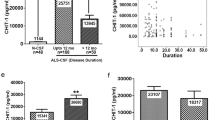
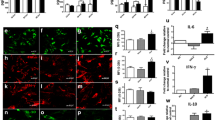
Abstract
In our laboratory, we have developed (1) an in vitro model of sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (sALS) involving exposure of motor neurons to cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from sALS patients and (2) an in vivo model involving intrathecal injection of sALS-CSF into rat pups. In the current study, we observed that spinal cord extract from the in vivo sALS model displayed elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial dysfunction. Quantitative proteomic analysis of sub-cellular fractions from spinal cord of the in vivo sALS model revealed down-regulation of 35 mitochondrial proteins and 4 lysosomal proteins. Many of the down-regulated mitochondrial proteins contribute to alterations in respiratory chain complexes and organellar morphology. Down-regulated lysosomal proteins Hexosaminidase, Sialidase and Aryl sulfatase also displayed lowered enzyme activity, thus validating the mass spectrometry data. Proteomic analysis and validation by western blot indicated that sALS-CSF induced the over-expression of the pro-apoptotic mitochondrial protein BNIP3L. In the in vitro model, sALS-CSF induced neurotoxicity and elevated ROS, while it lowered the mitochondrial membrane potential in rat spinal cord mitochondria in the in vivo model. Ultra structural alterations were evident in mitochondria of cultured motor neurons exposed to ALS-CSF. These observations indicate the first line evidence that sALS-CSF mediated mitochondrial and lysosomal defects collectively contribute to the pathogenesis underlying sALS.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- fALS:
-
Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- sALS:
-
Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
- CSF:
-
Cerebrospinal fluid
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- iTRAQ:
-
Isobaric tag for relative and absolute quantitation
- CI:
-
Mitochondrial complex I
- CII:
-
Mitochondrial complex II
- CIII:
-
Mitochondrial complex III
- CIV:
-
Mitochondrial complex IV
- CV:
-
Mitochondrial complex V
- LC–MS/MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry
- HEX:
-
Hexosaminidase
- ARS:
-
Arylsulphatase
References
Rowland LP, Shneider NA (2001) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. N Engl J Med 344(22):1688–1700. doi:10.1056/nejm200105313442207
Strong MJ (2003) The basic aspects of therapeutics in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Pharmacol Ther 98(3):379–414
Shi P, Gal J, Kwinter DM, Liu X, Zhu H (2010) Mitochondrial dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(1):45–51. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2009.08.012
Menzies FM, Ince PG, Shaw PJ (2002) Mitochondrial involvement in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurochem Int 40(6):543–551
Collard JF, Cote F, Julien JP (1995) Defective axonal transport in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nature 375(6526):61–64. doi:10.1038/375061a0
Menzies FM, Cookson MR, Taylor RW, Turnbull DM, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZM, Dong L, Figlewicz DA, Shaw PJ (2002) Mitochondrial dysfunction in a cell culture model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 125(Pt 7):1522–1533
Bowling AC, Schulz JB, Brown RH Jr, Beal MF (1993) Superoxide dismutase activity, oxidative damage, and mitochondrial energy metabolism in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 61(6):2322–2325
Fujita K, Yamauchi M, Shibayama K, Ando M, Honda M, Nagata Y (1996) Decreased cytochrome c oxidase activity but unchanged superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase activities in the spinal cords of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci Res 45(3):276–281. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19960801)45:3<276:AID-JNR9>3.0.CO;2-A
Li Q, Vande Velde C, Israelson A, Xie J, Bailey AO, Dong MQ, Chun SJ, Roy T, Winer L, Yates JR, Capaldi RA, Cleveland DW, Miller TM (2010) ALS-linked mutant superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) alters mitochondrial protein composition and decreases protein import. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(49):21146–21151. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014862107
Ferri A, Cozzolino M, Crosio C, Nencini M, Casciati A, Gralla EB, Rotilio G, Valentine JS, Carri MT (2006) Familial ALS-superoxide dismutases associate with mitochondria and shift their redox potentials. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(37):13860–13865. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605814103
