Abstract
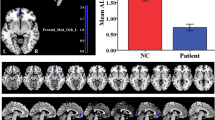
Nocturnal enuresis is a common developmental disorder in children; primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis (PMNE) is the dominant subtype. Previous literature has suggested that the prefrontal cortex and the pons are both involved in micturition control. This study aimed to investigate the metabolic levels of the left prefrontal cortex and the pons in children with PMNE by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS). Twenty-five children with PMNE and 25 healthy children took part in our experiments. Magnetic resonance examinations were performed on a Siemens 3T Trio Tim scanner. For each subject, localized 1H-MRS was acquired from the left prefrontal cortex (mainly in brodmann area 9) and the pons with a point-resolved spectroscopy sequence with repetition time 2,000 ms, echo time 30 ms and 64 averages. The LCModel software package was used to analyze the MRS raw data, and two-sample t tests were used to determine significant differences between the two groups. The results revealed a significant reduction in metabolite to total creatine ratios of N-acetylaspartate (NAA/tCr) in the left prefrontal cortex and the pons for children with PMNE compared to healthy children. Our study suggests that metabolism is disturbed in the prefrontal cortex and the pons in children with PMNE, which may be associated with the symptoms of enuresis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Riccabona M (2010) Evaluation and management of enuresis: An update. Urologe A 49(7):861–869 (quiz 870)
Theunis M, Van Hoecke E, Paesbrugge S, Hoebeke P, Vande Walle J (2002) Self-image and performance in children with nocturnal enuresis. Eur Urol 41(6):660–667 (discussion 667)
Neveus T, von Gontard A, Hoebeke P, Hjalmas K, Bauer S, Bower W, Jorgensen TM, Rittig S, Walle JV, Yeung CK, Djurhuus JC (2006) The standardization of terminology of lower urinary tract function in children and adolescents: report from the Standardisation Committee of the International Children’s Continence Society. J Urol 176(1):314–324
Neveus T (2009) Diagnosis and management of nocturnal enuresis. Curr Opin Pediatr 21(2):199–202. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e3283229b12
Toros F, Ozge A, Bozlu M, Cayan S (2003) Hyperventilation response in the electroencephalogram and psychiatric problems in children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 37(6):471–476. doi:10.1080/00365590310014544
Iscan A, Ozkul Y, Unal D, Soran M, Kati M, Bozlar S, Karazeybek AH (2002) Abnormalities in event-related potential and brainstem auditory evoked response in children with nocturnal enuresis. Brain Dev 24(7):681–687
Freitag CM, Rohling D, Seifen S, Pukrop R, von Gontard A (2006) Neurophysiology of nocturnal enuresis: evoked potentials and prepulse inhibition of the startle reflex. Dev Med Child Neurol 48(4):278–284. doi:10.1017/S0012162206000600
Fowler CJ, Griffiths DJ (2010) A decade of functional brain imaging applied to bladder control. Neurourol Urodyn 29(1):49–55. doi:10.1002/nau.20740
Griffiths D, Tadic SD (2008) Bladder control, urgency, and urge incontinence: evidence from functional brain imaging. Neurourol Urodyn 27(6):466–474. doi:10.1002/nau.20549
Yu B, Guo Q, Fan G, Ma H, Wang L, Liu N (2011) Evaluation of working memory impairment in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: evidence from event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Paediatr Child Health 47(7):429–435. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1754.2010.02000.x
Lei D, Ma J, Du X, Shen G, Tian M, Li G (2012) Altered brain activation during response inhibition in children with primary nocturnal enuresis: an fMRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 33(12):2913–2919. doi:10.1002/hbm.21411
Lei D, Ma J, Du X, Shen G, Tian M, Li G (2012) Spontaneous brain activity changes in children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a resting-state fMRI study. Neurourol Urodyn 31(1):99–104. doi:10.1002/nau.21205
Lei D, Ma J, Shen X, Du X, Shen G, Liu W, Yan X, Li G (2012) Changes in the brain microstructure of children with primary monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis: a diffusion tensor imaging study. PLoS ONE 7(2):e31023. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031023
Baruth JM, Wall CA, Patterson MC, Port JD (2013) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy as a probe into the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorders (ASD): a review. Autism Res 6(2):119–133. doi:10.1002/aur.1273
Perlov E, Philipsen A, Matthies S, Drieling T, Maier S, Bubl E, Hesslinger B, Buechert M, Henning J, Ebert D, Tebartz Van Elst L (2009) Spectroscopic findings in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: review and meta-analysis. World J Biol Psychiatry 10(4 Pt 2):355–365. doi:10.1080/15622970802176032
Pouwels PJ, Brockmann K, Kruse B, Wilken B, Wick M, Hanefeld F, Frahm J (1999) Regional age dependence of human brain metabolites from infancy to adulthood as detected by quantitative localized proton MRS. Pediatr Res 46(4):474–485. doi:10.1203/00006450-199910000-00019
Alkan A, Sharifov R, Akkoyunlu ME, Kilicarslan R, Toprak H, Aralasmak A, Kart L (2013) MR spectroscopy features of brain in patients with mild and severe obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Clin Imaging 37(6):989–992. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2013.07.010
