Abstract
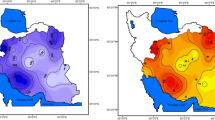
Yunnan is one of the provinces which had been frequently and heavily affected by drought disasters in China. Recently, large severe droughts struck Yunnan, caused considerable social, economic and ecological losses. A risk assessment of meteorological drought for Yunnan province is provided in this study. Based on the daily meteorological data of 29 stations during 1960–2010, duration and severity as two major drought characteristics, defined by the runs and the composite meteorological drought index, are abstracted from the observed drought events. Three bivariate Archimedean copulas are employed to construct the joint distributions of the drought characteristics. Based on the error analysis and tail dependence coefficient, the Gumbel–Hougaard copula is selected to analyze spatial distributions of the joint return periods of drought. The results indicate that a high risk is observed in the middle parts and the northeast parts of Yunnan province, while a relative lower drought risk is observed in the northwest of Yunnan province. The probabilistic properties can provide useful information for water resources planning and management.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capéraà P, Fougères A-L, Genest C (1997) A nonparametric estimation procedure for bivariate extreme value copulas. Biometrika 84:567–577
Demarta S, McNeil AJ (2005) The t copula and related copulas. Int Stat Rev 73:111–129
Ezzine H, Bouziane A, Ouazar D (2014) Seasonal comparisons of meteorological and agricultural drought indices in Morocco using open short time-series data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 26:36–48
Fan H, Hu J, He D (2013) Trends in precipitation over the low latitude highlands of Yunnan, China. J Geog Sci 23:1107–1122
Feng R, Zhang Y, Yu W, Hu W, Wu J, Ji R, Wang H, Zhao X (2013) Analysis of the relationship between the spectral characteristics of maize canopy and leaf area index under drought stress. Acta Ecol Sinica 33:301–307
Frahm G, Junker M, Schmidt R (2005) Estimating the tail-dependence coefficient: properties and pitfalls. Insur Math Econ 37:80–100
Frank J, Masse J (1951) The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for goodness of fit. J Am Stat Assoc 46:68–78
Fu G, Butler D (2014) Copula-based frequency analysis of overflow and flooding in urban drainage systems. J Hydrol 510:49–58
Genest C, Mackay J (1986) The joy of copulas: bivariate distributions with uniform marginals. Am Stat 40:280–283
Genest C, Rivest L-P (1993) Statistical inference procedures for bivariate Archimedean copulas. J Am Stat Assoc 88:1034–1043
Gocic M, Trajkovic S (2014) Spatiotemporal characteristics of drought in Serbia. J Hydrol 510:110–123
Heim RR (2002) A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1149–1165
Huang H, Li Q, Gao Y, Zhong A, Chen H, Li J (2011) Diagnosis of the severe drought in Autumn/Winer 2009-2010 in Yunnan Province. Trop Geogr 31:28–33 (in Chinese)
Keyantash J, Dracup JA (2002) The quantification of drought: an evaluation of drought indices. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 83:1167–1180
Kirono DGC, Kent DM, Hennessy KJ, Mpelasoka F (2011) Characteristics of Australian droughts under enhanced greenhouse conditions: results from 14 global climate models. J Arid Environ 75:566–575
Klein Tank A, Können G (2003) Trends in indices of daily temperature and precipitation extremes in Europe, 1946-99. J Clim 16:3665–3680
Li S, Liu R, Shi L, Ma Z (2009) Analysis on drought characteristic of Henan in resent 40 years based on meteorological drought composite index. J Arid Meteorol 27:97–102 (in Chinese)
Li J, Lu Z, Lin R, Liu X (2010) Variation characteristics of meteorological drought in Liaoning Province between 1961 and 2008. Meteorol Environ Res 1:50–53
Li Y, Xiaodong Z, Fan LU, Jing MA (2012) Analysis of drought evolvement characteristics based on standardized precipitation index in the Huaihe River Basin. Procedia Eng 28:434–437
Liu C-L, Zhang Q, Singh VP, Cui Y (2011) Copula-based evaluations of drought variations in Guangdong, South China. Nat Hazards 59:1533–1546
Liu K, Li R, Liu Z, Liu M (2012) Characteristics and variations of drought in Hubei based on comprehensive meteorological drought index. Resour Environ Yangtze Basin 21:1274–1280 (in Chinese)
Lu F, Wang H, Yan D, Zhang D, Xiao W (2013) Application of profile likelihood function to the uncertainty analysis of hydrometeorological extreme inference. Sci China Technol Sci 56:3151–3160
Lü J, Ju J, Ren J, Gan W (2012) The influence of the Madden-Julian Oscillation activity anomalies on Yunnan’s extreme drought of 2009–2010. Sci China Earth Sci 55:98–112
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. Proceedings of the 8th conference on applied climatology. American Meteorological Society, Boston, MA, pp 179–183
Mirabbasi R, Fakheri-Fard A, Dinpashoh Y (2012) Bivariate drought frequency analysis using the copula method. Theoret Appl Climatol 108:191–206
Mishra AK, Desai VR (2005) Drought forecasting using stochastic models. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 19:326–339