Grosskreutz J, Van Den Bosch L, Keller BU (2010) Calcium dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Cell Calcium 47(2):165–174. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2009.12.002
Pasinelli P, Belford ME, Lennon N, Bacskai BJ, Hyman BT, Trotti D, Brown RH Jr (2004) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-associated SOD1 mutant proteins bind and aggregate with Bcl-2 in spinal cord mitochondria. Neuron 43(1):19–30. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2004.06.021
Wiedemann FR, Manfredi G, Mawrin C, Beal MF, Schon EA (2002) Mitochondrial DNA and respiratory chain function in spinal cords of ALS patients. J Neurochem 80(4):616–625
Ferri A, Fiorenzo P, Nencini M, Cozzolino M, Pesaresi MG, Valle C, Sepe S, Moreno S, Carri MT (2010) Glutaredoxin 2 prevents aggregation of mutant SOD1 in mitochondria and abolishes its toxicity. Hum Mol Genet 19(22):4529–4542. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddq383
Kaal EC, Vlug AS, Versleijen MW, Kuilman M, Joosten EA, Bar PR (2000) Chronic mitochondrial inhibition induces selective motoneuron death in vitro: a new model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 74(3):1158–1165
Robberecht W (2000) Oxidative stress in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol 247(Suppl 1):I1–I6
Cookson MR, Shaw PJ (1999) Oxidative stress and motor neurone disease. Brain Pathol 9(1):165–186
Beal MF, Ferrante RJ, Browne SE, Matthews RT, Kowall NW, Brown RH Jr (1997) Increased 3-nitrotyrosine in both sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 42(4):644–654. doi:10.1002/ana.410420416
Chen J, Schenker S, Frosto TA, Henderson GI (1998) Inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase activity by 4-hydroxynonenal (HNE). Role of HNE adduct formation with the enzyme subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta 1380(3):336–344
Otomo A, Pan L, Hadano S (2012) Dysregulation of the autophagy-endolysosomal system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and related motor neuron diseases. Neurol Res Int 2012:498428. doi:10.1155/2012/498428
Garcia-Arencibia M, Hochfeld WE, Toh PP, Rubinsztein DC (2010) Autophagy, a guardian against neurodegeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol 21(7):691–698. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2010.02.008
Wong E, Cuervo AM (2010) Autophagy gone awry in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci 13(7):805–811. doi:10.1038/nn.2575
Lee J, Giordano S, Zhang J (2012) Autophagy, mitochondria and oxidative stress: cross-talk and redox signalling. Biochem J 441(2):523–540. doi:10.1042/bj20111451
Hashimoto M, Rockenstein E, Crews L, Masliah E (2003) Role of protein aggregation in mitochondrial dysfunction and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Neuromolecular Med 4(1–2):21–36. doi:10.1385/nmm:4:1-2:21
Gottlieb RA, Carreira RS (2010) Autophagy in health and disease. 5. Mitophagy as a way of life. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299(2):C203–C210. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00097.2010
Fukada K, Zhang F, Vien A, Cashman NR, Zhu H (2004) Mitochondrial proteomic analysis of a cell line model of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol Cell Proteomics 3(12):1211–1223. doi:10.1074/mcp.M400094-MCP200
Sasaki S (2011) Autophagy in spinal cord motor neurons in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 70(5):349–359. doi:10.1097/NEN.0b013e3182160690
Pratt AJ, Getzoff ED, Perry JJ (2012) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: update and new developments. Degener Neurol Neuromuscul Dis 2012(2):1–14. doi:10.2147/dnnd.s19803
Wijesekera LC, Leigh PN (2009) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis 4:3. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-4-3
Gaudette M, Hirano M, Siddique T (2000) Current status of SOD1 mutations in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(2):83–89
Shobha K, Vijayalakshmi K, Alladi PA, Nalini A, Sathyaprabha TN, Raju TR (2007) Altered in vitro and in vivo expression of glial glutamate transporter-1 following exposure to cerebrospinal fluid of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J Neurol Sci 254(1–2):9–16. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.12.004
Sankaranarayani R, Nalini A, Rao Laxmi T, Raju TR (2010) Altered neuronal activities in the motor cortex with impaired motor performance in adult rats observed after infusion of cerebrospinal fluid from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Behav Brain Res 206(1):109–119. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2009.09.009