Cecil KM, Jones BV (2001) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of the pediatric brain. Top Magn Reson Imaging 12(6):435–452
Bates TE, Strangward M, Keelan J, Davey GP, Munro PM, Clark JB (1996) Inhibition of N-acetylaspartate production: implications for 1H MRS studies in vivo. NeuroReport 7(8):1397–1400
Baslow MH (2010) Evidence that the tri-cellular metabolism of N-acetylaspartate functions as the brain’s “operating system”: how NAA metabolism supports meaningful intercellular frequency-encoded communications. Amino Acids 39(5):1139–1145. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0656-6
Unschuld PG, Edden RA, Carass A, Liu X, Shanahan M, Wang X, Oishi K, Brandt J, Bassett SS, Redgrave GW, Margolis RL, van Zijl PC, Barker PB, Ross CA (2012) Brain metabolite alterations and cognitive dysfunction in early Huntington’s disease. Mov Disord 27(7):895–902. doi:10.1002/mds.25010
Gasparovic C, Prestopnik J, Thompson J, Taheri S, Huisa B, Schrader R, Adair JC, Rosenberg GA (2013) 1H-MR spectroscopy metabolite levels correlate with executive function in vascular cognitive impairment. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 84(7):715–721. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2012-303878
Xi G, Hui J, Zhang Z, Liu S, Zhang X, Teng G, Chan KC, Wu EX, Nie B, Shan B, Li L, Reynolds GP (2011) Learning and memory alterations are associated with hippocampal N-acetylaspartate in a rat model of depression as measured by 1H-MRS. PLoS ONE 6(12):e28686. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0028686
Miller EK, Cohen JD (2001) An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:167–202
Roberts AC, Tomic DL, Parkinson CH, Roeling TA, Cutter DJ, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2007) Forebrain connectivity of the prefrontal cortex in the marmoset monkey (Callithrix jacchus): an anterograde and retrograde tract-tracing study. J Comp Neurol 502(1):86–112
Kavia RB, Dasgupta R, Fowler CJ (2005) Functional imaging and the central control of the bladder. J Comp Neurol 493(1):27–32
Holstege G (2010) The emotional motor system and micturition control. Neurourol Urodyn 29(1):42–48
Tadic SD, Griffiths D, Schaefer W, Cheng CI, Resnick NM (2010) Brain activity measured by functional magnetic resonance imaging is related to patient reported urgency urinary incontinence severity. J Urol 183(1):221–228. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2009.08.155
Namatame S, Mochizuki H, Ebitani M, Matsuda N, Ugawa Y (2010) Micturitional disturbance due to bilateral medial frontal lobe lesions in a patient with multiple sclerosis. Neurol Sci 31(2):205–207
Barbey AK, Koenigs M, Grafman J (2013) Dorsolateral prefrontal contributions to human working memory. Cortex 49(5):1195–1205. doi:10.1016/j.cortex.2012.05.022
Adinoff B (2004) Neurobiologic processes in drug reward and addiction. Harv Rev Psychiatry 12(6):305–320. doi:10.1080/10673220490910844
Perach-Barzilay N, Tauber A, Klein E, Chistyakov A, Ne’eman R, Shamay-Tsoory SG (2013) Asymmetry in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and aggressive behavior: a continuous theta-burst magnetic stimulation study. Soc Neurosci 8(2):178–188. doi:10.1080/17470919.2012.720602
Steinbeis N, Bernhardt BC, Singer T (2012) Impulse control and underlying functions of the left DLPFC mediate age-related and age-independent individual differences in strategic social behavior. Neuron 73(5):1040–1051. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2011.12.027
Dumontheil I, Burgess PW, Blakemore SJ (2008) Development of rostral prefrontal cortex and cognitive and behavioural disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol 50(3):168–181. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8749.2008.02026.x
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Leonard CM, Welcome SE, Kan E, Toga AW (2004) Longitudinal mapping of cortical thickness and brain growth in normal children. J Neurosci 24(38):8223–8231. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1798-04.2004
Blok BF, Holstege G (1998) The central nervous system control of micturition in cats and humans. Behav Brain Res 92(2):119–125
Griffiths DJ (2011) Use of functional imaging to monitor central control of voiding in humans. Handb Exp Pharmacol 202:81–97. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-16499-6_5
Watanabe H, Kawauchi A (1999) Locus coeruleus function in enuresis. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl 202:14–17 (discussion 18–19)
Neveus T (2003) The role of sleep and arousal in nocturnal enuresis. Acta Paediatr 92(10):1118–1123
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China 81201082 (X. Du). The authors would like to thank reviewers and editors for their useful advice and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jing Zhang and Du Lei have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Lei, D., Ma, J. et al. Brain Metabolite Alterations in Children with Primary Nocturnal Enuresis Using Proton Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Neurochem Res 39, 1355–1362 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1320-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1320-4