Abstract
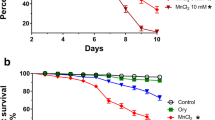
The toxicity caused by high concentrations of manganese (Mn) could be due to a production of free radicals. Minocycline is an effective antioxidant with a high potential to capture free radicals. We investigated the effect of minocycline in the activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase, and in the concentrations of nitric oxide (NO), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and mitochondrial malondialdehyde (MDA) in manganese-treated Drosophila melanogaster. Five groups of flies were used: (1) control: not treated; (2) continuously treated with minocycline (0.05 mM); (3) treated with 30 mM Mn for 6 days and then no additional treatment; (4) continuously treated with Mn; (5) treated only with Mn for 6 days and then treated with minocycline; (6) simultaneously treated with Mn and minocycline. On the 6th day, Mn treatment caused 50 % mortality; in the surviving flies increased levels of MDA (67.93 %), NO (11.04 %), H2O2 (14.62 %) and SOD and catalase activity (165.34 and 71.43 %, respectively) were detected. All the flies continuously treated with Mn died by the 21st day. On day 40, MDA levels were decreased in groups two, three and five (43.04, 29.67, and 34.72 % respectively), as well as NO in group two (29.21 %) and H2O2 in groups two and five (53.94 % and 78.69 %, respectively), while in group three the concentration of H2O2 was increased (408.25 %). In conclusion, Mn exerted a pro-oxidant effect on the 6th day as shown by the increased levels of oxidative markers. Minocycline extended the lifespan, increased the activity of SOD and reduced the levels of NO, H2O2 and mitochondrial MDA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soon-Il K, Je-Won J, Young-Joon A, Linda LR, Hyung-Wook K (2011) Drosophila as a model system for studying lifespan and neuroprotective activities of plant-derived compounds. J Asia Pac Entomol 14:509–517. doi:10.1016/j.aspen.2011.07.001
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M (2013) Role of astrocytes in manganese mediated neurotoxicity. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 18:14–23. doi:10.1186/2050-6511-14-23
Schmitt C, Strazielle N, Richaud P, Bouron A, Ghersi-Egea JF (2011) Active transport at the blood-CSF barrier contributes to manganese influx into the brain. J Neurochem 117:747–756. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07246
Gutierrez L, Zubow K, Nield J, Gambis A, Mollereau B, Lázaro F, Missirlis F (2013) Biophysical and genetic analysis of iron partitioning and ferritin function in Drosophila melanogaster. Metallomics 5:997–1005. doi:10.1039/c3mt00118k
Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz M, Aschner M (2013) Manganese toxicity in the central nervous system: the glutamine/glutamate-γ-aminobutyric acid cycle. J Intern Med 273:466–477. doi:10.1111/joim.12040
Racette BA, Aschner M, Guilarte TR, Dydak U, Criswell SR, Zheng W (2012) Pathophysiology of manganese-associated neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicology 33:881–886. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2011.12.010
Hyonok Y, Do-Sung K, Geum-Hwa L, Kee-Won K, Hyung-Ryong K, Han-Jung C (2011) Apoptosis induced by manganese on neuronal SK-N-MC cell line: endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondria dysfunction. Environ Health Toxicol 26:1–17. doi:10.5620/eht.2011.26.e2011017
Xu B, Wu SW, Lu CW, Deng Y, Liu W, Wei YG, Yang TY, Xu Z-F (2013) Oxidative stress involvement in manganese-induced alpha-synuclein oligomerization in organotypic brain slice cultures. Toxicology 305:71–78. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2013.01.006
Kraus RL, Pasieczny R, Lariosa-Willingham K, Turner MS, Jiang A, Trauger JWJ (2005) Antioxidant properties of minocycline: neuroprotection in an oxidative stress assay and direct radical-scavenging activity. Neurochem 94:819–827. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03219.x
Inamdar A, Chaudhuri A, O’Donnell J (2012) The protective effect of minocycline in a paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease model in Drosophila is modified in altered genetic backgrounds. Parkinson’s Dis 2012:1–16. doi:10.1155/2012/938528
Song Y, Wei EQ, Zhang WP, Ge QF, Liu JR, Wang ML, Huang XJ, Hu X, Chen Z (2006) Minocycline protects PC12 cells against NMDA-induced injury via inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase activation. Brain Res 1085:57–67 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16574083
Song X, Xu A, Pan W, Wallin B, Kivlin R, Lu S, Cao C, Bi Z, Wan Y (2008) Minocycline protects melanocytes against H2O2-induced cell death via JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Int J Mol Med 22:9–16 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18575770
Lin S, Zhang Y, Dodel R, Farlow MR, Paul SM, Du Y (2001) Minocycline blocks nitric-oxide induced neurotoxicity by inhibition of p38 MAP kinase in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Neurosci Lett 315: 61–64 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11711215
Bonilla E, Contreras R, Medina-Leendertz S, Mora M, Villalobos V, Bravo Y (2012) Minocycline increases the life span and motor activity and decreases lipid peroxidation in manganese treated Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicology 294:50–53. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2012.01.016
Bonilla E, Medina S, Díaz S (2002) Extension of life span and stress resistance of drosophila melanogaster by long-term supplementation with melatonin. Exp Gerontol 37:629–638 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11909680
