Abstract
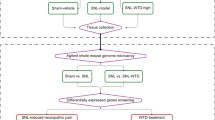
Increasing evidence has been accumulated for the effectiveness of acupuncture therapy in relieving pain. However, there are limited data on regulation of protein expression after electroacupuncture (EA) intervention. Thus, the present study is designed to determine changes in protein expression following EA stimulation in rats with sciatic nerve chronic constrictive injury (CCI) induced neuropathic pain. Sixty Wistar rats were equally randomized into normal control group, CCI group, and CCI with EA stimulation (EA) group. The CCI model was established by ligature of the left sciatic nerve. EA stimulation was applied at Zusanli (ST36) and Yanglingquan (GB34) in the EA group. Differentially expressed hypothalamic proteins in the three groups were identified by 2-D gel electrophoresis and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry. The functional clustering and pathway of the identified proteins were analyzed by Mascot software. Results showed that, after CCI, the thermal pain threshold of the affected hind footpad was decreased and was reversed gradually by 12 sessions of EA treatment. Following EA intervention, there were 17 hypothalamic proteins identified with significant changes in the expression (>twofold). Three gene-ontologies (oxidoreductase activity, oxidation reduction, and protein binding) were enriched, while there was a significant regulation of glycolysis/gluconeogenesis/hexose metabolism pathway. These data demonstrate that EA intervention can attenuate pain via regulation of expression of multiple proteins in the hypothalamus. Further, hypothalamic glucose metabolism may be important in supporting energy and neurotransmitter homeostasis in the effects of EA intervention.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leibing E, Leonhardt U, Koster G, Goerlitz A, Rosenfeldt JA, Hilgers R, Ramadori G (2002) Acupuncture treatment of chronic low-back pain—a randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial with 9-month follow-up. Pain 96(1–2):189–196
Carlsson CP, Sjolund BH (2001) Acupuncture for chronic low back pain: a randomized placebo-controlled study with long-term follow-up. Clin J Pain 17(4):296–305
Shen YF, Goddard G (2007) The short-term effects of acupuncture on myofascial pain patients after clenching. Pain Pract 7(3):256–264. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2007.00140.x
Kim HN, Park JH, Kim SK, Sun B, Koo S, Choi SM, Bae H, Min BI (2008) Electroacupuncture potentiates the antiallodynic effect of intrathecal neostigmine in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol Sci 58(5):357–360. doi:10.2170/physiolsci.SC008308
Yim YK, Lee H, Hong KE, Kim YI, Lee BR, Son CG, Kim JE (2007) Electro-acupuncture at acupoint ST36 reduces inflammation and regulates immune activity in collagen-induced arthritic mice. Evid Based Complement Altern Med 4(1):51–57. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel054
Huang W, Pach D, Napadow V, Park K, Long X, Neumann J, Maeda Y, Nierhaus T, Liang F, Witt CM (2012) Characterizing acupuncture stimuli using brain imaging with FMRI—a systematic review and meta-analysis of the literature. PLoS One 7(4):e32960. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032960
Bai L, Tian J, Zhong C, Xue T, You Y, Liu Z, Chen P, Gong Q, Ai L, Qin W, Dai J, Liu Y (2010) Acupuncture modulates temporal neural responses in wide brain networks: evidence from fMRI study. Mol Pain 6:73. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-6-73
Guo ZL, Longhurst JC (2007) Expression of c-Fos in arcuate nucleus induced by electroacupuncture: relations to neurons containing opioids and glutamate. Brain Res 1166:65–76. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2007.06.042
Zeng F, Song WZ, Liu XG, Xie HJ, Tang Y, Shan BC, Liu ZH, Yu SG, Liang FR (2009) Brain areas involved in acupuncture treatment on functional dyspepsia patients: a PET-CT study. Neurosci Lett 456(1):6–10. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.080
Blackburn-Munro G, Blackburn-Munro RE (2001) Chronic pain, chronic stress and depression: coincidence or consequence? J Neuroendocrinol 13(12):1009–1023
Han JS (2003) Acupuncture: neuropeptide release produced by electrical stimulation of different frequencies. Trends Neurosci 26(1):17–22
Wang SM, Kain ZN, White P (2008) Acupuncture analgesia: I. The scientific basis. Anesth Analg 106(2):602–610. doi:10.1213/01.ane.0000277493.42335.7b
Wang K, Zhang R, He F, Lin LB, Xiang XH, Ping XJ, Han JS, Zhao GP, Zhang QH, Cui CL (2012) Electroacupuncture frequency-related transcriptional response in rat arcuate nucleus revealed region-distinctive changes in response to low- and high-frequency electroacupuncture. J Neurosci Res 90(7):1464–1473. doi:10.1002/jnr.23028
