Abstract
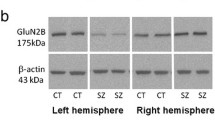
There is accumulating evidence that disturbances in N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA-R) functioning are associated with the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. To assess actual changes in the expression of the GluN1 subunit and its isoforms, we measured absolute differences in the levels of mRNA/protein for panGluN1 (eight isoforms altogether) as well as the mRNA individual isoforms in the postmortem left/right hippocampus of patients with schizophrenia in comparison with non-psychiatric subjects. There were no significant differences in the panGluN1 subunit mRNA expression, but the absolute left/right differences were much more pronounced in the patients with schizophrenia. Protein levels of the GluN1 subunit in the left hippocampus in male schizophrenic patients were lower than controls. The expression of the NR1-4b isoform was attenuated in the left, whereas the NR1-2b was reduced in the right hippocampus of schizophrenic patients. Isoforms associated with the efficiency of NMDA-induced gene expression and with phosphorylation occurred more commonly in schizophrenic hippocampi. In summary, our study suggests that NMDA-R hypofunction in schizophrenia might be selectively dependent on the dysregulation of GluN1 subunit expression, which exhibits a somewhat different expression in the left/right hippocampus of psychotic patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Haren NEM, Cahn W, Hulshoff HE et al (2008) Schizophrenia as a progressive brain disease. Eur Psychiatry 23:245–254
Harrison PJ, Weinberger DR (2005) Schizophrenia genes, gene expression, and neurobiology: on the matter of their convergence. Mol Psychiatry 10:40–68
Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:327–335
Kristiansen LV, Huerta I, Beneyto M et al (2007) NMDA receptors and schizophrenia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:48–55
Dracheva S, Marras SAE, Elhakem SL et al (2001) N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor expression in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of elderly patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158:1400–1410
Scherzer CR, Landwehrmeyer GB, Kerner JA et al (1998) Expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit mRNA in the human brain: hippocampus and cortex. J Comp Neurol 390:75–90
Foldes RL, Rampersad V, Kamboj RK (1993) Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding human hippocampal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits: evidence for alternative RNA splicing. Gene 131:293–298
Zimmer M, Fink TM, Franke Y et al (1995) Cloning and structure of the gene encoding the human N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR1). Gene 159:219–223
Tingley WG, Roche KW, Thompson AK et al (1993) Regulation of NMDA receptor phosphorylation by alternative splicing of the C-terminal domain. Nature 364:70–73
Kutsuwada T, Kashiwabuchi N, Mori H et al (1992) Molecular diversity of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature 358(6381):36–41
Chen L, Huang LY (1991) Sustained potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated glutamate responses through activation of protein kinase C by a mu opioid. Neuron 7(2):319–326
Zukin RS, Bennett VL (1995) Alternatively spliced isoforms of the NMDAR1 receptor subunit. Trends Neurosci 18:306–313
Kristiansen LV, Beneyto M, Haroutunian V et al (2006) Changes in NMDA receptor subunits and interacting PSD proteins in dorsolateral prefrontal and anterior cingulate cortex indicate abnormal regional expression in schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 11:737–747
Le Corre S, Harper CG, Lopez P et al (2000) Increased levels of expression of an NMDAR1 splice variant in the superior temporal gyrus in schizophrenia. NeuroReport 11:983–986
Gao X-M, Sakai K, Roberts RC et al (2000) Ionotropic glutamate receptors and expression of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits in subregions of human hippocampus: effects of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:1141–1149
Humphries C, Mortimer A, Hirsch S et al (1996) NMDA receptor mRNA correlation with antemortem cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. NeuroReport 7:2051–2055
Law AJ, Deakin JFW (2001) Asymetrical reductions of hippocampal NMDAR1 glutamate receptor mRNA in the psychoses. NeuroReport 12:2971–2974
Toro C, Deakin JFW (2005) NMDA receptor subunit NR1 and postsynaptic protein PSD-95 in hippocampus and orbitofrontal cortex in schizophrenia and mood disorder. Schizophr Res 80:323–330
