Abstract
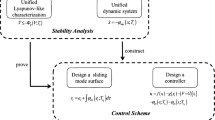
In order to solve the constrained-input problem and reduce the computing resources, a novel event-triggered optimal control method is proposed for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems. In the proposed method, the event-triggered control policy is applied to the globalized dual heuristic dynamic programming (GDHP) algorithm. Compared with the traditional adaptive dynamic programming (ADP) control, the event-triggered GDHP control can reduce the computation while ensuring the system performance. In this paper, a non-quadratic function is given to code the control constraints and the trigger condition with the stability analysis is provided. Neural networks (NN) are constructed in the GDHP structure, where the model network is designed to identify the unknown nonlinear system, the critic network is used to learn the cost function and its partial derivative, and the action network is designed to obtain the approximate optimal control law. Three simulation examples are presented to demonstrate the performance of the proposed event-triggered design for constrained discrete-time nonlinear systems.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao, L., Xiong, H., Zheng, Z., Li, Q.: Improving worst-case latency analysis for rate-constrained traffic in the time-triggered ethernet network. IEEE Commun. Lett. 18(11), 1927–1930 (2014)
Donkers, M., Heemels, W.: Output-based event-triggered control with guaranteed \({{\cal{L}}}_{\infty }\)-gain and improved and decentralized event-triggering. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 57(6), 1362–1376 (2012)
Molin, A., Hirche, S.: On the optimality of certainty equivalence for event-triggered control systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(2), 470–474 (2013)
Zhang, X., Han, Q., Zhang, B.: An overview and deep investigation on sampled-data-based event-triggered control and filtering for networked systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 13(1), 4–16 (2017)
Zhang, H., Han, J., Wang, Y., Jiang, H.: \(H_\infty \) consensus for linear heterogeneous multiagent systems based on event-triggered output feedback control scheme. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 49(6), 2268–2279 (2019)
Ma, Y., Wu, W., Görges, D., Cui, B.: Event-triggered feedback control for discrete-time piecewise affine systems subject to input saturation. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(3), 2353–2365 (2019)
Zhang, J., Feng, G.: Event-driven observer-based output feedback control for linear systems. Automatica 50, 1852–1859 (2014)
Tabuada, P.: Event-triggered real-time scheduling of stabilizing control tasks. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 52(9), 1680–1685 (2007)
Tallapragada, P., Chopra, N.: On event triggered tracking for nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(9), 2343–2348 (2013)
Qiu, J., Sun, K., Wang, T., Gao, H.: Observer-based fuzzy adaptive event-triggered control for pure-feedback nonlinear systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Trans. Fuzzy Syst. 27(11), 2152–2162 (2019)
Heemels, W.P.M.H., Donkers, M.C.F., Teel, A.R.: Periodic event-triggered control for linear systems. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 58(4), 847–861 (2013)
Yang, D., Li, T., Xie, X., Zhang, H.: Event-triggered integral sliding-mode control for nonlinear constrained-input systems with disturbances via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 50(11), 4086–4096 (2020)
Mu, C., Wang, K., Sun, C.: Policy-Iteration-Based Learning for Nonlinear Player Game Systems With Constrained Inputs. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. (in press). https://doi.org/10.1109/TSMC.2019.2962629
Luo, B., Yang, Y., Liu, D., Wu, H.: Event-triggered optimal control with performance guarantees using adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 31(1), 76–88 (2020)
Zhong, X., He, H.: An event-triggered ADP control approach for continuous-time system with unknown internal states. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 47(3), 683–694 (2017)
Shi, J., Yue, D., Yang, Y., Hu, S.: Event-triggered control based on adaptive dynamic programming for continuous-time nonlinear systems with completely unknown dynamics. In: 2016 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation, pp. 2035–2040 (2016)
Yang, Y., Xu, C., Meng, Q., Tan, J.: An event-triggered ADP controller for single link robot arm system based on output position. In: 2018 Chinese Control And Decision Conference, pp. 2271–2276 (2018)
