Abstract
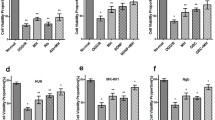
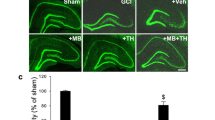
Recent studies provide solid evidence for the importance to delineate the co-relationship between preconditioning stimuli and therapeutic efficacy of drugs commonly used in clinic. However, very little is known about this important topic. In the present study, we investigated the effects of hyperthermia on the protective role of ginkgolides on astrocytes against ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury and also evaluated the effects of the timing of co-treatment of hyperthermia with ginkgolides on astrocytes against the I/R injury. We demonstrated that there is a synergistic action between hyperthermic and pharmacological preconditioning to protect astrocytes against the I/R injury. Our findings also showed that astrocytes have completely different responses to the treatment with hyperthermia or ginkgolides alone or co-treatment together at different stages of the I/R process. Hyperthermic preconditioning before the I/R can protect astrocytes against the I/R injury. However, if treated in the ischemia and reperfusion stage, hyperthermia exacerbates the cell injury and significantly attenuates the protective effectiveness of ginkgolides. These findings imply that the timing of treatment with hypothermia and/or ginkgolides is one of the key factors to determine their protective effects on the cells against the I/R injury.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H, Chopp M, Welch KMA (1991) Effect of mild hyperthermia on the ischemic infarct volume after middle cerebral artery occlusoin in the rat. Neurology 41:1133–1135
Chopp M, Chen H, Ho KL, Dereski MO, Brown E, Hetzel FW, Welch KM (1989) Transient hyperthermia protects against subsequent forebrain ischemic cell damage in the rat. Neurology 39(10):1396–1398
Dietrich WD, Busto R, Valdes I, Loor Y (1990) Effects of normothermic verses mild hyperthermic forebrain ischemia in rats. Stroke 21:1318–1325
Duveau V, Arthaud S, Serre H, Rougier A, Le Gal La Salle G (2005) Transient hyperthermia protects against subsequent seizures and epilepsy-induced cell damage in the rat. Neurobiol Dis 19(1–2):142–149
Duveau V, Arthaud S, Rougier A, Le Gal La Salle G (2007) Polysialylation of NCAM is upregulated by hyperthermia and participates in heat shock preconditioning- induced neuroprotection. Neurobiol Dis 26(2):385–395
Fang D, Li Z, Zhong-ming Q, Mei WX, Ho YW, Yuan XW, Ya K (2008) Expression of bystin in reactive astrocytes induced by ischemia/reperfusion and chemical hypoxia in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 1782(11):658–663
Fang D, Ming QZ, Li Z, Mei WX, Ya K (2009) Hypothermia attenuates protective effects of ginkgolides on astrocytes from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurochem Int 55(4):181–186
Ginsberg MD, Busto R (1998) Combating hyperthermia in acute stroke: a significant clinical concern. Stroke 29(2):529–534
He W, Qian Zhong M, Zhu L, Christopher Q, Du F, Yung WH, Ke Y (2008) Ginkgolides mimic the effects of hypoxic preconditioning to protect C6 cells against ischemic injury by up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and erythropoietin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40(4):651–662
Hotchkiss R, Nunnally I, Lindquist S, Taulien J, Perdrizet G, Karl I (1993) Hyperthermia protects mice against the lethal effects of endotoxin. Am J Physiol 265(6 Pt 2): R1447–R1457
Ikeda T, Xia XY, Xia YX, Ikenoue T (1999) Hyperthermic preconditioning prevents blood-brain barrier disruption produced by hypoxia-ischemia in newborn rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 117(1):53–58