Thompson PM, Egbufoama S, Vawter MP (2003) SNAP-25 reduction in the hippocampus of patients with schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 39:919–928
Woolley CS, Weiland NG, McEwen BS et al (1997) Estradiol increases the sensitivity of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells to NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic input: correlation with dendritic spine density. J Neurosci 17:1848–1859
McEwen B (2002) Estrogen activations through the brain. Recent Prog Horm Res 57:357–384
Huber TJ, Borsutzky M, Schneider U et al (2004) Psychotic gonadal function: evidence supporting the oestrogen hypothesis. Acta Psychiatr Scand 109:269–274
Toga AW, Thompson PM (2003) Mapping brain asymmetry. Nat Neurosci 4:37–48
Pilowsky LS, Bressan RA, Stone JM et al (2006) First in vivo evidence of an NMDA receptor deficit in medication-free schizophrenic patients. Mol Psychiatry 11:118–119
Hynd MR, Lewohl JM, Scott HL et al (2003) Biochemical and molecular studies using human brain tissue. J Neurochem 85:543–562
Rozozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 365–386
Bradley J, Carter SR, Rao VR et al (2006) Splice variants of the NR1 subunit differentially induce NMDA receptor-dependent gene expression. J Neurosci 26:1065–1076
Beneyto M, Kristiansen LV, Oni-Orisan A et al (2007) Abnormal glutamate receptor expression in the medial temporal lobe in schizophrenia and mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1888–1902
Harrison PJ, Law AJ, Eastwood SL (2003) Glutamate receptors and transporters in the hippocampus in schizophrenia. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1003:94–101
Kryštofíková Z, Kozmiková I, Hovorková P et al (2008) Lateralization of hippocampal nitric oxide mediator system in people with Alzheimer disease, multi-infarct dementia and schizophrenia. Neurochem Int 53:118–125
Leung A, Chue P (2000) Sex differences in schizophrenia, a review of evidence. Acta Psychiatr Scand 101:3–38
Akbarian S, Sucher NJ, Bradley D et al (1996) Selective alterations in gene expression for NMDA receptor subunits in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. J Neurosci 16:19–30
Scott DB, Blanpied TA, Swanson GT et al (2001) An NMDA receptor ER retention signal regulated by phosphorylation and alternative splicing. J Neurosci 21:3063–3072
Tingley WG, Ehlers MD, Kameyama K et al (1997) Characterization of protein kinase A and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit using phosphorylation site-specific antibodies. J Biol Chem 272:5157–5166
Sánchez-Pérez AM, Felipo V (2005) Serines 890 and 896 of the NMDA receptor subunit NR1 are differentially phosphorylated by protein kinase C isoforms. Neurochem Int 47:84–91
Standley S, Roche KW, McCallum J et al (2000) PDZ domain suppression of an ER retention signal in NMDA receptor NR1 splice variants. Neuron 28:887–898
Rutter AR, Freman FM, Stephenson FA (2002) Further characterization of the molecular interaction between PSD-95 and NMDA receptor: the effect of the NR1 splice variant and evidence of modulation of channel gating. J Neurochem 81:1298–1307
Toyoda H, Takahata R, Inayama Y et al (1997) Effect of antipsychotic drugs on the gene expression of NMDA receptor subunits in rats. Neurochem Res 22:249–252
Hanaoka T, Toyada H, Mizuna T et al (2003) Alterations in NMDA receptor subunit levels in the brain regions of rats chronically administered typical or atypical antipsychotic drugs. Neurochem Res 28:919–924
Schmitt A, Zink M, Muller B et al (2003) Effects of long-term antipsychotic treatment on NMDA receptor binding and gene expression of subunits. Neurochem Res 28:235–241
Riva MA, Tascedda F, Lovati E et al (1997) Regulation of NMDA receptor subunit messenger RNA levels in the rat brain following acute and chronic exposure to antipsychotic drugs. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 50:136–142
Acknowledgments
The research was supported by the Projects MZ00PCP2005 and IGA MZCR NR/9324. The authors thank Dr. Emerich Majer (Department of Pathology, Prague Mental Hospital Bohnice, Czech Rep.) for taking samples and Prof. Martin Alda MD, FRCPC (Dalhousie University, Halifax, Canada) for helpful comments.
Declaration of Interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures, related directly or indirectly to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vrajová, M., Šťastný, F., Horáček, J. et al. Expression of the Hippocampal NMDA Receptor GluN1 Subunit and Its Splicing Isoforms in Schizophrenia: Postmortem Study. Neurochem Res 35, 994–1002 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0145-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0145-z