Abstract
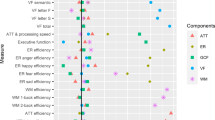
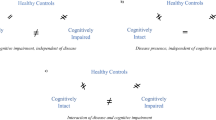
Considerable cognitive heterogeneity is present within the schizophrenia spectrum disorder (SSD) population. Several subgroups characterised by more homogenous cognitive profiles have been identified. It is not yet clear however, whether these subgroups represent different points along a continuum of cognitive symptom severity, or whether they reflect unique profiles of the disorder. One way to determine this is by comparing subgroups on their non-cognitive characteristics. The aim of the present review was to systematically summarise our current understanding of the non-cognitive features of the cognitive subgroups of schizophrenia spectrum disorder (SSD). Thirty-five relevant studies were identified from January 1980 to March 2020. Cognitive subgroups were consistently compared on age, sex, education, age of illness onset, illness duration, positive, negative and disorganised symptoms, depression and psychosocial functioning. It was revealed that subgroups were consistently distinguished by education, negative symptom severity and degree of functional impairment; with subgroups characterised by worse cognitive functioning performing/rated worse on these characteristics. The lack of consistent subgroup differences for the majority of the non-cognitive characteristics provides partial support for the notion that cognitive subgrouping in SSD is not simply reflecting a rehash of previously identified clinical subtypes. However, as subgroups were consistently distinguished by three characteristics known to be associated with cognition, our understanding of the extent to which the cognitive subgrouping approach is representing separate subtypes versus subdivisions along a continuum of symptom severity is still not definitive.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ammari, N., Heinrichs, R. W., & Miles, A. A. (2010). An investigation of 3 neurocognitive subtypes in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 121, 32–38.
Ammari, N., Walter Heinrichs, R., Pinnock, F., Miles, A. A., & Muharib, e. & Vaz, S. M. (2014). Preserved, deteriorated, and premorbidly impaired patterns of intellectual ability in schizophrenia. Neuropsychology, 28, 353–358.
Bobes, J., Arango, C., Garcia-Garcia, M. & Rejas, J. (2010). Prevalence of negative symptoms in outpatients with schizophrenia spectrum disorders treated with antipsychotics in routine clinical practice: findings from the CLAMORS study. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Bowie, C. R., Leung, W. W., Reichenberg, A., McClure, M. M., Patterson, T. L., Heaton, R. K., & Harvey, P. D. (2008). Predicting schizophrenia patients’ real-world behavior with specific neuropsychological and functional capacity measures. Biological Psychiatry, 63, 505–511.
Bowie, C. R., Reichenberg, A., Patterson, T. L., Heaton, R. K., & Harvey, P. D. (2006). Determinants of real-world functional performance in schizophrenia subjects: Correlations with cognition, functional capacity, and symptoms. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 163, 418–425.
Bowie, C. R., Reichenberg, A., Rieckmann, N., Parrella, M., White, L., & Harvey, P. D. (2004). Stability and functional correlates of memory-based classification in older schizophrenia patients. The American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 12, 376–386.
Butler, R. W., Jenkins, M. A., Sprock, J., & Braff, D. L. (1992). Wisconsin Card Sorting Test deficits in chronic paranoid schizophrneia – Evidence for a realatively discrete subgroup. Schizophrenia Research, 7, 169–176.
Carruthers, S. P., Gurvich, C. T., Meyer, D., Bousman, C., Everall, I. P., Neill, E., Pantelis, C., Sumner, P. J., Tan, E. J., & Thomas, E. H. (2019a). Exploring heterogeneity on the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: A cluster analytical investigation. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 25, 750–760.
Carruthers, S. P., Gurvich, C. T., & Rossell, S. L. (2015). The muscarinic system, cognition and schizophrenia. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 55, 393–402.
Carruthers, S. P., Van Rheenen, T. E., Gurvich, C., Sumner, P. J., & Rossell, S. L. (2019b). Characterising the structure of cognitive hetereogenity in schizophrenia spectrum disorder: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 107, 252–278.