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2011) Drought modeling: a review. J Hydrol 403:157–175
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological drought. US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau Washington, DC
Peng G, Liu Y, Zhang Y (2009) Research on characteristics of drought and climatic trend in Yunnan Province. J Catastrophol 24:40–44 (in Chinese)
Qian W, Shan X, Zhu Y (2011) Ranking regional drought events in China for 1960–2009. Adv Atmos Sci 28:310–321
Reddy MJ, Ganguli P (2013) Spatio-temporal analysis and derivation of copula-based intensity–area–frequency curves for droughts in western Rajasthan (India). Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 27:1975–1989
Salas J, Fernandez B (1993) Models for data generation in hydrology: Univariate Techniques. In: Marco JB, Harboe R, Salas JD (eds) Stochastic hydrology and its use in water resources systems simulation and optimization. Springer, Netherlands, pp 47–73
Salvadori G, De Michele C (2004) Frequency analysis via copulas: theoretical aspects and applications to hydrological events. Water Resour Res 40:W12511
Salvadori G, De Michele C, Durante F (2011) On the return period and design in a multivariate framework. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 15:3293–3305
Shiau J (2006) Fitting drought duration and severity with two-dimensional copulas. Water Resour Manage 20:795–815
Shiau J-T, Shen HW (2001) Recurrence analysis of hydrologic droughts of differing severity. J Water Res Plan Manag 127:30–40
Sklar M (1959) Fonctions de répartition à n dimensions et leurs marges. Université Paris 8
Sklar A (1973) Random variables, joint distribution functions, and copulas. Kybernetika 9:449–460
Su B, Jiang T, Jin W (2006) Recent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Theoret Appl Climatol 83:139–151
Tallaksen LM, Hisdal H, Lanen HAJV (2009) Space–time modelling of catchment scale drought characteristics. J Hydrol 375:363–372
Thornthwaite CW (1948) An approach toward a rational classification of climate. Geogr Rev 38:55–94
Vandenberghe S, Verhoest NEC, Onof C, De Baets B (2011) A comparative copula-based bivariate frequency analysis of observed and simulated storm events: a case study on Bartlett-Lewis modeled rainfall. Water Resour Res 47:W07529
Wilhite D (2000) Drought as a natural hazard: concepts and definitions. In: Wilhite DA (ed) Drought: global assessment. Routledge, pp 3–18
Willmott CJ, Ackleson SG, Davis RE, Feddema JJ, Klink KM, Legates DR, O’Donnell J, Rowe CM (1985) Statistics for the evaluation and comparison of models. J Geophys Res Oceans (1978–2012) 90:8995–9005
Yevjevich V, Ingenieur J, Yevjevich V, Ingénieur Y, Yevjevich V, Engineer Y (1967) An objective approach to definitions and investigations of continental hydrologic droughts. Colorado State University Fort Collins
Yu W, Shao M, Ren M, Zhou H, Jiang Z, Li D (2013) Analysis on spatial and temporal characteristics drought of Yunnan Province. Acta Ecol Sinica 33:317–324
Yusof F, Hui-Mean F, Suhaila J, Yusof Z (2013) Characterisation of drought properties with bivariate copula analysis. Water Resour Manage 27:4183–4207
Zhang Q, Zou X, Xiao F (2006) Classification of meteorological drought. Standards Press of China, Beijing
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP, Chen X (2012a) Copula-based risk evaluation of droughts across the Pearl River basin, China. Theoret Appl Climatol 111:119–131
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP, Chen X (2012b) Copula-based risk evaluation of hydrological droughts in the East River basin, China. Stoch Env Res Risk Assess 27:1397–1406
Zhang Q, Xiao M, Singh VP, Li J (2012c) Regionalization and spatial changing properties of droughts across the Pearl River basin, China. J Hydrol 472–473:355–366
Zhang T, Zhang B, Liu X, Li X, Zhao Y, Jin S (2012d) Trend analysis of the variation of meteorological drought in loess plateau of Gansu province based on comprehensive meteorological drought index. J Glaciol Geocryol 34:1076–1083 (in Chinese)
Zhang T, Zhang B, Wang Y, Liu X, An M, Zhang J (2013a) Drought characteristics in the Shiyang river basin during the recent 50 years based on a composite index. Acta Ecol Sinica 33:975–984 (in Chinese)
Zhang W, Zheng J, Ren J (2013b) Climate characteristics of extreme drought events in Yunnan. J Catastrophol 28:59–64 (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
The climate data are provided by the National Meteorological Information Center of China. This study is jointly funded by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2013CB036406, 2010CB951102) and the Innovation Research Group Foundation Program of Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51109224) and major program foundation of the Chinese academy of sciences (Grant No. 2012-ZD-13). Last but not the least, many thanks are given to two anonymous reviewers for their valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, DD., Yan, DH., Lu, F. et al. Copula-based risk assessment of drought in Yunnan province, China. Nat Hazards 75, 2199–2220 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1419-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-014-1419-6