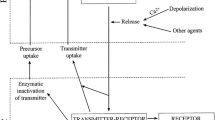
Abstract
Synapsins are a multigene family of neuron-specific phosphoproteins and comprise the most abundant synaptic vesicle proteins. They have been proposed to tether synaptic vesicles to each other to maintain a reserve pool in the vicinity of the active zone. Such a role is supported by the observation that disruption of synapsin function leads to a depletion of the reserve pool of vesicles and an increase in synaptic depression. However, other functions for synapsins have been proposed as well, and there currently exists no coherent picture of how these abundant proteins modulate synaptic transmission. Here, we discuss novel insights into how synapsins may regulate neurotransmitter release.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustine, G. J., Charlton, M. P., and Smith, S. J. (1985). Calcium entry and transmitter release at voltage-clamped nerve terminals of squid. J. Physiol. 367, 163–181
Bloom, O., Evergren, E., Tomilin, N., Kjaerulff, O., Low, P., Brodin, L., Pieribone, V. A., Greengard, P., and Shupliakov, O. (2003). Colocalization of synapsin and actin during synaptic vesicle recycling. J. Cell Biol. 161, 737–747
Browning, M. D., Huang, C. K., and Greengard, P. (1987). Similarities between protein IIIa and protein IIIb, two prominent synaptic vesicle-associated phosphoproteins. J. Neurosci. 7, 847–856
Bustos, R., Kolen, E. R., Braiterman, L., Baines, A. J., Gorelick, F. S., and Hubbard, A. L. (2001). Synapsin I is expressed in epithelial cells: Localization to a unique trans-Golgi compartment. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3695–3704
Ceccarelli, B., Hurlbut, W. P., and Mauro, A. (1973). Turnover of transmitter and synaptic vesicles at the frog neuromuscular junction. J. Cell Biol. 57, 499–524
Chandra, S., Gallardo, G., Fernandez-Chacón, R., Schlüter, O. M., and Südhof, T. C. (2005). Alpha-synuclein cooperates with CSPalpha in preventing neurodegeneration. Cell 123, 383–396
Chi, P., Greengard, P., and Ryan, T. A. (2001). Synapsin dispersion and reclustering during synaptic activity. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 1187–1193
Chi, P., Greengard, P., and Ryan, T. A. (2003). Synaptic vesicle mobilization is regulated by distinct synapsin I phosphorylation pathways at different frequencies. Neuron 38, 69–78
Czernik, A. J., Pang, D. T., and Greengard, P. (1987). Amino acid sequences surrounding the cAMP-dependent and calcium/calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation sites in rat and bovine synapsin I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 7518–7522
Daly, C., and Ziff, E. B. (1997). Post-transcriptional regulation of synaptic vesicle protein expression and the developmental control of synaptic vesicle formation. J. Neurosci. 17, 2365–2375
De Camilli, P., Harris, S. M. Jr., Huttner, W. B., and Greengard, P. (1983). Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J. Cell Biol. 96, 1355–1373
Duncan, R. R., Greaves, J, Wiegand, U. K., Matskevich, I., Bodammer, G., Apps, D. K., Shipston, M. J., and Chow, R. H. (2003). Functional and spatial segregation of secretory vesicle pools according to vesicle age. Nature 422, 176–180
Fernandez-Chacón, R., Wolfel, M., Nishimune, H., Tabares, L., Schmitz, F., Castellano-Munoz, M., Rosenmund, C., Montesinos, M. L., Sanes, J. R., Schneggenburger, R., and Südhof, T. C. (2004). The synaptic vesicle protein CSP alpha prevents presynaptic degeneration. Neuron 42, 237–251
Firestone, J., and Browning, M. (1992). Synapsin II phosphorylation and catecholamine release in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: Additive effects of histamine and nicotine. J. Neurochem. 58, 441–447
Gitler, D., Takagishi, Y., Feng, J., Ren, Y., Rodriguiz, R. M., Wetsel, W. C., Greengard, P., and Augustine, G. J. (2004). Different presynaptic roles of synapsins at excitatory and inhibitory synapses. J. Neurosci. 24, 11368–11380
Greengard, P., Valtorta, F., Czernik, A. J., and Benfenati, F. (1993). Synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins and regulation of synaptic function. Science 259, 780–785
Han, H. Q., Nichols, R. A., Rubin, M. R., Bähler, M., and Greengard, P. (1991). Induction of formation of presynaptic terminals in neuroblastoma cells by synapsin IIb. Nature 349, 697–700
