Abstract
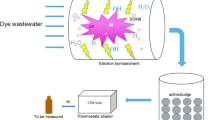
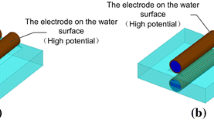
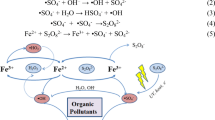
A multi-needle-to-plate pulsed discharge plasma reactor was designed to investigate its potential for polyvinyl alcohol-containing wastewater (PVA) treatment. The effects of some operational parameters such as PVA initial concentration, pulse peak discharge voltage, air flow rate, solution pH value, and iron additives on PVA degradation were examined. The results indicated that PVA could be effectively degraded from aqueous solutions. PVA degradation efficiency was 76.0 % within 60 min’s discharge plasma treatment with 1.5 mmol L−1 Fe2+ addition. Decreasing PVA initial concentration and increasing pulse peak discharge voltage were both beneficial for PVA degradation. There existed appropriate air flow rate for obtaining great PVA degradation efficiency in the present study. A little acid environment was conducive to PVA degradation. The presence of Fe2+ and Cu2+ could both benefit PVA degradation, and the increment of Fe2+ and Cu2+ concentrations to a certain extent could enhance its degradation efficiency, as well as energy yield. PVA possible degradation mechanisms were discussed, and the degradation processes were mainly triggered by the reactions of PVA with \(^{ \cdot } {\text{OH}}\) radicals.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giroto JA, Guardani R, Teixeira ACSC, Nascimento CAO (2006) Chem Eng Process 45:523–532
Yang QX, Zhang WY, Zhang H, Li YH, Li CM (2011) Bioresour Technol 102:3790–3798
Tokiwa Y, Kawabata G, Jarerat A (2001) Biotechnol Lett 23:1937–1941
Tsujiyama S, Okada A (2013) Biotechnol Lett. doi:10.1007/s10529-013-1281-8
Inoguchi Y, Chinn H (2011) Polyvinyl alcohols, SRI consulting. http://www.sriconsulting.com/CEH/Public/Reports/580.1810/. Accessed 14 Nov 2011
Zhang B, Zhou Y (2003) Cotton Text Technol 31:17–20 (in Chinese)
Shan JC, Guan Y, Zheng QK, Han JS, Liu QS, Pu ZY (2009) J Appl Polymer Sci 113:860–867
Schonberger H, Baumann A, Keller W (1997) Am Dyestuff Rep 86:9–18
Zhang YH, Chen W, Lv GC, Lv FZ, Chu PK, Guo WM, Cui BL, Zhang R, Wang H (2012) Water Sci Technol 65:2055–2060
Phugare SS, Kalyani DC, Surwase SN, Jadhav JP (2011) Ecotoxicol Environ Safe 74:1288–1296
Li M, Zhu Z, Pan X (2011) Starch-Starke 63:638–691
Yu H, Gu G, Song L (1996) Environ Technol 17:1261–1267
Mo JH, Lee YH, Kim J, Jeong JY, Jegal J (2008) Dyes Pigments 76:429–434
Ji ZJ, He YS, Zhang GJ (2006) Desalination 201:255–266
Sun YY, Hua XY, Ge R, Guo AT, Guo ZY, Dong DM, Sun WT (2013) Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:5797–5805
Wu Y, Lian Y, Liu J, Zhu TH (2008) Water Treat Technol 34:32–34
Oh SY, Kim HW, Park JM, Park HS, Yoon C (2009) J Hazard Mater 168:346–351
Hu Y, Bai Y, Yu H, Zhang C, Chen J (2013) Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 91:314–319
Sun B, Aye NN, Gao Z, Lv D, Zhu X, Sato M (2012) J Environ Sci (China) 24:840–845
Wang HJ, Chen XY (2011) J Hazard Mater 186:1888–1892
Finley JH (1961) Anal Chem 33:1925–1927
Sellers RM (1980) Analyst 105:950–954
Wang HJ, Li J, Quan X (2008) Appl Catal B Environ 83:72–77
Sun B, Sato M, Clements JS (1999) J Phys D Appl Phys 32:1908–1915
Bian WJ, Zhou MH, Lei LC (2007) Plasma Chem Plasma Process 27:337–348
Barbara F, Romuald W (1993) IEEE Trans Elect Insul 28:932–940
Zhang YZ, Zheng JT, Qu XF, Chen HG (2008) Chemosphere 70:1518–1524
Gai K (2007) J Hazard Mater 146:249–254
Zhang JB, Zheng Z, Zhang YN, Feng JW, Li JH (2008) J Hazard Mater 154:506–512
Deng Y (2007) J Hazard Mater 146:334–340
Kang YW, Hwang KY (2000) Water Res 34:2786–2790
Herney-Ramirez J, Vicente MA, Madeira LM (2010) Appl Catal B Environ 98:10–26
Kaplan LA, Reasoner DJ, Rice EW (1994) J Am Water Works Assoc 86:121–132
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) J Hazard Mater 98:33–50
Zhang S, Yu H (2004) Water Res 38:309–316
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation, P.R. China (Project No. 21107085) and the Initiative Funding Programs for Doctoral Research of Northwest A&F University (2013BSJJ121) for the financial supports to this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, T., Ma, T., Qu, G. et al. Performance Evaluation of Hybrid Gas–Liquid Pulse Discharge Plasma-Induced Degradation of Polyvinyl Alcohol-Containing Wastewater. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 34, 1115–1127 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-014-9565-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-014-9565-x