Choi, K.-H., Wykes, T., & Kurtz, M. M. (2013). Adjunctive pharmacotherapy for cognitive deficits in schizophrenia: Meta-analytical investigation of efficacy. British Journal of Psychiatry, 203, 172–178.
Clementz, B. A., Sweeney, J. A., Hamm, J. P., Ivleva, E. I., Ethridge, L. E., Pearlson, G. D., Keshavan, M. S., & Tamminga, C. A. (2016). Identification of distinct psychosis biotypes using brain-based biomarkers. American Journal of Psychiatry, 173, 373-384.
Cobia, D. J., Csernansky, J. G., & Wang, L. (2011). Cortical thickness in neuropsychologically near-normal schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 133, 68-76.
Czepielewski, L. S., Wang, L., Gama, C. S., & Barch, D. M. (2017). The relationship of intellectual functioning and cognitive performance to brain structure in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 43, 355–364.
Dawes, S. E., Jeste, D. V., & Palmer, B. W. (2011). Cognitive profiles in persons with chronic schizophrenia. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 33, 929–936.
de Gracia Dominguez, M., Viechtbauer, W., Simons, C. J. P., van Os, J., & Krabbendam, L. (2009). Are psychotic psychopathology and neurocognition orthogonal? A systematic review of their associations. Psychological Bulletin, 135, 157–171.
DeQuardo, J. R., Goldman, R. S., Tandon, R., McGrath-Giroux, M., & Kim, L. (1995). Comparison of indices of premorbid function in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 15, 283–290.
Fett, A. K. J., Viechtbauer, W., Dominguez, M. D. G., Penn, D. L., van Os, J., & Krabbendam, L. (2011). The relationship between neurocognition and social cognition with functional outcomes in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35, 573–588.
Fioravanti, M., Carlone, O., Vitale, B., Cinti, M. E., & Clare, L. (2005). A meta-analysis of cognitive deficits in adults with a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychology Review, 15, 73–95.
Foussias, G., & Remington, G. (2010). Negative symptoms in schizophrenia: Avolition and Occam;s Razor. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 36, 359–369.
Fusar-Poli, P., Papanastasiou, E., Stahl, D., Rocchetti, M., Carpenter, W., Shergill, S., & McGuire, P. (2015). Treatments of negative symptoms in schizophrenia: Meta-analysis of 168 randomized placebo-controlled trials. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 41, 892–899.
Geisler, D., Walton, E., Naylor, M., Roessner, V., Lim, K. O., Schulz, S. C., Gollub, R. L., Calhoun, V. D., Sponheim, S. R. & Ehrlich, S. (2015). Brain structure and function correlates of cognitive subtypes in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 234, 74–83.
Green, M. F., Horan, W. P., & Lee, J. (2019a). Nonsocial and social cognition in schizophrenia: Current evidence and future directions. World Psychiatr., 18, 146–161.
Green, M. J., Cairns, M. J., Wu, J., Dragovic, M., Jablensky, A., Tooney, P. A., Scott, R. J., Carr, V. J. & Australian Schizophrenia Research Bank. (2013). Genome-wide supported variant MIR137 and severe negative symptoms predict membership of an impaired cognitive subtype of schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatr., 18, 774–780.
Green, M. J., Girshkin, L., Kremerskothen, K., Watkeys, O. & Quidé, Y. (2019b). A systematic review of studies reporting data-driven cognitive subtypes across the psychosis spectrum. Neuropsychology Review, 1–15.
Guimond, S., Chakravarty, M. M., Bergeron-Gagnon, L., Patel, R. & Lepage, M. (2016). Verbal memory impairments in schizophrenia associated with cortical thinning. NeuroImage: Clinical, 11, 20–29.
