Abstract
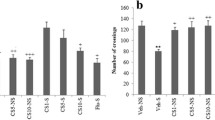
We studied the effect of chronic caffeine on parameters related to oxidative stress in different brain regions of stressed and non-stressed rats. Wistar rats were divided into three groups: control (receiving water), caffeine 0.3 g/L and caffeine 1.0 g/L (in the drinking water). These groups were subdivided into non-stressed and stressed (repeated restraint stress during 40 days). Lipid peroxide levels and the total radical-trapping potential were assessed, as well as antioxidant enzyme activities superoxide dismutase, gluthatione peroxidase, and catalase in hippocampus, striatum and cerebral cortex. Results showed interactions between stress and caffeine, especially in the cerebral cortex, since caffeine increased the activity of some antioxidant enzymes, but not in stressed animals. We concluded that chronic administration of caffeine led, in some cases, to increased activity of antioxidant enzymes. However, these effects were not observed in the stressed animals.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashton CH (1987) Caffeine and health. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 295:1293–1294
Kalda A, Yu L, Oztas E et al (2006) Novel neuroprotection by caffeine and adenosine A (2A) receptor antagonists in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Sci 248:9–15. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.003
Xu K, Xu Y, Brown-Jermyn D et al (2006) Estrogen prevents neuroprotection by caffeine in the mouse 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 26:535–541. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3008-05.2006
Ross GW, Abbott RD, Petrovitch H et al (2000) Relationship between caffeine intake and Parkinson’s disease. JAMA 284:1378–1379. doi:10.1001/jama.284.11.1378
Maia L, de Mendonça A (2002) Does caffeine intake protect from Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Neurol 9:377–382. doi:10.1046/j.1468-1331.2002.00421.x
Rothwell K (1974) Dose-related inhibition of chemical carcinogenesis in mouse skin by caffeine. Nature 252:69–70. doi:10.1038/252069a0
Fredholm BB, Battig K, Holmén J et al (1999) Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol Rev 51:83–133
Gómez-Ruiz JA, Leake DS, Ames JM (2007) In vitro antioxidant activity of coffee compounds and their metabolites. J Agric Food Chem 55:6962–6969. doi:10.1021/jf0710985
Lee C (2000) Antioxidant ability of caffeine and its metabolites based on the study of oxygen radical absorbing capacity and inhibition of LDL peroxidation. Clin Chim Acta 295:141–154. doi:10.1016/S0009-8981(00)00201-1
Shi X, Dalal NS, Jain AC (1991) Antioxidant behavior of caffeine: efficient scavenging of hydroxyl radicals. Food Chem Toxicol 29:1–6. doi:10.1016/0278-6915(91)90056-D
Mukhopadhyay S, Mondal A, Poddar MK (2003) Chronic administration of caffeine: effect on the activities of hepatic antioxidant enzymes of Ehrlich ascites tumor-bearing mice. Indian J Exp Biol 41:283–289
Rossowska MJ, Nakamoto T (1994) Effects of chronic caffeine feeding on the activities of oxygen free radical defense enzymes in the growing rat heart and liver. Experientia 50:465–468. doi:10.1007/BF01920748
Cochrane CG (1991) Mechanisms of oxidant injury of cells. Mol Aspects Med 12:137–147. doi:10.1016/0098-2997(91)90009-B
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (2007) Free radicals in biology and medicine, 4a edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Olanow CW (1992) An introduction to the free radical hypothesis in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 32(Suppl):S2–S9. doi:10.1002/ana.410320703
Bolaños JP, Almeida A, Stewart V et al (1997) Nitric oxide-mediated mitochondrial damage in the brain: mechanisms and implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 68:2227–2240
Tsigos C, Chrousos GP (2002) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and stress. J Psychosom Res 53:865–871. doi:10.1016/S0022-3999(02)00429-4
Derin N, Aydin S, Yargicoglu P et al (2006) Changes in visual evoked potentials, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in rats exposed to restraint stress: effects of l-carnitine. Int J Neurosci 116:205–221. doi:10.1080/00207450690969805
Das D, Banerjee RK (1993) Effects of stress on the antioxidant enzymes and gastric ulceration. Mol Cell Biochem 125:115–125. doi:10.1007/BF00936440
Vasconcellos AP, Nieto FB, Crema LM et al (2006) Chronic lithium treatment has antioxidant properties but does not prevent oxidative damage induced by chronic variate stress. Neurochem Res 31:1141–1151. doi:10.1007/s11064-006-9139-2
Fontella FU, Siqueira IR, Vasconcellos AP et al (2005) Repeated restraint stress induces oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res 30:105–111. doi:10.1007/s11064-004-9691-6
McIntosh LJ, Cortopassi KM, Sapolsky RM (1998) Glucocorticoids may alter antioxidant enzyme capacity in the brain: kainic acid studies. Brain Res 791:215–222. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(98)00104-8
Liu J, Wang X, Shigenaga MK et al (1996) Immobilization stress causes oxidative damage to lipid, protein, and DNA in the brain of rats. FASEB J 10:1532–1538
Gasior M, Jaszyna M, Peters J et al (2000) Changes in the ambulatory activity and discriminative stimulus effects of psychostimulant drugs in rats chronically exposed to caffeine: effect of caffeine dose. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1101–1111
Esterbauer H, Cheeseman KH (1990) Determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products: malonaldehyde and 4-hydroxynonenal. Methods Enzymol 186:407–421. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86134-H
Evelson P, Travacio M, Repetto M et al (2001) Evaluation of total reactive antioxidant potential (TRAP) of tissue homogenates and their cytosols. Arch Biochem Biophys 388:261–266. doi:10.1006/abbi.2001.2292
Delmas-Beauvieux MC, Peuchant E, Dumon MF et al (1995) Relationship between red blood cell antioxidant enzymatic system status and lipoperoxidation during the acute phase of malaria. Clin Biochem 28:163–169. doi:10.1016/0009-9120(94)00071-3
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Wendel A (1981) Glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 77:325–333. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(81)77046-0
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL et al (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Manoli LP, Gamaro GD, Silveira PP et al (2000) Effect of chronic variate stress on thiobarbituric-acid reactive species and on total radical-trapping potential in distinct regions of rat brain. Neurochem Res 25:915–921. doi:10.1023/A:1007592022575
Lores Arnaiz S, Travacio M, Llesuy S et al (1998) Regional vulnerability to oxidative stress in a model of experimental epilepsy. Neurochem Res 23:1477–1483
Oishi K, Yokoi M, Maekawa S et al (1999) Oxidative stress and haematological changes in immobilized rats. Acta Physiol Scand 165:65–69. doi:10.1046/j.1365-201x.1999.00482.x
Azam S, Hadi N, Khan NU et al (2003) