Abstract
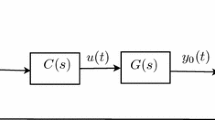
The Wiener model is a case of block-oriented model, which is suitable for modeling a large class of nonlinear systems. It consists of the cascade of two parts, where a linear dynamic part is followed by a static nonlinear part. On the other hand, fractional order models have gained increasing interest over the last decades due to their better representation of some physical phenomena. In this paper, the fractional Wiener system identification is aimed. The polynomial nonlinear fractional state space equations are used to describe the nonlinear model. Thus, the extension of an output error method (Levenberg Marquard algorithm) is developed to estimate the fractional Wiener system. The efficiency of the identification method is evaluated and confirmed by simulation examples.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu, Y.B., Liu, B.L., Zhou, Q., Yang, C.: Recursive extended least squares parameter estimation for Wiener nonlinear systems with moving average noises. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 33(2), 655–664 (2014)
Li, J., Ding, F., Hua, L.: Maximum likelihood Newton recursive and the Newton iterative estimation algorithms for Hammerstein CARAR systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 75, 235–245 (2014)
Mao, Y.W., Ding, F.: Multi-innovation stochastic gradient identification for Ham-merstein controlled autoregressive autoregressive systems based on the filter-ing technique. Nonlinear Dyn. 79(3), 1745–1755 (2015)
Ding, F., Liu, X.M., Liu, M.M.: The recursive least squares identification algorithm for a class of Wiener nonlinear systems. J. Franklin Inst. 353(7), 1518–1526 (2016)
Wills,A., Ljung, L.: Wiener system identification using the maximum likelihood method. In F. Giri and E.W. Bai (eds.), Block-Oriented Nonlinear System Identification, Lecture Notes in Control and Information Science. 404(404). Springer (2010)
Cao, P.F., Luo, X.L.: Soft sensor model derived from wiener model structure: modeling and identification. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 22(5), 538–548 (2014)
Wills, A.G., Schon, T.B., Ljung, L., Ninness, B.: Blind Identification of Wiener models. IFAC Proc. Vol. 44(1), 5597–5602 (2011)
Srinivasan, A., Lakshmi, P.: Wiener Model Based Real-Time Identification and Control of Heat Exchanger Process. J. Autom. Syst. Eng. (2008)
Liu, W., Na, W., Zhu, L., Ma, J., Zhang, Q.J.: A Wiener-type dynamic neural network approach to the modeling of nonlinear microwave devices. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory 65, 2043–2062 (2017)
Kilbas, A.A., Srivastava, H.M., Trujillo, J.J.: Theory and application of fractional differential equations. In: vanMill, J. (ed.) North HollandMathematics Studies. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2006)
Abu Arqub, O.: Numerical solutions for the Robin time-fractional partial differential equations of heat and fluid flows based on the reproducing kernel algorithm. Int. J. Numer. Method H. https://doi.org/10.1108/HFF-07-2016-0278 (2017)
Abu Arqub, O.: Fitted reproducing kernel Hilbert space method for the solutions of some certain classes of time-fractional partial differential equations subject to initial and Neumann boundary conditions. Comput. Math. Appl. 73, 1243–1261 (2017)
Abu Arqub, O., El-Ajou, A., Momani, S.: Constructing and predicting solitary pattern solutions for nonlinear time-fractional dispersive partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 293, 385–399 (2015)
Jalloul, A., Trigeassou, J.-C., Jelassi, K., Melchior, P.: Fractional order modeling of rotor skin effect in induction machines. Nonlinear Dyn. 73, 801–813 (2013)
Machado, J.A.T.: Entropy analysis of integer and fractional dynamical systems. Nonlinear Dyn. 62(12), 371378 (2010)
Machado, J.A.T., Galhano, A.M.S.F.: Fractional order inductive phenomena based on the skin effect. Nonlinear Dyn. 68(12), 107115 (2012)
Machado, J.T.: Accessing complexity from genome information. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17(6), 2237–2243 (2012)
