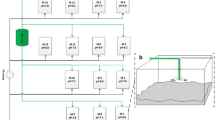
A Pilot-scale experiment for the treatment of red tide in the enclosure was done in sea area of Shandong Province, P.R. China on Aug. 25, 2002. With the method of micro-gap discharge, O2 in air and H2O in seawater are ionized and dissociated into large numbers of OH• radicals, and then dissolved into a part of seawater to form OH• solution of high concentration. With OH• concentration of 0.68 mg/L, the kill efficiencies of 29 kinds of red tide organisms such as Chaetoceros lorenzianus and so on reached 99.89%, in which bacterium and vibrio were reduced below the detection limit, also Gonyaulax cysts and Prei. Cysts with the crust were done the lowest limit of test. At the same time, the content of chlorophyll-a was decreased below the detection limit. DO (dissolved oxygen) saturation of seawater was greatly increased to 100% because the residual OH• radical was decomposed into H2O and O2 after 20 min. Therefore the treatment of red tide using OH• radicals is a kind of advanced oxidation technology, which realizes zero pollution, zero emission and zero residual in the process of the production of OH• radicals and the treatment of red tide.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
National Ocean Bureau of China, Ocean Environment Quality Bulletin of China in 2001 (in Chinese) 12–13, 2002.
Z. Ling Y. Pinghe L. Kunping (2001) Ocean Environ. Chem 20 1
Y. Zhiming S. Xiuxian Z. Bo (1999) Chinese Sci. Bull 44 IssueID1 65
B. Xiyao B. Mindong Z. Xiaojian (2002) J. Nat 24 IssueID1 1
B. Beth (1998) Bio. Science 48 12 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000022776
D.M. Anderson (1997) Nature 388 513 Occurrence Handle10.1038/41415
B. Xiyao Z. Zhitao H. Hui B. Mindong (2002) Chinese Sci. Bull 47 IssueID7 529 Occurrence Handle10.1360/02tb9121
B. Mindong Z. Zhitao B. Xiyao et al. (2003) IEEE Trans, Plasma Sci 31 IssueID6 1285
Bai X.Y., Zhang Z.T., Bai M.D., and Yang B., Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 25(1), (2005).
Z. Zhang M. Bai X. Bai et al. (2004) J. Adv. Oxidation Technol 7 IssueID2 178
J. Hoigne H. Bader (1976) Water Res 10 IssueID2 377 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(76)90055-5
W.H. Glaze J.W. Kang D.H. Chapin (1987) Ozone Sci. & Eng 9 IssueID4 355
J. Staehelin J. Hoigne (1982) Environ. Sci. & Tech 16 IssueID3 676
B. Horton (1999) Nature 400 IssueID19 797 Occurrence Handle10.1038/23528
W. Leitner (2000) Nature 405 IssueID11 129 Occurrence Handle10.1038/35012181 Occurrence Handle10821253
B.M. Penetrante J.N. Bardsley M.C. Hsiao (1997) Jpn. J. Appl. Phys 36 IssueID7B 507 Occurrence Handle10.1143/JJAP.36.5007
S. Chunpu Z. Jianzhong D. Shaojin (1999) China Science and Technology University Publication (in Chinese) Hefei China
“D3382-95 Standard Test Method for Measurement of Energy and Integrated charge Transfer Due to partial Discharge (Corona) Using Bridge Techniques”, in 1995 Book of Standards, Section 10, Vol. 10.02.
Z.T. Zhang Y.Z. Xian M.D. Bai (2003) J. Phys 32 IssueID7 458
R. Xin-rong T. Xiao-yan (2001) China Environ. Sci 21 IssueID2 115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*Key project of National Foundation Research from Science and Technology Ministry of China, (2002CCC00900); key project of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC; 60031001).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, M., Bai, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Treatment of Red Tide in Ocean Using Non-Thermal Plasma Based Advanced Oxidation Technology*. Plasma Chem Plasma Process 25, 539–550 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-004-4998-2
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11090-004-4998-2