of liposomal membranes with cholesterol the final state was faster reached than without cholesterol.
Conclusions
The study confirmed that the drug release from the CD cavity and its transfer into the model membrane was more enhanced by the competitive displacement of the drug from the ß-CD cavity by cholesterol, the membrane component. The ACE method here developed can be used to optimize the drug release from CD complexes and the drug transfer into model membranes.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACE:
-
Affinity capillary electrophoresis
- CD:
-
Cyclodextrin
- IBU:
-
Ibuprofen
- LD :
-
The distance from the capillary inlet to the detector
- LT :
-
The total length of the capillary
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- Pro:
-
Propranolol
- PS:
-
Phosphatidylserine
- tEOF :
-
The migration time of electroosmotic flow peak
- tm :
-
The migration time of drug peak
- U:
-
The applied voltage
References
Loftsson T, Brewster ME. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 1. Drug solubilization and stabilization. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85(10):1017–25.
Rajewski RA, Stella VJ. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. 2. In vivo drug delivery. J Pharm Sci. 1996;85(11):1142–69.
Loftsson T, Masson M. Cyclodextrins in topical drug formulations: theory and practice. Int J Pharm. 2001;225(1–2):15–30.
Stella VJ, Rajewski RA. Cyclodextrins: their future in drug formulation and delivery. Pharm Res. 1997;14(5):556–67.
Uekama K, Hirayama F, Irie T. Cyclodextrin drug carrier systems. Chem Rev. 1998;98(5):2045–76.
Challa R, Ahuja A, Ali J, Khar RK. Cyclodextrins in drug delivery: an updated review. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2005;6(2):E329–57.
Loftsson T, Stefánsson E. Effect of cyclodextrins on topical drug delivery to the eye. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 1997;23(5):473–81.
Stella VJ, Rao VM, Zannou EA, Zia VV. Mechanisms of drug release from cyclodextrin complexes. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;36(1):3–16.
Loftsson T, Vogensen SB, Brewster ME, Konradsdottir F. Effects of cyclodextrins on drug delivery through biological membranes. J Pharm Sci. 2007;96(10):2532–46.
Tokumura T, Tsushima Y, Kayano M, Machida Y, Nagai T. Enhancement of bioavailability of cinnarizine from its beta-cyclodextrin complex on oral administration with DL-phenylalanine as a competing agent. J Pharm Sci. 1985;74(4):496–7.
Legendre JY, Rault I, Petit A, Luijten W, Demuynck I, Horvath S, et al. Effects of β-cyclodextrins on skin: implications for the transdermal delivery of piribedil and a novel cognition enhancing-drug, S-9977. Eur J Pharm Sci. 1995;3(6):311–22.
Zidovetzki R, Levitan I. Use of cyclodextrins to manipulate plasma membrane cholesterol content: evidence, misconceptions and control strategies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768(6):1311–24.
Besenicar MP, Bavdek A, Kladnik A, Macek P, Anderluh G. Kinetics of cholesterol extraction from lipid membranes by methyl-beta-cyclodextrin--a surface plasmon resonance approach. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008;1778(1):175–84.
Piel G, Piette M, Barillaro V, Castagne D, Evrard B, Delattre L. Study of the relationship between lipid binding properties of cyclodextrins and their effect on the integrity of liposomes. Int J Pharm. 2007;338(1–2):35–42.
Frijlink H, Eissens A, Hefting N, Poelstra K, Lerk C, Meijer DF. The effect of parenterally administered cyclodextrins on cholesterol levels in the rat. Pharm Res. 1991;8(1):9–16.
Mouritsen OG, Jorgensen K. A new look at lipid-membrane structure in relation to drug research. Pharm Res. 1998;15(10):1507–19.
Lagerquist C, Beigi F, Karlen A, Lennernas H, Lundahl P. Effects of cholesterol and model transmembrane proteins on drug partitioning into lipid bilayers as analysed by immobilized-liposome chromatography. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2001;53(11):1477–87.
Wiedmer SK, Riekkola M-L, Jussila MS. Phospholipids and liposomes in liquid chromatographic and capillary electromigration techniques. Trends Anal Chem. 2004;23(8):562–82.
Wang Y, Sun J, Liu H, Wang Y, He Z. Prediction of human drug absorption using liposome electrokinetic chromatography. Chromatographia. 2007;65(3–4):173–7.
Wang Y, Sun J, Liu H, Liu J, Zhang L, Liu K, et al. Predicting skin permeability using liposome electrokinetic chromatography. Analyst. 2009;134(2):267–72.
Zhang Y, Zhang R, Hjerten S, Lundahl P. Liposome capillary electrophoresis for analysis of interactions between lipid bilayers and solutes. Electrophoresis. 1995;16(8):1519–23.
Rüttinger H-H. Theory of affinity electrophoresis. In: Neubert R, Rüttinger H-H, editors. Affinity capillary electrophoresis in pharmaceutics and biopharmaceutics. Hoboken: Informa Healthcare; 2003. p. 23–34.
Castronuovo G, Niccoli M. Thermodynamics of inclusion complexes of natural and modified cyclodextrins with propranolol in aqueous solution at 298 K. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14(11):3883–7.
Bisby RH, Botchway SW, Crisostomo AG, Karolin J, Parker AW, Schröder L. Interactions of the β-blocker drug, propranolol, with detergents, β-cyclodextrin and living cells studied using fluorescence spectroscopy and imaging. Spectroscopy. 2010;24(1–2):137–42.
Ghorab MK, Adeyeye MC. Enhancement of ibuprofen dissolution via wet granulation with beta-cyclodextrin. Pharm Dev Technol. 2001;6(3):305–14.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Darwish, K.A., Mrestani, Y., Rüttinger, HH. et al. Drug Release from ß-Cyclodextrin Complexes and Drug Transfer into Model Membranes Studied by Affinity Capillary Electrophoresis. Pharm Res 33, 1175–1181 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1862-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-016-1862-z