Abstract
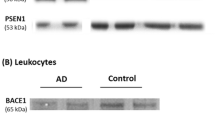
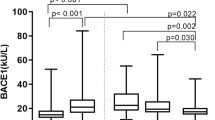
It has been suggested that mild cognitive impairment (MCI) patients deteriorate faster than the healthy elderly population and have an increased risk of developing dementia. Certain blood molecular biomarkers have been identified as prognostic markers in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The present study was aimed to assess the status of the platelet amyloid precursor protein (APP) metabolism in MCI and AD subjects and establish to what extent any variation could have a prognostic value suggestive of predictive AD in MCI patients. Thirty-four subjects diagnosed with MCI and 45 subjects with AD were compared to 28 healthy elderly individuals for assessing for protein levels of APP, β-APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1), presenilin 1 (PS1) and a disintegrin and metalloproteinase-10 (ADAM-10) by western blot, and for the enzyme activities of BACE1 and γ-secretase by using specific fluorogenic substrates, in samples of platelets. A similar pattern in the healthy elderly and MCI patients was found for BACE1 and PS1 levels. A reduction of APP levels in MCI and AD patients compared with healthy elderly individuals was found. Augmented levels of ADAM-10 in both MCI and AD were displayed in comparison with age-matched control subjects. The ratio ADAM-10/BACE1 was higher for the MCI group versus AD group. Whereas BACE1 and PS1 levels were only increased in AD regarding to controls, BACE1 and γ-secretase activities augmented significantly in both MCI and AD groups. Finally, differences and similarities between MCI and AD patients were observed in several markers of platelet APP processing. Larger sample sets from diverse populations need to be analyzed to define a signature for the presence of MCI or AD pathology and to early detect AD at the MCI stage.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- ADAM-10:
-
A disintegrin and metalloproteinase-10
- APH-1:
-
Anterior pharynx-defective-1
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- α-APPs and β-APPs:
-
Secreted forms of APP
- βA:
-
β-Amyloid
- BACE:
-
β-APP cleaving enzyme
- MCI:
-
Mild cognitive impairment
- PEN-2:
-
Presenilin enhancer-2
- PS1:
-
Presenilin 1
References
Escudero J, Zajicek JP, Ifeachor E (2011) Early detection and characterization of Alzheimer’s disease in clinical scenarios using bioprofile concepts and K-means. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2011:6470–6473
Ray S, Britschgi M, Herbert C, Takeda-Uchimura Y, Boxer A, Blennow K, Friedman LF, Galasko DR, Jutel M, Karydas A, Kaye JA, Leszek J, Miller BL, Minthon L, Quinn JF, Rabinovici GD, Robinson WH, Sabbagh MN, So YT, Sparks DL, Tabaton M, Tinklenberg J, Yesavage JA, Tibshirani R, Wyss-Coray T (2007) Classification and prediction of clinical Alzheimer’s diagnosis based on plasma signaling proteins. Nat Med 13:1359–1362
Catricala S, Torti M, Ricevuti G (2012) Alzheimer disease and platelets: how’s that relevant. Immun Ageing 9:20
Colciaghi F, Borroni B, Pastorino L, Marcello E, Zimmermann M, Cattabeni F, Padovani A, Di Luca M (2002) [Alpha]-secretase ADAM10 as well as [alpha] APPs is reduced in platelets and CSF of Alzheimer disease patients. Mol Med 8:67–74
Evin G, Zhu A, Holsinger RM, Masters CL, Li QX (2003) Proteolytic processing of the Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein in brain and platelets. J Neurosci Res 74:386–392
Esch FS, Keim PS, Beattie EC, Blacher RW, Culwell AR, Oltersdorf T, McClure D, Ward PJ (1990) Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science 248:1122–1124
Haass C, Schlossmacher MG, Hung AY, Vigo-Pelfrey C, Mellon A, Ostaszewski BL, Lieberburg I, Koo EH, Schenk D, Teplow DB et al (1992) Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature 359:322–325