Murray CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA (1986) Preconditioning with ischaemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischaemic myocardium. Circulation 74:1124–1136
Noor R, Wang C, Shuaib A (2003) Effects of hyperthermia on infarct volume in embolic model of cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett 349:130–132
Qian ZM, To Y, Tang PL, Feng YM (1999) Ansferrin receptors on the plasma membrane of cultured rat astrocytes. Exp Brain Res 129(3):473–476
Qian ZM, Liao QK, To Y, Ke Y, Tsoi YK, Wang GF, Ho KP (2000) Transferrinbound and transferrin-free iron uptake by the cultured brain astrocytes. Cell Mol Biol 46(3):541–548
Saini M, Saqqur M, Kamruzzaman A, Lees KR, Shuaib A, VISTA Investigators Collaborators (24), Lees KR, Bath PM, Bluhmki E, Claesson L, Curram J, Davis SM, Diener HC, Donnan GA, Fisher M, Gregson BA, Grotta J, Hacke W, Hennerici MG, Hommel M, Kaste M, Lyden P, Marler J, Muir K, Sacco RL, Shuaib A, Teal P, Wahlgren NG, Warach S, Weimar C (2009) Effect of hyperthermia on prognosis after acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 40(9):3051–3059
Shpargel KB, Jalabi W, Jin Y, Dadabayev A, Penn MS, Trapp BD (2008) Preconditioning paradigms and pathways in the brain. Cleve Clin J Med 75(suppl 2): S77–S82
Stone TW (2003) Pre-conditioning protection in the brain. Br J Pharmacol 140:229–230
Tortorici MA, Kochanek PM, Poloyac SM (2007) Effects of hypothermia on drug disposition, metabolism, and response: a focus of hypothermia-mediated alterations on the cytochrome P450 enzyme system. Crit Care Med 35(9):2196–2204
Wang Y, Mao BY, Deng YL, Xiao D (2006) An experimental research of hyperthermic preconditioning on the spinal cord injury. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 37(1):69–72
Xu H, Aibiki M, Nagoya J (2002) Neuroprotective effects of hyperthermic preconditioning on infarcted volume after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats: role of adenosine receptors. Crit Care Med 30(5):1126–1130
Yeo TP (2004) Heat stroke: a comprehensive review. AACN Clin Issues 15(2):280–293
Zaremba J (2004) Hyperthermia in ischemic stroke. Med Sci Monit 10(6):RA148–RA53
Zhang P, Abraham VS, Kraft KR, Rabchevsky AG, Scheff SW, Swain JA (2000) Hyperthermic preconditioning protects against spinal cord ischemic injury. Ann Thorac Surg 70(5):1490–1495
Zhu L, Wu XM, Yang L, Du F, Qian ZM (2007) Up-regulation of HIF-1alpha expression induced by ginkgolides in hypoxic neurons. Brain Res 1166:1–8
Zhu L, Xu YJ, Du F, Qian ZM (2007) Ginkgolides protect primary cortical neurons from potassium cyanide-induced hypoxic injury. Exp Brain Res 179(4):665–671
Zhu L, Ke Y, Wu XM, Yang L, Lu Y, Qian ZM (2008) Ginkgolides protect PC12 cells against hypoxia-induced injury by p42/p44 MAPK pathway-dependent upregulation of HIF-1a expression and HIF-1 DNA binding activity. J Cell Biochem 103:564–575
Acknowledgments
The studies in our laboratories were supported by The Competitive Earmarked Grants of The Hong Kong Research Grants Council (CUHK466907-KY), NSFC-RGC Joint Research Grant (N-CUHK433/08-KY), Key Project Grant of Jiangsu Province (BG2007607), Grants from Shenzhen-Hong Kong Innovation Circle Programa (2007, 2008, 2009), National Natural Science Foundation of China (30770806, 30971197) and Nantong City Applied Research Grant (K2007021). We declare that we have no financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, F., Qian, Zm., Zhu, L. et al. A Synergistic Role of Hyperthermic and Pharmacological Preconditioning to Protect Astrocytes Against Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Neurochem Res 36, 312–318 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0327-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0327-8