Abstract
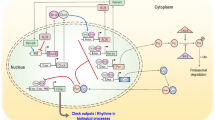
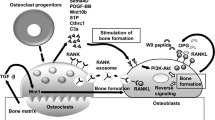
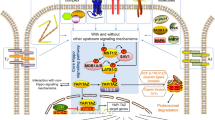
The clock system has been identified as one of the major mechanisms controlling cellular functions. Circadian clock gene oscillations also actively participate in the functions of various cell types including bone-related cells. Previous studies demonstrated that clock genes were expressed in bone tissue and also that their expression exhibited circadian rhythmicity. Recent findings have shown that sympathetic tone plays a central role in biological oscillations in bone. Adrenergic receptor (AR) signaling regulates the expression of clock genes in cancellous bone. Furthermore, α1-AR signaling in osteoblasts is known to negatively regulate the expression of bone morphogenetic protein-4 (Bmp4) by up-regulating nuclear factor IL-3 (Nfil3)/e4 promoter-binding protein 4 (E4BP4). The ablation of α1B-AR signaling also increases the expression of the Bmp4 gene in bone. The findings of transient overexpression and siRNA experiments have supported the involvement of the transcription factor CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta (C/EBPδ, Cebpd) in Nfil3 and Bmp4 expression in MC3T3-E1 cells. These findings suggest that the effects of Cebpd are due to the circadian regulation of Bmp4 expression, at least in part, by the up-regulated expression of the clock gene Nfil3 in response to α1B-AR signaling in osteoblasts. Therefore, AR signaling appears to modulate cellular functionality through the expression of clock genes that are circadian rhythm regulators in osteoblasts. The expression of clock genes regulated by the sympathetic nervous system and clock-controlled genes that affect bone metabolism are described herein.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AR:
-
Adrenergic receptor
- BMAL1:
-
Brain and muscle arnt-like protein 1
- BMP4:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein-4
- CEBPD:
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein delta
- CLOCK:
-
Circadian locomotor output cycles kaput
- CRY:
-
Cryptochromes
- E4BP4:
-
E4 promoter-binding protein 4
- M-CSF:
-
Macrophage colony-stimulating factor
- NFATc1:
-
Nuclear factor of activated T cells cytoplasmic 1
- Nfil3:
-
Nuclear factor IL-3
- PER:
-
Period
- PHE:
-
Phenylephrine
- RANKL:
-
Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-B ligand
- SCN:
-
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
- TRAP:
-
Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase
- ZT:
-
Zeitgeber time
References
Dunlap JC (1999) Molecular bases for circadian clocks. Cell 96:271–290
Reppert SM, Weaver DR (2001) Molecular analysis of mammalian circadian rhythms. Annu Rev Physiol 63:647–676. doi:https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.63.1.647
Reppert SM, Weaver DR (2002) Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature 418:935–941. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00965
Dibner C, Schibler U, Albrecht U (2010) The mammalian circadian timing system: organization and coordination of central and peripheral clocks. Annu Rev Physiol 72:517–549. doi:https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021909-135821
Kume K, Zylka MJ, Sriram S, Shearman LP, Weaver DR, Jin X, Maywood ES, Hastings MH, Reppert SM (1999) mCRY1 and mCRY2 are essential components of the negative limb of the circadian clock feedback loop. Cell 98:193–205
Duong HA, Robles MS, Knutti D, Weitz CJ (2011) A molecular mechanism for circadian clock negative feedback. Science 332:1436–1439. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1196766
Shearman LP, Sriram S, Weaver DR, Maywood ES, Chaves I, Zheng B, Kume K, Lee CC, van der Horst GT, Hastings MH, Reppert SM (2000) Interacting molecular loops in the mammalian circadian clock. Science 288:1013–1019
Yagita K, Yamaguchi S, Tamanini F, van Der Horst GT, Hoeijmakers JH, Yasui A, Loros JJ, Dunlap JC, Okamura H (2000) Dimerization and nuclear entry of mPER proteins in mammalian cells. Genes Dev 14:1353–1363
Lee C, Etchegaray JP, Cagampang FR, Loudon AS, Reppert SM (2001) Posttranslational mechanisms regulate the mammalian circadian clock. Cell 107:855–867
Chaix A, Zarrinpar A, Panda S (2016) The circadian coordination of cell biology. J Cell Biol 215:15–25. doi:https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201603076
Stratmann M, Schibler U (2012) REV-ERBs: more than the sum of the individual parts. Cell Metab 15:791–793. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.05.006
Zhang Y, Fang B, Emmett MJ, Damle M, Sun Z, Feng D, Armour SM, Remsberg JR, Jager J, Soccio RE, Steger DJ, Lazar MA (2015) GENE REGULATION. Discrete functions of nuclear receptor Rev-erbα couple metabolism to the clock. Science 348:1488–1492. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aab3021