Shoji M, Golde TE, Ghiso J, Cheung TT, Estus S, Shaffer LM, Cai XD, McKay DM, Tintner R, Frangione B et al (1992) Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science 258:126–129
Verdile G, Gandy SE, Martins RN (2007) The role of presenilin and its interacting proteins in the biogenesis of Alzheimer’s beta amyloid. Neurochem Res 32:609–623
Krishnaswamy S, Verdile G, Groth D, Kanyenda L, Martins RN (2009) The structure and function of Alzheimer’s gamma secretase enzyme complex. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 46:282–301
Bush AI, Martins RN, Rumble B, Moir R, Fuller S, Milward E, Currie J, Ames D, Weidemann A, Fischer P, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1990) The amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer’s disease is released by human platelets. J Biol Chem 265:15977–15983
Colciaghi F, Marcello E, Borroni B, Zimmermann M, Caltagirone C, Cattabeni F, Padovani A, Di Luca M (2004) Platelet APP, ADAM 10 and BACE alterations in the early stages of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 62:498–501
Tang K, Hynan LS, Baskin F, Rosenberg RN (2006) Platelet amyloid precursor protein processing: a bio-marker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Sci 240:53–58
Smith CC (1997) Stimulated release of the beta-amyloid protein of Alzheimer’s disease by normal human platelets. Neurosci Lett 235:157–159
Di Luca M, Pastorino L, Bianchetti A, Perez J, Vignolo LA, Lenzi GL, Trabucchi M, Cattabeni F, Padovani A (1998) Differential level of platelet amyloid beta precursor protein isoforms: an early marker for Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 55:1195–1200
Padovani A, Borroni B, Colciaghi F, Pettenati C, Cottini E, Agosti C, Lenzi GL, Caltagirone C, Trabucchi M, Cattabeni F, Di Luca M (2002) Abnormalities in the pattern of platelet amyloid precursor protein forms in patients with mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 59:71–75
Rosenberg RN, Baskin F, Fosmire JA, Risser R, Adams P, Svetlik D, Honig LS, Cullum CM, Weiner MF (1997) Altered amyloid protein processing in platelets of patients with Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 54:139–144
Zlokovic BV (2004) Clearing amyloid through the blood-brain barrier. J Neurochem 89:807–811
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC, Ivnik RJ, Tangalos EG, Kokmen E (1999) Mild cognitive impairment: clinical characterization and outcome. Arch Neurol 56:303–308
Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rabins PV, Ritchie K, Rossor M, Thal L, Winblad B (2001) Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol 58:1985–1992
The Canadian Study of Health and Aging Working Group (2000) The incidence of dementia in Canada. Neurology 55:66–73
Winblad B, Palmer K, Kivipelto M, Jelic V, Fratiglioni L, Wahlund LO, Nordberg A, Backman L, Albert M, Almkvist O, Arai H, Basun H, Blennow K, de Leon M, DeCarli C, Erkinjuntti T, Giacobini E, Graff C, Hardy J, Jack C, Jorm A, Ritchie K, van Duijn C, Visser P, Petersen RC (2004) Mild cognitive impairment–beyond controversies, towards a consensus: report of the international working group on mild cognitive impairment. J Intern Med 256:240–246
Borroni B, Anchisi D, Paghera B, Vicini B, Kerrouche N, Garibotto V, Terzi A, Vignolo LA, Di Luca M, Giubbini R, Padovani A, Perani D (2006) Combined 99mTc-ECD SPECT and neuropsychological studies in MCI for the assessment of conversion to AD. Neurobiol Aging 27:24–31
Chertkow H (2008) Diagnosis and treatment of dementia: introduction. Introducing a series based on the third Canadian consensus conference on the diagnosis and treatment of dementia. CMAJ 178:316–321