Fernández-Vizarra E, Ferrín G, Pérez-Martos A, Fernández-Silva P, Zeviani M, Enríquez JA (2009) Isolation of mitochondria for biogenetical studies: an update. Mitochondrion 10:253–262. doi:10.1016/j.mito.2009.12.148
Bonilla-Ramirez L, Jimenez-Del-Rio M, Velez-Pardo C (2011) Acute and chronic metal exposure impairs locomotion activity in Drosophila melanogaster: a model to study Parkinsonism. Biometals 24:1045–1057. doi:10.1007/s10534-011-9463-0
Cordova FM, Aguiar AS Jr, Peres TV, Lopes MW, Gonçalves FM, Remor AP, Lopes SC, Pilati C, Latini AS, Prediger RD, Erikson KM, Aschner M, Leal RB (2012) In vivo manganese exposure modulates Erk, Akt and Darpp-32 in the striatum of developing rats, and impairs their motor function. PLoS One 7:e33057. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033057
Taka E, Mazzio E, Soliman KFA, Reams RR (2012) Microarray genomic profile of mitochondrial and oxidant response in manganese chloride treated PC12 cells. Neurotoxicology 33:162–168. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2012.01.001
Zhang P, Hatter A, Liu B (2007) Manganese chloride stimulates rat microglia to release hydrogen peroxide. Toxicol Lett 173:88–100 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17669604
Bornhorst J, Meyer S, Weber T, Böker C, Marschall T, Mangerich A, Beneke S, Bürkle A, Schwerdtle T (2013) Molecular mechanisms of Mn induced neurotoxicity: RONS generation, genotoxicity, and DNA-damage response. Mol Nutr Food Res 57:1255–1269. doi:10.1002/mnfr.201200758
Bornhorst J, Ebert F, Hartwig A, Michalke B, Schwerdtle T (2010) Manganese inhibits poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in human cells: a possible mechanism behind manganese-induced toxicity? J Environ Monit 12:2062–2069. doi:10.1039/c0em00252f
Katyal S, McKinnon PJ (2008) DNA strand breaks, neurodegeneration and aging in the brain. Mech Ageing Dev 129:483–491. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2013.06.018
Bürkle A, Grube K, Küpper JH (1992) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation: its role in inducible DNA amplification, and its correlation with the longevity of mammalian species. Exp Clin Immunogenet 9:230–240 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/1307244
Virág L (2005) Structure and function of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1: role in oxidative stress-related pathologies. Curr Vasc Pharmacol 3:209–214 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16026317
Kreutzmann P, Franz C, Schönfeld P (2012) Minocycline forms complexes with manganese in vitro: explaining reported beneficial effect in manganese treated Drosophila melanogaster. Toxicology 300:100–101. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2012.04.010
Liu M, Cai T, Zhao F, Zheng G, Wang Q, Chen Y, Huang C, Luo W, Chen J (2009) Effect of microglia activation on dopaminergic neuronal injury induced by manganese, and its possible mechanism. Neurotox Res 16:42–49. doi:10.1007/s12640-009-9045-x
Yoon H, Kim DS, Lee GH, Kim KW, Kim HR, Chae HJ (2011) Apoptosis induced by manganese on neuronal SK-N-MC cell line: endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and mitochondria dysfunction. Environ Health Toxicol 26:e2011017. doi:10.5620/eht.2011.26.e2011017
Reaney SH, Smith DR (2005) Manganese oxidation state mediates toxicity in PC12 cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 205:271–281 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15922012
Yin Z, Aschner JL, Dos Santos AP, Aschner M (2008) Mitochondrial-dependent manganese neurotoxicity in rat primary astrocyte cultures. Brain Res 1203:1–11. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.01.079
Stephenson AP, Schneider JA, Nelson BC, Atha DH, Jain A, Soliman KF, Aschner M, Mazzio E, Renee R (2013) Manganese-induced oxidative DNA damage in neuronal SH-SY5Y cells: attenuation of thymine base lesions by glutathione and N-acetylcysteine. Toxicol Lett 218:299–307. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.12.024
Marreilha dos Santos AP, Santos D, Au C, Milatovic D, Aschner M, Batoréu MC (2008) Antioxidants prevent the cytotoxicity of manganese in RBE4 cells. Brain Res 1236:200–205. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.07.125
Sl Schildknecht, Pape R, Müller N, Robotta M, Marquardt A, Bürkle A, Drescher M, Leist M (2011) Neuroprotection by minocycline caused by direct and specific scavenging of peroxynitrite. J Biol Chem 286(7):4991–5002. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.169565
Zhao F, Cai T, Liu M, Zheng G, Luo W, Chen J (2009) Manganese induces dopaminergic neurodegeneration via microglial activation in a rat model of manganism. Toxicol Sci 107:156–164. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfn213
Ponzoni S (2012) Macrophages-mediated neurotoxic effects of intra-nigral manganese administration are attenuated by minocycline. Neurosci Lett 506:136–140. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2011.10.066
Thomas M, Le WD (2004) Minocycline: neuroprotective mechanisms in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 10(6): 679–686 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14965330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mora, M., Bonilla, E., Medina-Leendertz, S. et al. Minocycline Increases the Activity of Superoxide Dismutase and Reduces the Concentration of Nitric Oxide, Hydrogen Peroxide and Mitochondrial Malondialdehyde in Manganese Treated Drosophila melanogaster . Neurochem Res 39, 1270–1278 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1309-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1309-z