Varghese AM, Sharma A, Mishra P, Vijayalakshmi K, Harsha HC, Sathyaprabha TN, Bharath SM, Nalini A, Alladi PA, Raju TR (2013) Chitotriosidase—a putative biomarker for sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Clin Proteomics 10(1):19. doi:10.1186/1559-0275-10-19
Vijayalakshmi K, Alladi PA, Sathyaprabha TN, Subramaniam JR, Nalini A, Raju TR (2009) Cerebrospinal fluid from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients induces degeneration of a cultured motor neuron cell line. Brain Res 1263:122–133. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2009.01.041
Ramamohan PY, Gourie-Devi M, Nalini A, Shobha K, Ramamohan Y, Joshi P, Raju TR (2007) Cerebrospinal fluid from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients causes fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus in the neonatal rat spinal cord. Amyotroph Lateral Scler 8(2):79–82. doi:10.1080/08037060601145489
Gunasekaran R, Narayani RS, Vijayalakshmi K, Alladi PA, Shobha K, Nalini A, Sathyaprabha TN, Raju TR (2009) Exposure to cerebrospinal fluid of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients alters Nav1.6 and Kv1.6 channel expression in rat spinal motor neurons. Brain Res 1255:170–179. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.11.099
Vijayalakshmi K, Alladi PA, Ghosh S, Prasanna VK, Sagar BC, Nalini A, Sathyaprabha TN, Raju TR (2011) Evidence of endoplasmic reticular stress in the spinal motor neurons exposed to CSF from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Neurobiol Dis 41(3):695–705. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2010.12.005
Vijayalakshmi K, Ostwal P, Sumitha R, Shruthi S, Varghese AM, Mishra P, Manohari SG, Sagar BC, Sathyaprabha TN, Nalini A, Raju TR, Alladi PA (2014) Role of VEGF and VEGFR2 receptor in reversal of ALS-CSF induced degeneration of NSC-34 motor neuron cell line. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8757-y
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M, Munsat TL (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1(5):293–299
Deepa P, Shahani N, Alladi PA, Vijayalakshmi K, Sathyaprabha TN, Nalini A, Ravi V, Raju TR (2011) Down regulation of trophic factors in neonatal rat spinal cord after administration of cerebrospinal fluid from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J Neural Transm (Vienna, Austria: 1996) 118(4):531–538. doi:10.1007/s00702-010-0520-6
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Trounce IA, Kim YL, Jun AS, Wallace DC (1996) Assessment of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in patient muscle biopsies, lymphoblasts, and transmitochondrial cell lines. Methods Enzymol 264:484–509
Cohen G, Farooqui R, Kesler N (1997) Parkinson disease: a new link between monoamine oxidase and mitochondrial electron flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(10):4890–4894
Reers M, Smith TW, Chen LB (1991) J-aggregate formation of a carbocyanine as a quantitative fluorescent indicator of membrane potential. Biochemistry 30(18):4480–4486
Ramadasan-Nair R, Gayathri N, Mishra S, Sunitha B, Mythri RB, Nalini A, Subbannayya Y, Harsha HC, Kolthur-Seetharam U, Srinivas Bharath MM (2014) Mitochondrial alterations and oxidative stress in an acute transient mouse model of muscle degeneration: implications for muscular dystrophy and related muscle pathologies. J Biol Chem 289(1):485–509. doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.493270
Rustin P, Chretien D, Bourgeron T, Gerard B, Rotig A, Saudubray JM, Munnich A (1994) Biochemical and molecular investigations in respiratory chain deficiencies. Clin Chim Acta 228(1):35–51
Kirby DM, Thorburn DR, Turnbull DM, Taylor RW (2007) Biochemical assays of respiratory chain complex activity. Methods Cell Biol 80:93–119. doi:10.1016/s0091-679x(06)80004-x
Barber SC, Higginbottom A, Mead RJ, Barber S, Shaw PJ (2009) An in vitro screening cascade to identify neuroprotective antioxidants in ALS. Free Radic Biol Med 46(8):1127–1138. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.01.019
Venkateshappa C, Harish G, Mythri RB, Mahadevan A, Bharath MM, Shankar SK (2012) Increased oxidative damage and decreased antioxidant function in aging human substantia nigra compared to striatum: implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res 37(2):358–369. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0619-7
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193(1):265–275
