Purpose
The purpose of this work was to demonstrate the iontophoretic delivery of granisetron hydrochloride by novel, self-contained iontophoretic patches and to determine the subcutaneous and dermal absorption kinetics using microdialysis.
Methods
In vitro iontophoretic delivery of granisetron hydrochloride was evaluated at 5, 10, or 20 mg/ml concentrations of donor using Franz diffusion cells and hairless rat skin as a membrane. In vivo studies were performed in hairless rats. Animals received either subcutaneous or dermal microdialysis probes and iontophoretic patches filled with drug formulation were applied on the abdominal area such that the probe lies below the anode chamber. Blood and microdialysate samples were collected at different time intervals. Intravenous administration of granisetron was also done to determine the basic pharmacokinetic parameters.
Results
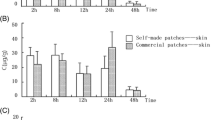
Iontophoretic patches delivered current constantly throughout the patch application. The patches delivered granisetron hydrochloride at a rate of 14.91 ± 4.53 μg/min/kg. Similar concentrations of granisetron hydrochloride in dermal and subcutaneous tissue were observed. Depot formation was identified in the subcutaneous and dermal profiles, indicating that subcutaneous structures are also responsible for the depot formation of the drug in the dermis.
Conclusion
The patches successfully delivered granisetron hydrochloride by iontophoresis and depot formation was observed in the dermal and subcutaneous structures in the skin.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUC:
-
area under the curve
- ECF:
-
extracellular fluid
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- NCA:
-
noncompartmental analysis
- RF:
-
recovery factor
References
R. H. Guy Y. N. Kalia M. B. Delgado-Charro V. Merino A. Lopez D. Marro (2000) ArticleTitleIontophoresis: electrorepulsion and electroosmosis J. Control. Release 64 129–132 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00132-7 Occurrence Handle10640651
R. Conjeevaram A. K. Banga L. Zhang (2002) ArticleTitleElectrically modulated transdermal delivery of fentanyl Pharm. Res. 19 440–444 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015135426838 Occurrence Handle12033377
G. Stagni C. Shukla (2003) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of methotrexate in rabbit skin and plasma after i.v.-bolus and iontophoretic administrations J. Control. Release 93 283–292 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jconrel.2003.08.011 Occurrence Handle14644578
G. Stagni M. E. Ali D. Weng (2004) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of acyclovir in rabbit skin after i.v.-bolus, ointment, and iontophoretic administrations Int. J. Pharm. 274 201–211 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.ijpharm.2004.01.024 Occurrence Handle15072796
J. Y. Fang K. C. Sung H. H. Lin C. L. Fang (1999) ArticleTitleTransdermal iontophoretic delivery of diclofenac sodium from various polymer formulations: in vitro and in vivo studies Int. J. Pharm. 178 83–92 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5173(98)00361-5 Occurrence Handle10205628
J. Y. Fang L. R. Hsu Y. B. Huang Y. H. Tsai (1999) ArticleTitleEvaluation of transdermal iontophoresis of enoxacin from polymer formulations: in vitro skin permeation and in vitro microdialysis using Wistar rat as an animal model Int. J. Pharm. 180 137–149 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5173(98)00287-7 Occurrence Handle10370184
G. Stagni D. O’Donnell Y. J. Liu D. L. Kellogg T. Morgan A. M. Shepherd (2000) ArticleTitleIntradermal microdialysis: kinetics of iontophoretically delivered propranolol in forearm dermis J. Control. Release 63 331–339 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-3659(99)00214-X Occurrence Handle10601728
J. F. Graumlich R. G. McLaughlin D. Birkhahn N. Shah A. Burk P. C. Jobe J. W. Dailey (2000) ArticleTitleSubcutaneous microdialysis in rats correlates with carbamazepine concentrations in plasma and brain Epilepsy Res. 40 25–32 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0920-1211(00)00110-8 Occurrence Handle10771255
L. Groth A. Jorgensen J. Serup (1998) ArticleTitleCutaneous microdialysis in the rat: insertion trauma studied by ultrasound imaging Acta Dermatol. Venereol. 78 10–14 Occurrence Handle10.1080/00015559850135742
L. Groth J. Serup (1998) ArticleTitleCutaneous microdialysis in man: effects of needle insertion trauma and anaesthesia on skin perfusion, erythema and skin thickness Acta Derm.-Venereol. 78 5–9 Occurrence Handle10.1080/00015559850135733 Occurrence Handle9498017
S. E. Clarke N. E. Austin J. C. Bloomer R. E. Haddock F. C. Higham F. J. Hollis M. Nash P. C. Shardlow T. C. Tasker F. R. Woods (1994) ArticleTitleMetabolism and disposition of 14C-granisetron in rat, dog and man after intravenous and oral dosing Xenobiotica 24 1119–1131 Occurrence Handle7701853