Halverson, T. F., Orleans-Pobee, M., Merritt, C., Sheeran, P., Fett, A. K., & Penn, D. L. (2019). Pathways to functional outcomes in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: Meta-analysis of social cognitive and neurocognitive predictors. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 105, 212–219.
Heinrichs, R. W., Miles, A. A., Smith, D., Zargarian, T., Vaz, S. M., Goldberg, J. O., & Ammari, N. (2008). Cognitive, clinical, and functional characteristics of verbally superior schizophrenia patients. Neuropsychol., 22, 321–328.
Heinrichs, R. W., Parlar, M., & Pinnock, F. (2017). Normal-Range Verbal-Declarative Memory in Schizophrenia. Neuropsychology, 31, 778–786.
Heinrichs, R. W., Pinnock, F., Muharib, E., Hartman, L., Goldberg, J. & McDermid Vaz, S. (2015). Neurocognitive normality in schizophrenia revisited. Schizophrenia Research: Cognition, 2, 227–232.
Henry, J. D., & Crawford, J. R. (2005). A meta-analytic review of verbal fluency deficits in schizophrenia relative to other neurocognitive deficits. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 10, 1–33.
Hill, S. K., Ragland, J. D., Gur, R. C., & Gur, R. E. (2002). Neuropsychological profiles delineate distinct profiles of schizophrenia, an interaction between memory and executive function, and uneven distribution of clinical subtypes. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 24, 765–780.
Hovington, C. L., & Lepage, M. (2014). Neurocognition and neuroimaging of persistent negative symptoms of schizophrenia. Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics, 12, 53–69.
Karantonis, J. A., Carruthers, S. P., Burdick, K. E., Pantelis, C., Green, M. F., Rossell, S., Hughes, M., Cropley, V. & Van Rheenen, T. E. (2020a). Brain morphological characteristics of cognitive subgroups of schizophrenia-spectrum disorders and bipolar disorder: A systematic review with narrative synthesis. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Karantonis, J. A., Rossell, S., Carruthers, S. P., Sumner, P., Hughes, M., Green, M. F., Pantelis, C., Burdick, K. E., Cropley, V. & Van Rheenen, T. E. (2020b). Brain morphology does not clearly map to cognition in individuals on the bipolar-schizophrenia-spectrum: A cross diagnostic cognitive subgroups study. Manuscript submitted for publication.
Karantonis, J. A., Rossell, S. L., Carruthers, S. P., Sumner, P., Hughes, M., Green, M. J., Pantelis, C., Burdick, K. E., Cropley, V., & Van Rheenen, T. E. (2020c). Cognitive validation of cross-diagnostic cognitive subgroups on the schizophrenia-bipolar spectrum. Journal of Affective Disorders, 266, 710–721.
Keefe, R. S. E., Eesley, C. E., & Poe, M. P. (2005). Defining a cognitive function decrement in schizophrenia. Biological Psychiatry, 57, 688–691.
Kremen, W. S., Seidman, L. J., Faraone, S. V., Toomey, R., & Tsuang, M. T. (2000). The paradox of normal neuropsychological function in schizophrenia. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 109, 743.
Kremen, W. S., Seidman, L. J., Faraone, S. V., & Tsuang, M. T. (2001). Intelligence quotient and neuropsychological profiles in patients with schizophrenia and in normal volunteers. Biological Psychiatry, 50, 453-462.
Kremen, W. S., Seidman, L. J., Faraone, S. V., & Tsuang, M. T. (2008). IQ decline in cross-sectional studies of schizophrenia: Methodology and interpretation. Psychiatry Research, 158, 181–194.
Le Carret, N., Lafont, S., Letenneur, L., Dartigues, J. F., Mayo, W., & Fabrigoule, C. (2003). The effect of education on cognitive performances and its implication for the constitution of the cognitive reserve. Developmental Neuropsychology, 23, 317–337.
Lewandowski, K. E., Baker, J. T., McCarthy, J. M., Norris, L. A., & Öngür, D. (2018). Reproducibility of cognitive profiles in psychosis using cluster analysis. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 24, 382–390.