Pawar H, Kashyap MK, Sahasrabuddhe NA, Renuse S, Harsha HC, Kumar P, Sharma J, Kandasamy K, Marimuthu A, Nair B, Rajagopalan S, Maharudraiah J, Premalatha CS, Kumar KV, Vijayakumar M, Chaerkady R, Prasad TS, Kumar RV, Kumar RV, Pandey A (2011) Quantitative tissue proteomics of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma for novel biomarker discovery. Cancer Biol Ther 12(6):510–522. doi:10.4161/cbt.12.6.16833
Padeh B, Navon R (1971) Diagnosis of Tay-Sachs disease by hexosaminidase activity in leukocytes and amniotic fluid cells. Isr J Med Sci 7(2):259–263
Potier M, Mameli L, Belisle M, Dallaire L, Melancon SB (1979) Fluorometric assay of neuraminidase with a sodium (4-methylumbelliferyl-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminate) substrate. Anal Biochem 94(2):287–296
Lee-Vaupel M, Conzelmann E (1987) A simple chromogenic assay for arylsulfatase A. Clin Chim Acta 164(2):171–180
Hwu WL, Wang TR (1991) Quantification of arylsulfatase B activity and diagnosis of Maroteaux–Lamy syndrome. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi 32(5):280–285
Sheehan DC, Hrapchak BB (1980) Theory and practice of histotechnology, 2nd edn. The CV Mosby Company, St Louis
Barber SC, Mead RJ, Shaw PJ (2006) Oxidative stress in ALS: a mechanism of neurodegeneration and a therapeutic target. Biochim Biophys Acta 1762(11–12):1051–1067. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2006.03.008
Bowling AC, Beal MF (1995) Bioenergetic and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Life Sci 56(14):1151–1171
Baron M, Kudin AP, Kunz WS (2007) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Biochem Soc Trans 35(Pt 5):1228–1231. doi:10.1042/bst0351228
Palomo GM, Manfredi G (2014) Exploring new pathways of neurodegeneration in ALS: the role of mitochondria quality control. Brain Res. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.065
Krasnianski A, Deschauer M, Neudecker S, Gellerich FN, Muller T, Schoser BG, Krasnianski M, Zierz S (2005) Mitochondrial changes in skeletal muscle in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and other neurogenic atrophies. Brain 128(Pt 8):1870–1876. doi:10.1093/brain/awh540
Dupuis L, di Scala F, Rene F, de Tapia M, Oudart H, Pradat PF, Meininger V, Loeffler JP (2003) Up-regulation of mitochondrial uncoupling protein 3 reveals an early muscular metabolic defect in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. FASEB J 17(14):2091–2093. doi:10.1096/fj.02-1182fje
Echaniz-Laguna A, Zoll J, Ribera F, Tranchant C, Warter JM, Lonsdorfer J, Lampert E (2002) Mitochondrial respiratory chain function in skeletal muscle of ALS patients. Ann Neurol 52(5):623–627. doi:10.1002/ana.10357
Faes L, Callewaert G (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43(6):587–592. doi:10.1007/s10863-011-9393-0
Manfredi G, Xu Z (2005) Mitochondrial dysfunction and its role in motor neuron degeneration in ALS. Mitochondrion 5(2):77–87. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2005.01.002
Oladzad Abbasabadi A, Javanian A, Nikkhah M, Meratan AA, Ghiasi P, Nemat-Gorgani M (2013) Disruption of mitochondrial membrane integrity induced by amyloid aggregates arising from variants of SOD1. Int J Biol Macromol 61:212–217. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.07.007
Bahadorani S, Mukai ST, Rabie J, Beckman JS, Phillips JP, Hilliker AJ (2013) Expression of zinc-deficient human superoxide dismutase in Drosophila neurons produces a locomotor defect linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. Neurobiol Aging 34(10):2322–2330. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.03.024
Dupuis L, Gonzalez de Aguilar JL, Oudart H, de Tapia M, Barbeito L, Loeffler JP (2004) Mitochondria in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a trigger and a target. Neurodegener Dis 1(6):245–254. doi:10.1159/000085063
Cozzolino M, Ferri A, Valle C, Carri MT (2013) Mitochondria and ALS: implications from novel genes and pathways. Mol Cell Neurosci 55:44–49. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2012.06.001
Xu YF, Zhang YJ, Lin WL, Cao X, Stetler C, Dickson DW, Lewis J, Petrucelli L (2011) Expression of mutant TDP-43 induces neuronal dysfunction in transgenic mice. Mol Neurodegener 6:73. doi:10.1186/1750-1326-6-73
Xu YF, Gendron TF, Zhang YJ, Lin WL, D’Alton S, Sheng H, Casey MC, Tong J, Knight J, Yu X, Rademakers R, Boylan K, Hutton M, McGowan E, Dickson DW, Lewis J, Petrucelli L (2010) Wild-type human TDP-43 expression causes TDP-43 phosphorylation, mitochondrial aggregation, motor deficits, and early mortality in transgenic mice. J Neurosci 30(32):10851–10859. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.1630-10.2010