A. C. Sintov I. Krymberk D. Daniel T. Hannan Z. Sohn G. Levin (2003) ArticleTitleRadiofrequency-driven skin microchanneling as a new way for electrically assisted transdermal delivery of hydrophilic drugs J. Control. Release 89 311–320 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-3659(03)00123-8 Occurrence Handle12711453
T. M. Ludden S. L. Beal L. B. Sheiner (1994) ArticleTitleComparison of the Akaike Information Criterion, the Schawarz criterion and the F test as guides to model selection J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 22 431–435 Occurrence Handle7791040
D. Marro Y. N. Kalia M. B. Delgado-Charro R. H. Guy (2001) ArticleTitleContributions of electromigration and electroosmosis to iontophoretic drug delivery Pharm. Res. 18 1701–1708 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1013318412527 Occurrence Handle11785689
Y. N. Kalia A. Naik J. Garrison R. H. Guy (2004) ArticleTitleIontophoretic drug delivery Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 56 619–658 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.addr.2003.10.026 Occurrence Handle15019750
P. L. Williams J. E. Riviere (1995) ArticleTitleA biophysically based dermatopharmacokinetic compartment model for quantifying percutaneous penetration and absorption of topically applied agents. I. Theory J. Pharm. Sci. 84 599–608 Occurrence Handle7658351
A. Luzardo-Alvarez M. B. Delgado-Charro J. Blanco-Mendez (2003) ArticleTitleIn vivo iontophoretic administration of ropinirole hydrochloride J. Pharm. Sci. 92 2441–2448 Occurrence Handle10.1002/jps.10502 Occurrence Handle14603489
T. Kankkunen R. Sulkava M. Vuorio K. Kontturi J. Hirvonen (2002) ArticleTitleTransdermal iontophoresis of tacrine in vivo Pharm. Res. 19 704–707 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1015374600683 Occurrence Handle12069176
M. R. Prausnitz C. S. Lee C. H. Liu J. C. Pang T.-P. Singh R. Langer J. C. Weaver (1996) ArticleTitleTransdermal transport efficiency during skin electroporation and iontophoresis J. Control. Release 38 205–217 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-3659(95)00121-2
P. Singh M. S. Roberts H. I. Maibach (1995) ArticleTitleModelling of plasma levels of drugs following transdermal iontophoresis J. Control. Release 33 293–298 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-3659(94)00101-Y
C. T. Huang C. F. Chen T. H. Tsai (1999) ArticleTitlePharmacokinetics of granisetron in rat blood and brain by microdialysis Life Sci. 64 1921–1931 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0024-3205(99)00143-5 Occurrence Handle10353590
F. X. Mathy A. R. Denet B. Vroman P. Clarys A. Barel R. K. Verbeeck V. Preat (2003) ArticleTitleIn vivo tolerance assessment of skin after insertion of subcutaneous and cutaneous microdialysis probes in the rat Skin Pharmacol. Appl. Skin Physiol. 16 18–27 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000068290 Occurrence Handle12566825
P. Singh M. S. Roberts (1993) ArticleTitleIontophoretic transdermal delivery of salicylic acid and lidocaine to local subcutaneous structures J. Pharm. Sci. 82 127–131 Occurrence Handle8445523
A. K. Banga S. Bose T. K. Ghosh (1999) ArticleTitleIontophoresis and electroporation: comparisons and contrasts Int. J. Pharm. 179 1–19 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-5173(98)00360-3 Occurrence Handle10053197
N. G. Turner R. H. Guy (1997) ArticleTitleIontophoretic transport pathways: dependence on penetrant physicochemical properties J. Pharm. Sci. 86 1385–1389 Occurrence Handle10.1021/js970046z Occurrence Handle9423151
S. K. Li A. H. Ghanem K. D. Peck W. I. Higuchi (1999) ArticleTitlePore induction in human epidermal membrane during low to moderate voltage iontophoresis: a study using AC iontophoresis J. Pharm. Sci. 88 419–427 Occurrence Handle10.1021/js980331y Occurrence Handle10187752
P. Singh M. S. Roberts (1993) ArticleTitleBlood flow measurements in skin and underlying tissues by microsphere method: application to dermal pharmacokinetics of polar nonelectrolytes J. Pharm. Sci. 82 873–879 Occurrence Handle8229683
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by Travanti Pharma Inc., Oakdale, MN 55128. We would like to thank Pharsight Inc., Mountain View, CA, for providing us the academic license for WinNonlin Pro software.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaturvedula, A., Joshi, D.P., Anderson, C. et al. Dermal, Subdermal, and Systemic Concentrations of Granisetron by Iontophoretic Delivery. Pharm Res 22, 1313–1319 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5335-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-005-5335-z