Takeshige C, Oka K, Mizuno T, Hisamitsu T, Luo CP, Kobori M, Mera H, Fang TQ (1993) The acupuncture point and its connecting central pathway for producing acupuncture analgesia. Brain Res Bull 30(1–2):53–67
Napadow V, Kettner N, Liu J, Li M, Kwong KK, Vangel M, Makris N, Audette J, Hui KK (2007) Hypothalamus and amygdala response to acupuncture stimuli in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Pain 130(3):254–266. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2006.12.003
Zhang WT, Jin Z, Cui GH, Zhang KL, Zhang L, Zeng YW, Luo F, Chen AC, Han JS (2003) Relations between brain network activation and analgesic effect induced by low vs. high frequency electrical acupoint stimulation in different subjects: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Brain Res 982(2):168–178
Zhao ZQ (2008) Neural mechanism underlying acupuncture analgesia. Prog Neurobiol 85(4):355–375. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.05.004
Millan MJ (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 57(1):1–164
Liu JL, Chen SP, Gao YH, Meng FY, Wang SB, Wang JY (2010) Effects of repeated electroacupuncture on beta-endorphin and adrencorticotropic hormone levels in the hypothalamus and pituitary in rats with chronic pain and ovariectomy. Chin J Integr Med 16(4):315–323. doi:10.1007/s11655-010-0503-3
Jungblut PR, Schluter H (2011) Towards the analysis of protein species: an overview about strategies and methods. Amino Acids 41(2):219–222. doi:10.1007/s00726-010-0828-4
Bennett GJ, Xie YK (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33(1):87–107
Junker H, Venz S, Zimmermann U, Thiele A, Scharf C, Walther R (2011) Stage-related alterations in renal cell carcinoma—comprehensive quantitative analysis by 2D-DIGE and protein network analysis. PLoS One 6(7):e21867. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0021867
Gorg A, Weiss W, Dunn MJ (2004) Current 2-D electrophoresis technology for proteomics. Proteomics 4(12):3665–3685. doi:10.1002/pmic.200401031
Liu JL, Chen SP, Gao YH, Meng FY, Wang JY (2007) Observation on the analgesic effect of repeated electroacupuncture and its relation to changes of plasma beta-EP, ACTH and COR levels. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 32(5):306–312
Gao YH, Chen SP, Wang JY, Qiao LN, Meng FY, Xu QL, Liu JL (2012) Differential proteomics analysis of the analgesic effect of electroacupuncture intervention in the hippocampus following neuropathic pain in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 12:241. doi:10.1186/1472-6882-12-241
Hajszan T, MacLusky NJ, Leranth C (2005) Short-term treatment with the antidepressant fluoxetine triggers pyramidal dendritic spine synapse formation in rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 21(5):1299–1303. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2005.03968.x
Zhou L, Huang KX, Kecojevic A, Welsh AM, Koliatsos VE (2006) Evidence that serotonin reuptake modulators increase the density of serotonin innervation in the forebrain. J Neurochem 96(2):396–406. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03562.x
Goecks CS, Horst A, Moraes MS, Scheid T, Kolberg C, Bello-Klein A, Partata WA (2012) Assessment of oxidative parameters in rat spinal cord after chronic constriction of the sciatic nerve. Neurochem Res 37(9):1952–1958. doi:10.1007/s11064-012-0815-0
Ibi M, Matsuno K, Matsumoto M, Sasaki M, Nakagawa T, Katsuyama M, Iwata K, Zhang J, Kaneko S, Yabe-Nishimura C (2011) Involvement of NOX1/NADPH oxidase in morphine-induced analgesia and tolerance. J Neurosci 31(49):18094–18103. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4136-11.2011
Millan MJ (2002) Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol 66(6):355–474
Ossipov MH, Dussor GO, Porreca F (2010) Central modulation of pain. J Clin Invest 120(11):3779–3787. doi:10.1172/JCI43766
Lin JG, Chen WL (2008) Acupuncture analgesia: a review of its mechanisms of actions. Am J Chin Med 36(4):635–645
Kavoussi B, Ross BE (2007) The neuroimmune basis of anti-inflammatory acupuncture. Integr Cancer Ther 6(3):251–257. doi:10.1177/1534735407305892
Yang J, Yang Y, Chen JM, Liu WY, Lin BC (2008) Effect of hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus on acupuncture analgesia in the rat. Brain Res Bull 75(5):681–686. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2007.11.004
Burnstock G (2009) Acupuncture: a novel hypothesis for the involvement of purinergic signalling. Med Hypotheses 73(4):470–472. doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2009.05.031
