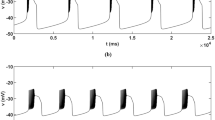
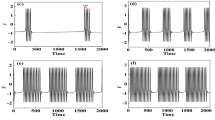
Abstract
Two-coupled excitatory neurons model containing both calcium-activated non-specific cationic and persistent sodium current in the pre-Bötzinger complex (pre-BötC) is studied. A new type of mixed burst similar to a depolarization block bursting (DB-bursting) is observed in the model of pre-BötC neurons. The multi-time scale dynamics, one- and two-parameter bifurcation analysis, are used to study the types of mixed burst and their transition mechanisms. The results show that the periodic fluctuation of calcium concentration has a great influence on the generation of mixed bursting. The change of time scale caused by fluctuation of calcium concentration and the relative position of bifurcation curves have great influence on patterns of bursting.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, J.C., Ellenberger, H.H., Ballanyi, K., et al.: Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science 254(5032), 726–729 (1991)
Smith, J.C.: Realistic computational models of respiratory neurons and networks. In: Bioengineering Approaches to Pulmonary Physiology and Medicine, pp. 77–92. Springer, Boston (1996)
Mellen, N.M., Janczewski, W.A., Bocchiaro, C.M., et al.: Opioid-induced quantal slowing reveals dual networks for respiratory rhythm generation. Neuron 37(5), 821–826 (2003)
Feldman, J.L., Smith, J.C.: Cellular mechanisms underlying modulation of breathing pattern in mammals. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 563(1), 114–130 (1989)
Brockhaus, J., Ballanyi, K.: Synaptic inhibition in the isolated respiratory network of neonatal rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10(12), 3823–3839 (1998)
Shao, X.M., Feldman, J.L.: Respiratory rhythm generation and synaptic inhibition of expiratory neurons in pre-Bötzinger complex: differential roles of glycinergic and GABAergic neural transmission. J. Neurophysiol. 77(4), 1853–1860 (1997)
Ren, J., Greer, J.J.: Modulation of respiratory rhythmogenesis by chloride-mediated conductances during the perinatal period. J. Neurosci. 26(14), 3721–3730 (2006)
Butera, R.J., John, R., Smith, J.C.: Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. I. Bursting pacemaker neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82(1), 382–397 (1999)
Butera, R.J., John, R., Smith, J.C.: Models of respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex. II. Populations of coupled pacemaker neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 82(1), 398–415 (1999)
Rubin, J.E., Hayes, J.A., Mendenhall, J.L., et al.: Calcium-activated nonspecific cation current and synaptic depression promote network-dependent burst oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 106(8), 2939–2944 (2009)
Negro, C.A.D., Koshiya, N., Butera, R.J., et al.: Persistent sodium current, membrane properties and bursting behavior of pre-Bötzinger complex inspiratory neurons in vitro. J. Neurophysiol. 88(5), 2242–2250 (2002)
Ptak, K., Zummo, G.G., Alheid, G.F., et al.: Sodium currents in medullary neurons isolated from the pre-Bötzinger complex region. J. Neurosci. 25(21), 5159–5170 (2005)
Koizumi, H., Smith, J.C.: Persistent \(\text{ Na }^+\) and \(\text{ K }^+\)-dominated leak currents contribute to respiratory rhythm generation in the pre-Bötzinger complex in vitro. J. Neurosci. 28(7), 1773–1785 (2008)
Pace, R.W., Mackay, D.D., Feldman, J.L., et al.: Inspiratory bursts in the pre-Bötzinger complex depend on a calcium activated nonspecific cation current linked to glutamate receptors in neonatal mice. J. Physiol. 582(1), 113–125 (2007)
Toporikova, N., Butera, R.J.: Two types of independent bursting mechanisms in inspiratory neurons: an integrative model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 30(3), 515–528 (2011)
Park, C., Rubin, J.E.: Cooperation of intrinsic bursting and calcium oscillations underlying activity patterns of model pre-Bötzinger complex neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 34(2), 345–366 (2013)
Duan, L., Zhai, D., Tang, X.: Bursting induced by excitatory synaptic coupling in the pre-Bötzinger complex. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 22(05), 1107–283 (2012)
Duan, L., Liu, J., Chen, X., et al.: Dynamics of in-phase and anti-phase bursting in the coupled pre-Bötzinger complex cells. Cogn. Neurodyn. 11(1), 1–7 (2017)
Wang, Z., Duan, L., Cao, Q., et al.: Multi-stability involved mixed bursting within the coupled pre-Bötzinger complex neurons. Chin. Phys. B 27(7), 70502–070502 (2018)