Ionescu, C., Desager, K., De Keyser, R.: Fractional order model parameters for the respiratory input impedance in healthy and in asthmatic children. Comput. Meth. Prog. Bio. 101, 315–323 (2011)
Battaglia, J.L., Le Lay, L., Batsale, J.C., Oustaloup, A., Cois, O.: Heat flow estimate through inverted not integer identification models. Int. J. Therm. Sci. 39(3), 374–389 (2000)
Djouambi, A., Voda, A., Charef, A.: Recursive prediction error identification of fractional order models. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17, 2517–2524 (2011)
Djamah, T., Bettayeb, M., Djennoune, S.: Identification of multivariable fractional order systems. Asian J. Control 15(2), 1–10 (2013)
Zhou, S., Cao, J., Chen, Y.: Genetic algorithm-based identification of fractional-order systems. Entropy 15(5), 1624–1642 (2013)
Mansouri, R., Bettayeb, M., Djamah, T., Djennoune, S.: Vector fitting fractional system identification using particle swarm optimization. Appl. Math. Comput. 206, 510–520 (2008)
Benoit Marand, F., Signac, L., Poinot, T., Trigeassou, J.C.: Identification of non linear fractional systems using continuous time neural networks. IFAC Proc. Volumes 39(11), 402–407 (2006)
Maachou, A., Malti, R., Melchior, P., Battaglia, J.-L., Oustaloup, A., Hay, B.: Nonlinear thermal system identification using fractional Volterra series. Control Eng. Pract. 29, 50–60 (2014)
Liao, Z., Zhu, Z., Liang, S., et al.: Subspace identification for fractional order Hammerstein systems based on instrumental variables. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 10(5), 947953 (2012)
Rahmani, M.R., Farrokhi, M.: Identification of neuro-fractional Hammerstein systems: a hybrid frequency-/time-domain approach. Soft Comput. 1–10 (2017)
Stanislawski, R., Latawiec, KJ., Galek, M., Lukaniszyn, M.: Modeling and identification of a fractional-order discrete-time SISO Laguerre-Wiener system. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Methods and Models in Automation and Robotics (MMAR), Miedzyzdroje, Poland, 165168 (2014)
Kianpour, N., Asad, M.: A novel identification method for fractional-order Wiener systems with PRBS input. In: 4th International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, and Automation (ICCIA), Qazvin, Iran (2016)
Sersour, L., Djamah, T., Bettayeb, M.: Identification of Wiener fractional model using Self-Adaptive Velocity Particle Swarm Optimization. In: 7th International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control (ICMIC), Sousse, Tunisia (2015)
Vanbeylen, L.: A fractional approch to identify Wiener-Hammerstein systems. Automatica 50(3), 903–909 (2014)
Mozyrska, D., Girejko, E., Wyrwas, M.: Comparison of h-difference fractional operators. In: Mitkowski, W., Kacprzyk, J., Baranowski, J. (eds.) Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, pp. 251–256. Springer, New York (2013)
Dzielinski, A., Sierociuk,D.: Stability of discrete fractional order state-space systems. J. Vib. Control 14 (09–10):1543–1556 (2008)
Paduart, J., Lauwers, L., Pintelon, R., Schoukens, J.: Identification of a Wiener Hammerstein system using the polynomial nonlinear state space approach. Control Eng. Pract. 20, 1133–1139 (2012)
Van Mulders, A., Schoukensa, J., Volckaert, M., Diehl, M.: Two nonlinear optimization methods for black box identification compared. Automatica 46, 1675–1681 (2010)
Djamah, T., Mansouri, R., Djennoune, S., Bettayeb, M.: Heat transfer modeling and identification using fractional order state space models. J. Eur. Des Syst. Autom. (JESA) 42, 939–951 (2008)
Marquardt, D.W.: An algorithm for least squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 11(2), 413–441 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sersour, L., Djamah, T. & Bettayeb, M. Nonlinear system identification of fractional Wiener models. Nonlinear Dyn 92, 1493–1505 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4142-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-018-4142-0