Liu, C. M., Fann, C. S., Chen, C. Y., Liu, Y. L., Oyang, Y. J., Yang, W. C., Chang, C. C., Wen, C. C., Chen, W. J., Hwang, T. J., Hsieh, M. H., Liu, C. C., Faraone, S. V., Tsuang, M. T., & Hwu, H. G. (2011). ANXA7, PPP3CB, DNAJC9, and ZMYND17 genes at chromosome 10q22 associated with the subgroup of schizophrenia with deficits in attention and executive function. Biological Psychiatry, 70, 51–58.
MacCabe, J. H., Brébion, G., Reichenberg, A., Ganguly, T., McKenna, P., Murray, R. M., & David, A. S. (2012). Superior intellectual ability in schizophrenia: Neuropsychological characteristics. Neuropsychol., 26, 181–190.
Marriott, M. E., & Care, E. (2004). Fluid and crystallised intelligence and their relationship to school outcome. Australian Journal of Educational and Developmental Psychology, 19, 97–108.
McDermid Vaz, S., & Heinrichs, R. W. (2006). Stability and validity of memory-based subtypes of schizophrenia. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12, 782–791.
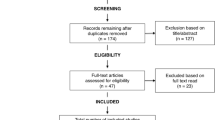
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., Altman, D., Antes, G., Atkins, D., Barbour, V., Barrowman, N., Berlin, J. A., Clark, J., Clarke, M., Cook, D., D'Amico, R., Deeks, J. J., Devereaux, P. J., Dickersin, K., Egger, M., Ernst, E., Gøtzsche, P. C., Grimshaw, J., Guyatt, G., Higgins, J., Ioannidis, J. P. A., Kleijnen, J., Lang, T., Magrini, N., McNamee, D., Moja, L., Mulrow, C., Napoli, M., Oxman, A., Pham, B., Rennie, D., Sampson, M., Schulz, K. F., Shekelle, P. G., Tovey, D., & Tugwell, P. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6
Muharib, E., Heinrichs, R. W., Miles, A., Pinnock, F., Vaz, S. M., & Ammari, N. (2014). Community outcome in cognitively normal schizophrenia patients. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 20, 805–811.
Ortiz-Gil, J., Pomarol-Clotet, E., Salvador, R., Canales-Rodríguez, E. J., Sarró, S., Gomar, J. J., Guerrero, A., Sans-Sansa, B., Capdevila, A., Junqué, C., & McKenna, P. J. (2011). Neural correlates of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. British Journal of Psychiatry, 199, 202–210.
Palmer, B. W., Heaton, R. K., Paulsen, J. S., Kuck, J., Braff, D., Harris, M. J., Zisook, S., & Jeste, D. V. (1997). Is it possible to be schizophrenic yet neuropsychologically normal? Neuropsychology, 11, 437-446.
Potter, A. I., & Nestor, P. G. (2010). IQ subtypes in schizophrenia: Distinct symptom and neuropsychological profiles. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 198, 580–585.
Reser, M. P., Slikboer, R., & Rossell, S. L. (2019). A systematic review of factors that influence the efficacy of cognitive remediation therapy in schizophrenia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry, 53, 624–641.
Rüsch, N., Spoletini, I., Wilke, M., Bria, P., Di Paola, M., Di Iulio, F., Martinotti, G., Caltagirone, C., & Spalletta, G. (2007). Prefrontal-thalamic-cerebellar gray matter networks and executive functioning in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 93, 79–89.
Seaton, B. E., Allen, D. N., Goldstein, G., Kelley, M. E., & Van Kammen, D. P. (1999). Relations between cognitive and symptom profile heterogeneity in schizophrenia. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 187, 414–419.
Stern, Y. (2002). What is cognitive reserve? Theory and research application of the reserve concept. Journal of the international neuropsychological society, 8(3), 448-460.