Harata, N., Pyle, J. L., Aravanis, A. M., Mozhayeva, M., Kavalali, E. T., and Tsien, R. W. (2001). Limited numbers of recycling vesicles in small CNS nerve terminals: implications for neural signaling and vesicular cycling. Trends. Neurosci. 24, 637–643
Haycock, J. W., Greengard, P., and Browning, M. D. (1988). Cholinergic regulation of protein III phosphorylation in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J. Neurosci. 8, 3233–3239
Heuser, J. E., and Reese, T. S. (1973). Evidence for recycling of synaptic vesicle membrane during transmitter release at the frog neuromuscular function. J. Cell Biol. 57, 315–344
Hilfiker, S., Schweizer, F. E., Kao, H. T., Czernik, A. J., Greengard, P., and Augustine, G. J. (1998). Two sites of action for synapsin domain E in regulating neurotransmitter release. Nat. Neurosci. 1, 29–35
Hilfiker, S., Pieribone, V. A., Czernik, A. J., Kao, H. T., Augustine, G. J., and Greengard, P. (1999). Synapsins as regulators of neurotransmitter release. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 354, 269–279
Hirokawa, N., Sobue, K., Kanda, K., Harada, A., and Yorifuji, H. (1989). The cytoskeletal architecture of the presynaptic terminal and molecular structure of synapsin I. J. Cell Biol. 108, 111–126
Hosaka, M., and Südhof, T. C. (1998). Synapsin III, a novel synapsin with an unusual regulation by Ca2+. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 13371–13374
Hosaka, M., and Südhof, T. C. (1999a). Homo- and heterodimerization of synapsins. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16747–16753
Hosaka, M, Hammer, R. E., and Südhof, T. C. (1999b). A phospho-switch controls the dynamic association of synapsins with synaptic vesicles. Neuron 24, 377–387
Humeau, Y., Doussau, F., Vitiello, F., Greengard, P., Benfenati, F., and Poulain, B. (2001). Synapsin controls both reserve and releasable synaptic vesicle pools during neuronal activity and short-term plasticity in Aplysia. J. Neurosci. 21, 4195–4206
Jovanovic, J. N., Benfenati, F., Siow, Y. L., Sihra, T. S., Sanghera, J. S., Pelech, S. L., Greengard, P., and Czernik, A. J. (1996). Neurotrophins stimulate phosphorylation of synapsin I by MAP kinase and regulate synapsin I-actin interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 3679–3683
Jovanovic, J. N., Sihra, T. S., Nairn, A. C., Hemmings, H. C. Jr., Greengard, P., and Czernik, A. J. (2001). Opposing changes in phosphorylation of specific sites in synapsin I during Ca2+-dependent glutamate release in isolated nerve terminals. J. Neurosci. 21, 7944–7953
Katz, B. (1969). The Release of Neural Transmitter Substances. Liverpool, Liverpool Univ. Press
Kao, H. T., Porton, B., Czernik, A. J., Feng, J., Yiu, G., Häring, M., Benfenati, F., and Greengard, P. (1998). A third member of the synapsin gene family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4667–4672
Kao, H. T., Porton, B., Hilfiker, S., Stefani, G., DeSalle, R., Pieribone, V. A., and Greengard, P. (1999). Molecular evolution of the synapsin gene family. J. Exp. Zool. 285, 360–377
Liu, X. B., and Jones, E. G. (1996). Localization of alpha type II calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase at glutamatergic but not gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAergic) synapses in thalamus and cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 7332–7336
Matsubara, M., Kusubata, M., Ishiguro, K., Uchida, T., Titani, K., and Taniguchi, H. (1996). Site-specific phosphorylation of synapsin I by mitogen-activated protein kinase and Cdk5 and its effects on physiological functions. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 21108–21113
Menegon, A, Bonanomi, D., Albertinazzi, C., Lotti, F., Ferrari, G., Kao, H. T., Benfenati, F., Baldelli, P., and Valtorta, F. (2006). Protein kinase A-mediated synapsin I phosphorylation is a central modulator of Ca2+-dependent synaptic activity. J. Neurosci. 26, 11670–11681
Moulder, K. L., and Mennerick, S. (2005). Reluctant vesicles contribute to the total readily releasable pool in glutamatergic hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 25, 3842–3850
Moulder, K. L., and Mennerick, S. (2006). Synaptic vesicles: turning reluctance into action. Neuroscientist 12, 11–15