Mancuso M, Conforti FL, Rocchi A, Tessitore A, Muglia M, Tedeschi G, Panza D, Monsurro M, Sola P, Mandrioli J, Choub A, DelCorona A, Manca ML, Mazzei R, Sprovieri T, Filosto M, Salviati A, Valentino P, Bono F, Caracciolo M, Simone IL, La Bella V, Majorana G, Siciliano G, Murri L, Quattrone A (2004) Could mitochondrial haplogroups play a role in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? Neurosci Lett 371(2–3):158–162. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.08.060
Dhaliwal GK, Grewal RP (2000) Mitochondrial DNA deletion mutation levels are elevated in ALS brains. NeuroReport 11(11):2507–2509
Bowling AC, Barkowski EE, McKenna-Yasek D, Sapp P, Horvitz HR, Beal MF, Brown RH Jr (1995) Superoxide dismutase concentration and activity in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 64(5):2366–2369
Bergemalm D, Forsberg K, Jonsson PA, Graffmo KS, Brannstrom T, Andersen PM, Antti H, Marklund SL (2009) Changes in the spinal cord proteome of an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis murine model determined by differential in-gel electrophoresis. Mol Cell Proteom 8(6):1306–1317. doi:10.1074/mcp.M900046-MCP200
Dangond F, Hwang D, Camelo S, Pasinelli P, Frosch MP, Stephanopoulos G, Stephanopoulos G, Brown RH Jr, Gullans SR (2004) Molecular signature of late-stage human ALS revealed by expression profiling of postmortem spinal cord gray matter. Physiol Genomics 16(2):229–239. doi:10.1152/physiolgenomics.00087.2001
Borthwick GM, Johnson MA, Ince PG, Shaw PJ, Turnbull DM (1999) Mitochondrial enzyme activity in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: implications for the role of mitochondria in neuronal cell death. Ann Neurol 46(5):787–790
Vielhaber S, Kunz D, Winkler K, Wiedemann FR, Kirches E, Feistner H, Heinze HJ, Elger CE, Schubert W, Kunz WS (2000) Mitochondrial DNA abnormalities in skeletal muscle of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 123(Pt 7):1339–1348
Jung C, Higgins CM, Xu Z (2002) Mitochondrial electron transport chain complex dysfunction in a transgenic mouse model for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurochem 83(3):535–545
Ilieva EV, Ayala V, Jove M, Dalfo E, Cacabelos D, Povedano M, Bellmunt MJ, Ferrer I, Pamplona R, Portero-Otin M (2007) Oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress interplay in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 130(Pt 12):3111–3123. doi:10.1093/brain/awm190
Crugnola V, Lamperti C, Lucchini V, Ronchi D, Peverelli L, Prelle A, Sciacco M, Bordoni A, Fassone E, Fortunato F, Corti S, Silani V, Bresolin N, Di Mauro S, Comi GP, Moggio M (2010) Mitochondrial respiratory chain dysfunction in muscle from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arch Neurol 67(7):849–854. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2010.128
Vielhaber S, Winkler K, Kirches E, Kunz D, Buchner M, Feistner H, Elger CE, Ludolph AC, Riepe MW, Kunz WS (1999) Visualization of defective mitochondrial function in skeletal muscle fibers of patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 169(1–2):133–139
Swerdlow RH, Parks JK, Cassarino DS, Trimmer PA, Miller SW, Maguire DJ, Sheehan JP, Maguire RS, Pattee G, Juel VC, Phillips LH, Tuttle JB, Bennett JP Jr, Davis RE, Parker WD Jr (1998) Mitochondria in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Exp Neurol 153(1):135–142. doi:10.1006/exnr.1998.6866
Shrivastava M, Das TK, Behari M, Pati U, Vivekanandhan S (2011) Ultrastructural variations in platelets and platelet mitochondria: a novel feature in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ultrastruct Pathol 35(2):52–59. doi:10.3109/01913123.2010.541985
Sasaki S, Horie Y, Iwata M (2007) Mitochondrial alterations in dorsal root ganglion cells in sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 114(6):633–639. doi:10.1007/s00401-007-0299-1
Guegan C, Vila M, Rosoklija G, Hays AP, Przedborski S (2001) Recruitment of the mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurosci 21(17):6569–6576
Martin LJ (1999) Neuronal death in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is apoptosis: possible contribution of a programmed cell death mechanism. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58(5):459–471
Pedersen WA, Luo H, Kruman I, Kasarskis E, Mattson MP (2000) The prostate apoptosis response-4 protein participates in motor neuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. FASEB J 14(7):913–924
Sassone J, Colciago C, Marchi P, Ascardi C, Alberti L, Di Pardo A, Zippel R, Sipione S, Silani V, Ciammola A (2010) Mutant Huntingtin induces activation of the Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19-kDa interacting protein (BNip3). Cell Death Dis 1:e7. doi:10.1038/cddis.2009.6