Dunmyre, J.R., Negro, C.A.D., Rubin, J.E.: Interactions of persistent sodium and calcium-activated nonspecific cationic currents yield dynamically distinct bursting regimes in a model of respiratory neurons. J. Comput. Neurosci. 31(2), 305–328 (2011)
Liu, X., Liu, S.: Codimension-two bifurcation analysis in two-dimensional Hindmarsh–Rose model. Nonlinear Dyn. 67(1), 847–857 (2012)
Huang, C., Sun, W., Zheng, Z., et al.: Hopf bifurcation control of the M–L neuron model with type I. Nonlinear Dyn. 87(2), 755–766 (2017)
Wechselberger, M., Weckesser, W.: Bifurcations of mixed-mode oscillations in a stellate cell model. Physica D 238(16), 1598–1614 (2009)
Desroches, M., Guckenheimer, J., Krauskopf, B., et al.: Mixed-mode oscillations with multiple time scales. SIAM Rev. 54(2), 211–288 (2012)
Feibiao, Z., Shenquan, L., Xiaohan, Z., et al.: Mixed-mode oscillations and bifurcation analysis in a pituitary model. Nonlinear Dyn. 94(2), 807–826 (2018)
Wang, Y., Rubin, J.E.: Multiple timescale mixed bursting dynamics in a respiratory neuron model. J. Comput. Neurosci. 41(3), 245–268 (2016)
Lu, Z., Chen, L., Duan, L.: Bifurcation analysis of mixed bursting in the pre-Bötzinger complex. Appl. Math. Modell. 67, 234–251 (2019)
Ge, M., Jia, Y., Xu, Y., et al.: Mode transition in electrical activities of neuron driven by high and low frequency stimulus in the presence of electromagnetic induction and radiation. Nonlinear Dyn. 91(1), 515–523 (2018)
Sun, X., Li, G.: Synchronization transitions induced by partial time delay in a excitatory-inhibitory coupled neuronal network. Nonlinear Dyn. 89(4), 2509–2520 (2017)
Yoshioka, M.: Cluster synchronization in an ensemble of neurons interacting through chemical synapses. Phys. Rev. E 71(6), 061914 (2005)
Shi, X., Lu, Q.: Complete synchronization of coupled Hindmarsh-Rose neurons with ring structure. Chin. Phys. Lett. 21(9), 1695–1698 (2004)
Mainieri, M.S., Erichsen, R., Brunnet, L.G.: Time evolution of coherent structures in networks of Hindmarch–Rose neurons. Phys. A 354, 663–671 (2005)
Best, J., Borisyuk, A., Rubin, J., et al.: The dynamic range of bursting in a model respiratory pacemaker network. SIAM J. Appl. Dyn. Syst. 4(4), 1107–1139 (2005)
Kenny, A., Plank, M.J., David, T.: Minimal model of calcium dynamics in two heterogeneous coupled cells. Neurocomputing 323, 128–138 (2019)
Yilmaz, E., Ozer, M., Baysal, V., et al.: Autapse-induced multiple coherence resonance in single neurons and neuronal networks. Sci. Rep. 6, 30914 (2016)
Yilmaz, E., Baysal, V., Ozer, M., et al.: Autaptic pacemaker mediated propagation of weak rhythmic activity across small-world neuronal networks. Physica A 444, 538–546 (2016)
Erkan, Y., Sarac, Z., Yilmaz, E.: Effects of astrocyte on weak signal detection performance of Hodgkin–Huxley neuron. Nonlinear Dyn. 95(4), 3411–3421 (2019)
Duan, L., Yuan, D., Chen, X., et al.: Transition mechanisms of bursting in a two-cell network model of the pre-Bötzinger complex. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 25(05), 1550069 (2015)
Rubin, J.E., Krauskopf, B., Osinga, H.M.: Natural extension of fast-slow decomposition for dynamical systems. Phys. Rev. E 97(1), 012215 (2018)
Barreto, E., Cressman, J.R.: Ion concentration dynamics as a mechanism for neuronal bursting. J. Biol. Phys. 37(3), 361–373 (2011)
Lieske, S., Thoby-Brisson, M., Telgkamp, P., et al.: Reconfiguration of the neural network controlling multiple breathing patterns: eupnea, sighs and gasps. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 600–607 (2000)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 11872003), Cultivation Plan for “Yujie” Team of North China University of Technology (No. 107051360019XN137/002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
For \(x\in \{mp,m,h,n,s\}\), the function of \(x_{\infty }(V)\) takes the form \(x_{\infty }(V)=\{1+exp(V-\theta _{x}/\sigma _{x})\}^{-1}\). For \(x\in \{h,n,s\}\), the function of \(\tau _{x}(V)\) takes the form \(\tau _{x}(V)= {\bar{\tau }}_{x}/\cosh [(V-\theta _{x})/2\sigma _{x}]\). The parameter values are shown in Table 1.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, L., Liang, T., Zhao, Y. et al. Multi-time scale dynamics of mixed depolarization block bursting. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 1043–1053 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05744-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-05744-x