Strassnig, M., Bowie, C., Pinkham, A. E., Penn, D., Twamley, E. W., Patterson, T. L., & Harvey, P. D. (2018). Which levels of cognitive impairments and negative symptoms are related to functional deficits in schizophrenia? Journal of Psychiatric Research, 104, 124–129.
Tandon, R., Nasrallah, H. A., & Keshavan, M. S. (2009). Schizophrenia, “just the facts” 4. Clinical Features and Conceptualization. Schizophrenia Research, 110, 1–23.
Turetsky, B. I., Moberg, P. J., Mozley, L. H., Moelter, S. T., Agrin, R. N., Gur, R. C., & Gur, R. E. (2002). Memory-delineated subtypes of schizophrenia: Relationship to clinical, neuroanatomical, and neurophysiological measures. Neuropsychology, 16, 481–490.
Van Der Elst, W., Van Boxtel, M. P. J., Van Breukelen, G. J. P., & Jolles, J. (2006). The stroop color-word test: Influence of age, sex, and education; and normative data for a large sample across the adult age range. Assessment, 13, 62–79.
Van Rheenen, T. E., Cropley, V., Fagerlund, B., Wannan, C., Bruggemann, J., Lenroot, R. K., Sundram, S., Weickert, C. S., Weickert, T. W. & Zalesky, A. (2019). Cognitive reserve attenuates age-related cognitive decline in the context of putatively accelerated brain ageing in schizophrenia-spectrum disorders. Psychological Medicine, 1–15.
Van Rheenen, T. E., Cropley, V., Zalesky, A., Bousman, C., Wells, R., Bruggemann, J., Sundram, S., Weinberg, D., Lenroot, R. K., Pereira, A., Shannon Weickert, C., Weickert, T. W., & Pantelis, C. (2018). Widespread Volumetric Reductions in Schizophrenia and Schizoaffective Patients Displaying Compromised Cognitive Abilities. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 44, 560–574.
Van Rheenen, T. E., Lewandowski, K. E., Tan, E. J., Ospina, L. H., Ongur, D., Neill, E., Gurvich, C., Pantelis, C., Malhotra, A. K., Rossell, S. L., & Burdick, K. E. (2017). Characterizing cognitive heterogeneity on the schizophrenia-bipolar disorder spectrum. Psychological Medicine, 47, 1848–1864.
Vaskinn, A., Hartberg, C. B., Sundet, K., Westlye, L. T., Andreassen, O. A., Melle, I., & Agartz, I. (2015). Brain structure characteristics in intellectually superior schizophrenia. Psychiatry Research - Neuroimaging, 232, 123–129.
Vaskinn, A., Sundet, K., Friis, S., Ueland, T., Simonsen, C., Birkenaes, A. B., Engh, J. A., Opjordsmoen, S., & Andreassen, O. A. (2008). Can learning potential in schizophrenia be assessed with the standard CVLT-II? An exploratory study. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 49, 179–186.
Vaskinn, A., Ueland, T., Melle, I., Agartz, I., Andreassen, O. A., & Sundet, K. (2014). Neurocognitive decrements are present in intellectually superior schizophrenia. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 5.
Ventura, J., Hellemann, G. S., Thames, A. D., Koellner, V., & Nuechterlein, K. H. (2009). Symptoms as mediators of the relationship between neurocognition and functional outcome in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis. Schizophrenia Research, 113, 189–199.
Weickert, T. W., Goldberg, T. E., Gold, J. M., Bigelow, L. B., Egan, M. F., & Weinberger, D. R. (2000). Cognitive impairments in patients with schizophrenia displaying preserved and compromised intellect. Archives Of General Psychiatry, 57, 907–913.
Weinberg, D., Lenroot, R., Jacomb, I., Allen, K., Bruggemann, J., Wells, R., Balzan, R., Liu, D., Galletly, C., Catts, S. V., Weickert, C. S., & Weickert, T. W. (2016). Cognitive subtypes of schizophrenia characterized by differential brain volumetric reductions and cognitive decline. JAMA Psychiatry, 73, 1251–1259.