Storch KF, Lipan O, Leykin I, Viswanathan N, Davis FC, Wong WH, Weitz CJ (2002) Extensive and divergent circadian gene expression in liver and heart. Nature 417:78–83. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature744
Zvonic S, Ptitsyn AA, Conrad SA, Scott LK, Floyd ZE, Kilroy G, Wu X, Goh BC, Mynatt RL, Gimble JM (2006) Characterization of peripheral circadian clocks in adipose tissues. Diabetes 55:962–970
Yoo SH, Yamazaki S, Lowrey PL, Shimomura K, Ko CH, Buhr ED, Siepka SM, Hong HK, Oh WJ, Yoo OJ, Menaker M, Takahashi JS (2004) PERIOD2::LUCIFERASE real-time reporting of circadian dynamics reveals persistent circadian oscillations in mouse peripheral tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5339–5346. doi:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0308709101
Maywood ES, O’Neill JS, Chesham JE, Hastings MH (2007) The circadian clockwork of the suprachiasmatic nuclei-analysis of a cellular oscillator that drives endocrine rhythms. Endocrinology 148:5624–5634. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2007-0660
Schibler U, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) A web of circadian pacemakers. Cell 111:919–922
Mohawk JA, Green CB, Takahashi JS (2012) Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev Neurosci 35:445–462. doi:https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-neuro-060909-153128
Takeda S, Elefteriou F, Levasseur R, Liu X, Zhao L, Parker KL, Armstrong D, Ducy P, Karsenty G (2002) Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell 111:305–317
Elefteriou F, Ahn JD, Takeda S, Starbuck M, Yang X, Liu X, Kondo H, Richards WG, Bannon TW, Noda M, Clement K, Vaisse C, Karsenty G (2005) Leptin regulation of bone resorption by the sympathetic nervous system and CART. Nature 434:514–520. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03398
Swanson CM, Shea SA, Stone KL, Cauley JA, Rosen CJ, Redline S, Karsenty G, Orwoll ES (2015) Obstructive sleep apnea and metabolic bone disease: insights into the relationship between bone and sleep. J Bone Miner Res 30:199–211. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2446
Hirai T, Tanaka K, Togari A (2015) α1B-Adrenergic receptor signaling controls circadian expression of Tnfrsf11b by regulating clock genes in osteoblasts. Biol Open 4:1400–1409. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/bio.012617.
Maury E, Hong HK, Bass J (2014) Circadian disruption in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Metab 40:338–346. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabet.2013.12.005
Kashiwada M, Cassel SL, Colgan JD, Rothman PB (2011) NFIL3/E4BP4 controls type 2 T helper cell cytokine expression. EMBO J 30:2071–2082. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.111
Takeda N, Maemura K (2010) Circadian clock and vascular disease. Hypertens Res 33:645–651. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/hr.2010.68
Xu C, Ochi H, Fukuda T, Sato S, Sunamura S, Takarada T, Hinoi E, Okawa A, Takeda S (2016) Circadian clock regulates bone resorption in mice. J Bone Miner Res 31:1344–1355. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.2803
Takarada T, Xu C, Ochi H, Nakazato R, Yamada D, Nakamura S, Kodama A, Shimba S, Mieda M, Fukasawa K, Ozaki K, Iezaki T, Fujikawa K, Yoneda Y, Numano R, Hida A, Tei H, Takeda S, Hinoi E (2017) Bone resorption is regulated by circadian clock in osteoblasts. J Bone Miner Res 32:872–881. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.3053
Hirai T, Tanaka K, Togari A (2014) α1-adrenergic receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates clock genes and bone morphogenetic protein 4 expression through up-regulation of the transcriptional factor nuclear factor IL-3 (Nfil3)/E4 promoter-binding protein 4 (E4BP4). J Biol Chem 289:17174–17183. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.546135
Fujihara Y, Kondo H, Noguchi T, Togari A (2014) Glucocorticoids mediate circadian timing in peripheral osteoclasts resulting in the circadian expression rhythm of osteoclast-related genes. Bone 61:1–9. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2013.12.026
Takayanagi H (2007) The role of NFAT in osteoclast formation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1116:227–237. doi:https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1402.071
Asagiri M, Takayanagi H (2007) The molecular understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone 40:251–264. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2006.09.023
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E, Gillespie MT, Martin TJ (1999) Modulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev 20:345–357. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/edrv.20.3.0367
Boyce BF (2013) Advances in osteoclast biology reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 28:711–722. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jbmr.1885