Warita H, Hayashi T, Murakami T, Manabe Y, Abe K (2001) Oxidative damage to mitochondrial DNA in spinal motoneurons of transgenic ALS mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 89(1–2):147–152
Pattee GL, Post GR, Gerber RE, Bennett JP Jr (2003) Reduction of oxidative stress in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis following pramipexole treatment. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 4(2):90–95
Soraru G, Vergani L, Fedrizzi L, D’Ascenzo C, Polo A, Bernazzi B, Angelini C (2007) Activities of mitochondrial complexes correlate with nNOS amount in muscle from ALS patients. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 33(2):204–211. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2990.2006.00791.x
Kikuchi H, Furuta A, Nishioka K, Suzuki SO, Nakabeppu Y, Iwaki T (2002) Impairment of mitochondrial DNA repair enzymes against accumulation of 8-oxo-guanine in the spinal motor neurons of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 103(4):408–414. doi:10.1007/s00401-001-0480-x
Drory VE, Birnbaum M, Peleg L, Goldman B, Korczyn AD (2003) Hexosaminidase A deficiency is an uncommon cause of a syndrome mimicking amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Muscle Nerve 28(1):109–112. doi:10.1002/mus.10371
Cassina P, Cassina A, Pehar M, Castellanos R, Gandelman M, de León A, Robinson KM, Mason RP, Beckman JS, Barbeito L, Radi R (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction in SOD1G93A-bearing astrocytes promotes motor neuron degeneration: prevention by mitochondrial-targeted antioxidants. J Neurosci 28(16):4115–4122
Hizarcioglu-Gulsen H, Yuce A, Akcoren Z, Berberoglu-Ates B, Aydemir Y, Sag E, Ceylaner S (2014) A rare cause of elevated chitotriosidase activity: glycogen storage disease type IV. JIMD Rep 17:63–66. doi:10.1007/8904_2014_335
Alexianu ME, Kozovska M, Appel SH (2001) Immune reactivity in a mouse model of familial ALS correlates with disease progression. Neurology 57(7):1282–1289
Alkali NH, Pullen AH (2006) Activation of microglia in mice spinal cords following passive transfer of purified IgG from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurosciences (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia) 11(3):135–139
Engelhardt JI, Soos J, Obal I, Vigh L, Siklos L (2005) Subcellular localization of IgG from the sera of ALS patients in the nervous system. Acta Neurol Scand 112(2):126–133. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00445.x
Demestre M, Pullen A, Orrell RW, Orth M (2005) ALS-IgG-induced selective motor neurone apoptosis in rat mixed primary spinal cord cultures. J Neurochem 94(1):268–275. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03184.x
Andjus PR, Khiroug L, Nistri A, Cherubini E (1996) ALS IgGs suppress [Ca2+]i rise through P/Q-type calcium channels in central neurones in culture. NeuroReport 7(12):1914–1916
Pullen AH, Humphreys P (2000) Ultrastructural analysis of spinal motoneurones from mice treated with IgG from ALS patients, healthy individuals, or disease controls. J Neurol Sci 180(1–2):35–45
Milosevic M, Stenovec M, Kreft M, Petrusic V, Stevic Z, Trkov S, Andjus PR, Zorec R (2013) Immunoglobulins G from patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis affects cytosolic Ca2+ homeostasis in cultured rat astrocytes. Cell Calcium 54(1):17–25. doi:10.1016/j.ceca.2013.03.005
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by funded by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India (BT/PR/4054/Med/30/349/2010). The authors thank the all the patients for permitting to utilize the CSF samples for this study. The authors are grateful to the Director, Sanjay Gandhi Institute of Trauma and Orthopedics Centre, Bangalore, for facilitating the collection of control CSF. A.M.V., S.S. and K.K.D. are senior research fellows of the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India. R.R.S. is a senior research fellow of the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). H.G. is supported by an early career fellowship from Welcome Trust-DBT India Alliance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, A., Varghese, A.M., Vijaylakshmi, K. et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid from Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients Induces Mitochondrial and Lysosomal Dysfunction. Neurochem Res 41, 965–984 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1779-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1779-7