Wells, R., Swaminathan, V., Sundram, S., Weinberg, D., Bruggemann, J., Jacomb, I., Cropley, V., Lenroot, R., Pereira, A. M. & Zalesky, A. (2015). The impact of premorbid and current intellect in schizophrenia: cognitive, symptom, and functional outcomes. NPJ Schizophrenia, 1, 15043.
Yasuda, Y., Okada, N., Nemoto, K., Fukunaga, M., Yamamori, H., Ohi, K., Koshiyama, D., Kudo, N., Shiino, T., Morita, S., Morita, K., Azechi, H., Fujimoto, M., Miura, K., Watanabe, Y., Kasai, K., & Hashimoto, R. (2020). Brain morphological and functional features in cognitive subgroups of schizophrenia. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 74, 191–203.
Yolland, C. O. B., Carruthers, S. P., Toh, W. L., Neill, E., Sumner, P. J., Thomas, E. H. X., Tan, E. J., Gurvich, C., Phillipou, A., Van Rheenen, T. E. & Rossell, S. (2020). The relationship between negative symptoms and both social and non-social cognition in schizophrenia spectrum disorders. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC; Project grant to Rossell, S., [GNT1060664], Early Career Fellowships to Van Rheenen, T [GNT1088785]), and a Senior Research Fellowship to Rossell, S [GNT154651]).
Funding
This work was supported by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (NHMRC; Project grant to Rossell, S., [GNT1060664], Early Career Fellowships to Van Rheenen, T [GNT1088785]), and a Senior Research Fellowship to Rossell, S [GNT154651]).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest/Competing Interests
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
Scopus Search Syntax
(TITLE-ABS-KEY (schizo* OR psychosis) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (cognit* AND cluster) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (cognit* AND heterogeneity) OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (cognit* AND "neuropsychologically normal") OR TITLE-ABS-KEY (cognit* AND subgroup)) AND DOCTYPE (ar) AND PUBYEAR> 1979
PubMed Search Syntax
((schizophrenia spectrum and other psychotic disorders[MeSH Terms])) AND (cognition[Title/Abstract] OR cognitive[Title/Abstract] OR neuropsychology[Title/Abstract] OR neuropsychologically[Title/Abstract] OR intelligence[Title/Abstract] OR intellect[Title/Abstract] OR memory[Title/Abstract] OR learning[Title/Abstract] OR attention[Title/Abstract] OR vigilance[Title/Abstract] OR speed of processing[Title/Abstract] OR executive[Title/Abstract] OR flexibility[Title/Abstract] OR reasoning[Title/Abstract] OR problem solving[Title/Abstract]) AND (cluster[Title/Abstract] OR subgroup[Title/Abstract] OR subtyp[Title/Abstract] OR heterogeneity[Title/Abstract])) AND ("1980/01/01"[Date - Publication] : "3000"[Date - Publication]))
Web of Science Search Syntax
((TS=(schizo* OR psychosis) AND (TS=(cognit* AND cluster) OR TS=(cognit* AND subgroup) OR TS=(cognit* AND subtype) OR TS=(cognit* AND heterogeneity) or TS=(cognit* AND "neuropsychologically normal"))) OR (TI=(schizo* OR psychosis) AND (TI=(cognit* AND cluster) OR TI=(cognit* AND subgroup) OR TI=(cognit* AND subtype) OR TI=(cognit* AND heterogeneity) or TI=(cognit* AND "neuropsychologically normal")))) AND LANGUAGE:(English) AND DOCUMENT TYPES: (Article)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carruthers, S.P., Van Rheenen, T.E., Karantonis, J.A. et al. Characterising Demographic, Clinical and Functional Features of Cognitive Subgroups in Schizophrenia Spectrum Disorders: A Systematic Review. Neuropsychol Rev 32, 807–827 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-021-09525-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11065-021-09525-0