Mu, C., Wang, K.: Single-network ADP for near optimal control of continuous-time zero-sum games without using initial stabilising control laws. IET Control Theory Appl. 12(18), 2449–2458 (2018)
Werbos, P. J.: Advanced forecasting methods for global crisis warning and models of intelligence. Gen. Syst. Yearb. 22, 25–38 (1977)
John, M., Chadwick, C., George, L., Richard, S.: Applications and reviews. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C 32, 140–153 (2002)
Jiang, Y., Jiang, Z.: Computational adaptive optimal control for continuous-time linear systems with completely unknown dynamics. Automatica 48, 2699–2704 (2012)
Al-Tamimi, A., Lewis, F.L., Abu-Khalaf, M.: Discrete-time nonlinear HJB solution using approximate dynamic programming: convergence proof. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B 38(4), 943–949 (2008)
Zhang, H., Wei, Q., Luo, Y.: A novel infinite-time optimal tracking control scheme for a class of discrete-time nonlinear systems via the greedy HDP iteration algorithm. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B Cybern. 38(4), 937–942 (2008)
Prokhorov, D., Wunsch, D.: Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 8, 997–1007 (1997)
Eun, Y., Kabamba, P.T., Meerkov, S.M.: Analysis of random reference tracking in systems with saturating actuators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 50(11), 1861–1866 (2005)
Mu, C., Wang, K.: Approximate-optimal control algorithm for constrained zero-sum differential games through event-triggering mechanism. Nonlinear Dyn. 95, 2639–2657 (2019)
Eun, Y., Kabamba, P.T., Meerkov, S.M.: System types in feedback control with saturating actuators. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 49(2), 287–291 (2004)
He, W., Ge, S.: Vibration control of a flexible string with both boundary input and output constraints. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 23(4), 1245–1254 (2015)
Na, J., Wang, B., Li, G., Zhan, S., He, W.: Nonlinear constrained optimal control of wave energy converters with adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 66(10), 7904–7915 (2019)
Fan, B., Yang, Q., Tang, X., Sun, Y.: Robust ADP design for continuous-time nonlinear systems with output constraints. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 29(6), 2127–2138 (2018)
Zhu, Y., Zhao, D., He, H., Ji, J.: Event-triggered optimal control for partially unknown constrained-input systems via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 64(5), 4101–4109 (2017)
Zhang, L., Chen, M.: Event-based global stabilization of linear systems via a saturated linear controller. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 26(5), 1073–1091 (2016)
Ni, W., Zhao, P., Wang, X.: Event-triggered control of linear systems with saturated inputs. Asian J. Control 17(4), 1196–1208 (2015)
Lewis, F.L., Syrmos, V.: Optimal Control. Wiley, New York (1995)
Abu-Khalaf, M., Lewis, F.L.: Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach. Automatica 41(5), 779–791 (2005)
Eqtami, A., Dimarogonas, D.V., Kyriakopoulos, K.J.: Event-triggered control for discrete-time systems. In: Proceedings of the 2010 American Control Conference, pp. 4719–4724 (2010)
Jiang, Z.P., Wang, Y.: Input-to-state stability for discrete-time nonlinear systems. Automatica 37(6), 857–869 (2001)
Wang, F., Jin, N., Liu, D., Wei, Q.: Adaptive dynamic programming for finite-Horizon optimal control of discrete-time nonlinear systems with \(\varepsilon \)-wrror bound. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 22(1), 24–36 (2011)
Mu, C., Wang, D., He, H.: Novel iterative neural dynamic programming for data-based approximate optimal control design. Automatica 81, 240–252 (2017)
Liu, D., Wei, Q.: Policy iteration adaptive dynamic programming algorithm for discrete-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 25(3), 621–634 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 62022061, 61773284, and in part by Tianjin Natural Science Foundation under Grant 20JCYBJC00880.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
No conflict of interest exits in this submission, and the research work does not involve any human participants and/or animals. The manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mu, C., Liao, K. & Wang, K. Event-triggered design for discrete-time nonlinear systems with control constraints. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 2645–2657 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06218-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-06218-4