Nakata, T., and Hirokawa, N. (1992). Organization of cortical cytoskeleton of cultured chromaffin cells and involvement in secretion as revealed by quick-freeze, deep-etching, and double-label immunoelectron microscopy. J. Neurosci. 12, 2186–2197
Navone, F., Greengard, P., and De Camilli, P. (1984). Synapsin I in nerve terminals: selective association with small synaptic vesicles. Science 226, 1209–1211
Pieribone, V. A., Shupliakov, O., Brodin, S., Hilfiker-Rothenfluh, S., Czernik, A. J., and Greenggard, P. (1995). Distinct pools of synaptic vesicles in neurotransmitter release. Nature 375, 493–497
Rizzoli, S. O., and Betz, W. J. (2004). The structural organization of the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. Science 303, 2037–2039
Rosahl, T. W., Spillane, E., Missler, M., Herz, J., Selig, D. K., Wolff, J. R., Hammer, R. E., Malenka, R. C., and Südhof, T. C. (1995). Essential functions of synapsins I and II in synaptic vesicle regulation. Nature 375, 488–493
Sankaranarayanan, S., Atluri, P. P., and Ryan, T. A. (2003). Actin has a molecular scaffolding, not propulsive, role in presynaptic function. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 127–135
Schiebler, W., Jahn, R., Doucet, J. P., Rothlein, J., and Greengard, P. (1986). Characterization of synapsin I binding to small synaptic vesicles. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8383–8390
Schikorski, T., and Stevens, C. F. (2001). Morphological correlates of functionally defined synaptic vesicle populations. Nat. Neurosci. 4, 391–395
Schweizer, F. E., and Ryan, T. A. (2006). The synaptic vesicle: cycle of exocytosis and endocytosis. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 16, 298–304
Südhof, T. C., Czernik, A. J., Kao, H. T., Takei, K., Johnston, P. A., Horiuchi, A., Kanazir, S. D., Wagner, M. A., Perin, M. S., de Camilli, P., and Greengard, P. (1989). Synapsins: mosaic of shared and individual domains in a family of synaptic vesicle phosphoproteins. Science 245, 1474–1480
Südhof, T. C. (2004). The synaptic vesicle cycle. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 509–547
Sugiyama, T., Shinoe, T., Ito, Y., Misawa, H., Tojima, T., Ito, E., and Yoshioka, T. (2000). A novel function of synapsin II in neurotransmitter release. Mol. Brain Res. 85, 133–143
Sun, J., Bronk, P., Liu, X., Han, W., and Südhof, T. C. (2006). Synapsins regulate use-dependent synaptic plasticity in the calyx of Held by a Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 2880–2885
Tao-Cheng, J. H., Dosemeci, A., Winters, C. A., Reese, T. S. (2007). Changes in the distribution of calcium calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II at the presynaptic bouton after depolarization. Brain Cell Biology.
Terada, S., Tsujimoto, T., Takei, Y., Takahashi, T., and Hirokawa, N. (1999). Impairment of inhibitory synaptic transmission in mice lacking synapsin I. J. Cell Biol. 145, 1039–1048
Torri-Tarelli, F., Villa, A., Valtorta, F., De Camilli, P., and Greengard, P. (1990). Redistribution of synaptophysin and synapsin I during alpha-latrotoxin-induced release of neurotransmitter at the neuromuscular junction. J. Cell Biol. 110, 449–459
Valtorta, F., Iezzi, N., Benfenati, F., Lu, B., Poo, M. M., and Greengard, P. (1995). Accelerated structural maturation induced by synapsin I at developing neuromuscular synapses of Xenopus laevis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 7, 261–270
Venton, B. J., Seipel, A. T., Phillips, P. E. M., Wetsel, W. C., Gitler, D., Greengard, P, Augustine, G. J., and Wightman, R. M. (2006). Cocaine increases dopamine release by mobilization of a synapsin-dependent reserve pool. J. Neurosci. 26, 3206–3209
Villanueva, M., Augustine, G. J., and Wightman, R. M. (2007). Synapsin II negatively regulates catecholamine release. Brain Cell Biology 35(2/3), 125–136
Acknowledgments
Work in the laboratory is supported by a grant from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (MEC). SH is a Ramón y Cajal Fellow.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fdez, E., Hilfiker, S. Vesicle pools and synapsins: New insights into old enigmas. Brain Cell Bio 35, 107–115 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-007-9013-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11068-007-9013-4