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, Xu Q, Peng W, Liu W, Jensen TK, Pei Y, Wang F, Han X, Chen JF, Schnermann J, Takano T, Bekar L, Tieu K, Nedergaard M (2010) Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 13(7):883–888. doi:10.1038/nn.2562
Rokyta R, Holecek V, Pekarkova I, Krejcova J, Racek J, Trefil L, Yamamotova A (2003) Free radicals after painful stimulation are influenced by antioxidants and analgesics. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 24(5):304–309
Chi CH, Shiesh SC, Lin XZ (2002) Total antioxidant capacity and malondialdehyde in acute abdominal pain. Am J Emerg Med 20(2):79–82
Lee SH, Kim SY, Kim JH, Jung HY, Moon JH, Bae KH, Choi BT (2012) Phosphoproteomic analysis of electroacupuncture analgesia in an inflammatory pain rat model. Mol Med Report 6(1):157–162. doi:10.3892/mmr.2012.879
Swanson RA, Choi DW (1993) Glial glycogen stores affect neuronal survival during glucose deprivation in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 13(1):162–169. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.1993.19
Wilson JX (1997) Antioxidant defense of the brain: a role for astrocytes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 75(10–11):1149–1163
Arantes C, Nomizo R, Lopes MH, Hajj GN, Lima FR, Martins VR (2009) Prion protein and its ligand stress inducible protein 1 regulate astrocyte development. Glia 57(13):1439–1449. doi:10.1002/glia.20861
Holland-Fischer P, Greisen J, Grofte T, Jensen TS, Hansen PO, Vilstrup H (2009) Increased energy expenditure and glucose oxidation during acute nontraumatic skin pain in humans. Eur J Anaesthesiol 26(4):311–317. doi:10.1097/EJA.0b013e328324b5e9
Brown AM, Ransom BR (2007) Astrocyte glycogen and brain energy metabolism. Glia 55(12):1263–1271. doi:10.1002/glia.20557
Tanne D (2008) Impaired glucose metabolism and cerebrovascular diseases. Adv Cardiol 45:107–113. doi:10.1159/0000115190
Ruskin DN, Kawamura M, Masino SA (2009) Reduced pain and inflammation in juvenile and adult rats fed a ketogenic diet. PLoS One 4(12):e8349. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008349
Bak LK, Schousboe A, Waagepetersen HS (2006) The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: aspects of transport, neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem 98(3):641–653. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03913.x
Yan X, Yan E, Gao M, Weng HR (2013) Endogenous activation of presynaptic NMDA receptors enhances glutamate release from the primary afferents in the spinal dorsal horn in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.250522
Yang J, Chen JM, Yang Y, Liu WY, Song CY, Lin BC (2008) Investigating the role of hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in nociception of the rat. Int J Neurosci 118(4):473–485. doi:10.1080/00207450601123563
Yang J, Yang Y, Chen JM, Liu WY, Lin BC (2008) Investigating the role of the hypothalamic supraoptic nucleus in nociception in the rat. Life Sci 82(3–4):166–173. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2007.10.023
Yang J, Liu WY, Song CY, Lin BC (2006) Through central arginine vasopressin, not oxytocin and endogenous opiate peptides, glutamate sodium induces hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus enhancing acupuncture analgesia in the rat. Neurosci Res 54(1):49–56. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2005.10.006
Milligan ED, Watkins LR (2009) Pathological and protective roles of glia in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(1):23–36. doi:10.1038/nrn2533
Halassa MM, Fellin T, Takano H, Dong JH, Haydon PG (2007) Synaptic islands defined by the territory of a single astrocyte. J Neurosci 27(24):6473–6477. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1419-07.2007
Hertz L, Dringen R, Schousboe A, Robinson SR (1999) Astrocytes: glutamate producers for neurons. J Neurosci Res 57(4):417–428. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4547(19990815)57:4<417:AID-JNR1>3.0.CO;2-N
Sung HJ, Kim YS, Kim IS, Jang SW, Kim YR, Na DS, Han KH, Hwang BG, Park DS, Ko J (2004) Proteomic analysis of differential protein expression in neuropathic pain and electroacupuncture treatment models. Proteomics 4(9):2805–2813. doi:10.1002/pmic.200300821
Acknowledgments
This study was jointly supported by the National Nature Science Foundation (90709031, 81102647) and the Special Project of Chinese Medicine (973) of the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CB531904).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Chen, S., Xu, Q. et al. Proteomic Analysis of Differential Proteins Related to Anti-nociceptive Effect of Electroacupuncture in the Hypothalamus Following Neuropathic Pain in Rats. Neurochem Res 38, 1467–1478 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1047-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1047-7