Bermejo P, Martin-Aragon S, Benedi J, Susin C, Felici E, Gil P, Ribera JM, Villar AM (2008) Peripheral levels of glutathione and protein oxidation as markers in the development of Alzheimer’s disease from mild cognitive impairment. Free Radic Res 42:162–170
Bermejo P, Martin-Aragon S, Benedi J, Susin C, Felici E, Gil P, Ribera JM, Villar AM (2008) Differences of peripheral inflammatory markers between mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Immunol Lett 117:198–202
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of department of health and human services task force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Tinetti ME (1986) Performance-oriented assessment of mobility problems in elderly patients. J Am Geriatr Soc 34:119–126
Ankri J, Andrieu S, Beaufils B, Grand A, Henrard JC (2005) Beyond the global score of the Zarit burden interview: useful dimensions for clinicians. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 20:254–260
Cockrell JR, Folstein MF (1988) Mini-mental state examination (MMSE). Psychopharmacol Bull 24:689–692
Schmand B, Walstra G, Lindeboom J, Teunisse S, Jonker C (2000) Early detection of Alzheimer’s disease using the Cambridge cognitive examination (CAMCOG). Psychol Med 30:619–627
Makatura TJ, Lam CS, Leahy BJ, Castillo MT, Kalpakjian CZ (1999) Standardized memory tests and the appraisal of everyday memory. Brain Inj 13:355–367
Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg-Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J (1994) The neuropsychiatric inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 44:2308–2314
Torres RM, Miralles R, Garcia-Caselles MP, Arellano M, Aguilera A, Pi-Figueras M, Cervera AM (2004) Observational scale and geriatric depression scale of Yesavage to identify depressive symptoms in older patients. Arch Gerontol Geriatr Suppl 9:437–442
Ready RE, Ott BR, Grace J, Fernandez I (2002) The Cornell-Brown scale for quality of life in dementia. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 16:109–115
Vignini A, Sartini D, Morganti S, Nanetti L, Luzzi S, Provinciali L, Mazzanti L, Emanuelli M (2011) Platelet amyloid precursor protein isoform expression in Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for peripheral marker. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 24:529–534
Padovani A, Pastorino L, Borroni B, Colciaghi F, Rozzini L, Monastero R, Perez J, Pettenati C, Mussi M, Parrinello G, Cottini E, Lenzi GL, Trabucchi M, Cattabeni F, Di Luca M (2001) Amyloid precursor protein in platelets: a peripheral marker for the diagnosis of sporadic AD. Neurology 57:2243–2248
Yang LB, Lindholm K, Yan R, Citron M, Xia W, Yang XL, Beach T, Sue L, Wong P, Price D, Li R, Shen Y (2003) Elevated beta-secretase expression and enzymatic activity detected in sporadic Alzheimer disease. Nat Med 9:3–4
Johnston JA, Liu WW, Todd SA, Coulson DT, Murphy S, Irvine GB, Passmore AP (2005) Expression and activity of beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1096–1100
Zetterberg H, Andreasson U, Hansson O, Wu G, Sankaranarayanan S, Andersson ME, Buchhave P, Londos E, Umek RM, Minthon L, Simon AJ, Blennow K (2008) Elevated cerebrospinal fluid bace1 activity in incipient Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 65:1102–1107
Geslani DM, Tierney MC, Herrmann N, Szalai JP (2005) Mild cognitive impairment: an operational definition and its conversion rate to Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 19:383–389
Visser PJ, Kester A, Jolles J, Verhey F (2006) Ten-year risk of dementia in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 67:1201–1207
Zhong Z, Ewers M, Teipel S, Burger K, Wallin A, Blennow K, He P, McAllister C, Hampel H, Shen Y (2007) Levels of beta-secretase (BACE1) in cerebrospinal fluid as a predictor of risk in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:718–726