Kearns AE, Khosla S, Kostenuik PJ (2008) Receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand and osteoprotegerin regulation of bone remodeling in health and disease. Endocr Rev 29:155–192. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/er.2007-0014
Jubiz W, Canterbury J, Reiss E, Tyler F (1972) Circadian rhythm in serum parathyroid hormone concentration in human subjects: correlation with serum calcium, phosphate, albumin, and growth hormone levels. J Clin Invest 51:2040–2046. doi:https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI107010
el-Hajj Fuleihan G, Klerman EB, Brown EN, Choe Y, Brown EM, Czeisler CA (1997) The parathyroid hormone circadian rhythm is truly endogenous: a general clinical research center study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:281–286. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.1.3683
Joseph F, Chan BY, Durham BH, Ahmad AM, Vinjamuri S, Gallagher JA, Vora JP, Fraser WD (2007) The circadian rhythm of osteoprotegerin and its association with parathyroid hormone secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:3230–3238. doi:https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2006-1832
Salazar VS, Gamer LW, Rosen V (2016) BMP signalling in skeletal development, disease and repair. Nat Rev Endocrinol 12:203–221. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.12
Terazono H, Mutoh T, Yamaguchi S, Kobayashi M, Akiyama M, Udo R, Ohdo S, Okamura H, Shibata S (2003) Adrenergic regulation of clock gene expression in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:6795–6800. doi:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0936797100
Travnickova-Bendova Z, Cermakian N, Reppert SM, Sassone-Corsi P (2002) Bimodal regulation of mPeriod promoters by CREB dependent signaling and CLOCK/BMAL1 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7728–7733. doi:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.102075599
Yagita K, Okamura H (2000) Forskolin induces circadian gene expression of rPer1, rPer2 and dbp in mammalian rat-1 fibroblasts. FEBS Lett 465:79–82
Coogan AN, Piggins HD (2004) MAP kinases in the mammalian circadian system-key regulators of clock function. J Neurochem 90:769–775. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02554.x
Komoto S, Kondo H, Fukuta O, Togari A (2012) Comparison of β-adrenergic and glucocorticoid signaling on clock gene and osteoblast-related gene expressions in human osteoblast. Chronobiol Int 29:66–74. doi:https://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2011.636496
Hirai T, Tanaka K, Togari A (2014) ß-adrenergic receptor signaling regulates Ptgs2 by driving circadian gene expression in osteoblasts. J Cell Sci 127:3711–3719. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.148148
Kodama D, Togari A (2013) Store-operated calcium entry induced by activation of Gq-coupled alpha1B adrenergic receptor in human osteoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 437:239–244. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.047
Suzuki A, Palmer G, Bonjour JP, Caverzasio J (1998) Catecholamines stimulate the proliferation and alkaline phosphatase activity of MC3T3-E1 osteoblast-like cells. Bone 23:197–203
Kodama D, Togari A (2013) Noradrenaline stimulates cell proliferation by suppressing potassium channels via G(i/o)-protein-coupled α1(1B)-adrenoceptors in human osteoblasts. Br J Pharmacol 168:1230–1239. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.12000
Blau J, Young MW (1999) Cycling vrille expression is required for a functional Drosophila clock. Cell 99:661–671
Cyran SA, Buchsbaum AM, Reddy KL, Lin MC, Glossop NR, Hardin PE, Young MW, Storti RV, Blau J (2003) vrille, Pdp1, and dClock form a second feedback loop in the Drosophila circadian clock. Cell 112:329–341
Glossop NR, Houl JH, Zheng H, Ng FS, Dudek SM, Hardin PE (2003) VRILLE feeds back to control circadian transcription of Clock in the Drosophila circadian oscillator. Neuron 37:249–261
Ohno T, Onishi Y, Ishida N (2007) The negative transcription factor E4BP4 is associated with circadian clock protein PERIOD2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:1010–1015. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.084
Yu X, Rollins D, Ruhn KA, Stubblefield JJ, Green CB, Kashiwada M, Rothman PB, Takahashi JS, Hooper LV (2013) TH17 cell differentiation is regulated by the circadian clock. Science 342:727–730. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1243884
Nishimura Y, Tanaka T (2001) Calcium-dependent activation of nuclear factor regulated by interleukin 3/adenovirus E4 promoter-binding protein gene expression by calcineurin/nuclear factor of activated T cells and calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase signaling. J Biol Chem 276:19921–19928. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M010332200