Liu WW, Todd S, Craig D, Passmore AP, Coulson DT, Murphy S, Irvine GB, Johnston JA (2007) Elevated platelet beta-secretase activity in mild cognitive impairment. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 24:464–468
Postina R, Schroeder A, Dewachter I, Bohl J, Schmitt U, Kojro E, Prinzen C, Endres K, Hiemke C, Blessing M, Flamez P, Dequenne A, Godaux E, van Leuven F, Fahrenholz F (2004) A disintegrin-metalloproteinase prevents amyloid plaque formation and hippocampal defects in an Alzheimer disease mouse model. J Clin Invest 113:1456–1464
Endres K, Fahrenholz F (2010) Upregulation of the alpha-secretase ADAM10–risk or reason for hope? FEBS J 277:1585–1596
Lammich S, Kojro E, Postina R, Gilbert S, Pfeiffer R, Jasionowski M, Haass C, Fahrenholz F (1999) Constitutive and regulated alpha-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by a disintegrin metalloprotease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3922–3927
Marcinkiewicz M, Seidah NG (2000) Coordinated expression of beta-amyloid precursor protein and the putative beta-secretase BACE and alpha-secretase ADAM10 in mouse and human brain. J Neurochem 75:2133–2143
Tyler SJ, Dawbarn D, Wilcock GK, Allen SJ (2002) Alpha- and beta-secretase: profound changes in Alzheimer’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299:373–376
Gatta LB, Albertini A, Ravid R, Finazzi D (2002) Levels of beta-secretase BACE and alpha-secretase ADAM10 mRNAs in Alzheimer hippocampus. Neuroreport 13:2031–2033
Li QX, Whyte S, Tanner JE, Evin G, Beyreuther K, Masters CL (1998) Secretion of Alzheimer’s disease Abeta amyloid peptide by activated human platelets. Lab Invest 78:461–469
Kim MJ, Lee KM, Son YD, Jeon HA, Kim YB, Cho ZH (2012) Increased basal forebrain metabolism in mild cognitive impairment: an evidence for brain reserve in incipient dementia. J Alzheimers Dis 32:927–938
Gorham P, Bark N, Bjorkhem I, Meaney S, Crisby M (2010) Platelet alpha- and beta-secretase activities are not significantly affected by dementia or mild cognitive impairment in Swedish patients. Curr Alzheimer Res 7:134–139
Hata S, Fujishige S, Araki Y, Taniguchi M, Urakami K, Peskind E, Akatsu H, Araseki M, Yamamoto K, Martins RN, Maeda M, Nishimura M, Levey A, Chung KA, Montine T, Leverenz J, Fagan A, Goate A, Bateman R, Holtzman DM, Yamamoto T, Nakaya T, Gandy S, Suzuki T (2011) Alternative processing of gamma-secretase substrates in common forms of mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease: evidence for gamma-secretase dysfunction. Ann Neurol 69:1026–1031
Farfara D, Trudler D, Segev-Amzaleg N, Galron R, Stein R, Frenkel D (2011) Gamma-secretase component presenilin is important for microglia beta-amyloid clearance. Ann Neurol 69:170–180
Cai D, Leem JY, Greenfield JP, Wang P, Kim BS, Wang R, Lopes KO, Kim SH, Zheng H, Greengard P, Sisodia SS, Thinakaran G, Xu H (2003) Presenilin-1 regulates intracellular trafficking and cell surface delivery of beta-amyloid precursor protein. J Biol Chem 278:3446–3454
Kakuda N, Shoji M, Arai H, Furukawa K, Ikeuchi T, Akazawa K, Takami M, Hatsuta H, Murayama S, Hashimoto Y, Miyajima M, Nagashima Y, Yamaguchi H, Kuwano R, Nagaike K, Ihara Y (2012) Altered gamma-secretase activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. EMBO Mol Med 4:344–352
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by a Grant (PI021745) from the National Research Foundation of the Spanish Ministry of Health (FIS).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no financial or other conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bermejo-Bescós, P., Martín-Aragón, S., Jiménez-Aliaga, K. et al. Processing of the Platelet Amyloid Precursor Protein in the Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI). Neurochem Res 38, 1415–1423 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1039-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1039-7