MacGillavry HD, Stam FJ, Sassen MM, Kegel L, Hendriks WT, Verhaagen J, Smit AB, van Kesteren RE (2009) NFIL3 and cAMP response element-binding protein form a transcriptional feedforward loop that controls neuronal regeneration-associated gene expression. J Neurosci 29:15542–15550. doi:https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3938-09.2009
Chen F, Zhang L, OuYang Y, Guan H, Liu Q, Ni B (2014) Glucocorticoid induced osteoblast apoptosis by increasing E4BP4 expression via up-regulation of Bim. Calcif Tissue Int 94:640–647. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-014-9847-6
Pellicelli M, Taheri M, St-Louis M, Bériault V, Desgroseillers L, Boileau G, Moreau A (2012) PTHrP(1–34)-mediated repression of the PHEX gene in osteoblastic cells involves the transcriptional repressor E4BP4. J Cell Physiol 227:2378–2387. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.22973
Silvestris F, Cafforio P, De Matteo M, Calvani N, Frassanito MA, Dammacco F (2008) Negative regulation of the osteoblast function in multiple myeloma through the repressor gene E4BP4 activated by malignant plasma cells. Clin Cancer Res 14:6081–6091. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0219
Johnson PF (2005) Molecular stop signs: regulation of cell-cycle arrest by C/EBP transcription factors. J Cell Sci 118:2545–2555. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02459
Nerlov C (2007) The C/EBP family of transcription factors: a paradigm for interaction between gene expression and proliferation control. Trends Cell Biol 17:318–324. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2007.07.004
Ramji DP, Foka P (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J 365:561–575. doi:https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20020508
Gutierrez S, Javed A, Tennant DK, van Rees M, Montecino M, Stein GS, Stein JL, Lian JB (2002) CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins (C/EBP) ß and δ activate osteocalcin gene transcription and synergize with runx2 at the C/EBP element to regulate bone-specific expression. J Biol Chem 277:1316–1323. doi:https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M106611200
Alam T, An MR, Papaconstantinou J (1992) Differential expression of three C/EBP isoforms in multiple tissues during the acute phase response. J Biol Chem 267:5021–5024
O’Rourke JP, Newbound GC, Hutt JA, DeWille J (1999) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ regulates mammary epithelial cell G0 growth arrest and apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:16582–16589
Thangaraju M, Rudelius M, Bierie B, Raffeld M, Sharan S, Hennighausen L, Huang AM, Sterneck E (2005) C/EBPδ is a crucial regulator of pro-apoptotic gene expression during mammary gland involution. Development 132:4675–4685. doi:https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02050
Gery S, Tanosaki S, Hofmann WK, Koppel A, Koeffler HP (2005) C/EBPδ expression in a BCR-ABL-positive cell line induces growth arrest and myeloid differentiation. Oncogene 24:1589–1597. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1208393
Barbaro V, Testa A, Di Iorio E, Mavilio F, Pellegrini G, De Luca M (2007) C/EBPδ regulates cell cycle and self-renewal of human limbal stem cells. J Cell Biol 177:1037–1049. doi:https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200703003
Sarkar TR, Sharan S, Wang J, Pawar SA, Cantwell CA, Johnson PF, Morrison DK, Wang JM, Sterneck E (2012) Identification of a Src tyrosine kinase/SIAH2 E3 ubiquitin ligase pathway that regulates C/EBPδ expression and contributes to transformation of breast tumor cells. Mol Cell Biol 32:320–332. doi:https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.05790-11
Balamurugan K, Sterneck E (2013) The many faces of C/EBPδ and their relevance for inflammation and cancer. Int J Biol Sci 9:917–933. doi:https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.7224
Umayahara Y, Billiard J, Ji C, Centrella M, McCarthy TL, Rotwein P (1999) CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ is a critical regulator of insulin-like growth factor-I gene transcription in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem 274:10609–10617
Tanaka K, Hirai T, Kodama D, Kondo H, Hamamura K, Togari A (2016) α1B-Adrenoceptor signalling regulates bone formation through the up-regulation of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein δ expression in osteoblasts. Br J Pharmacol 173:1058–1069. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13418
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research to T.H. (16K11495) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirai, T. Regulation of Clock Genes by Adrenergic Receptor Signaling in Osteoblasts. Neurochem Res 43, 129–135 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2365-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2365-y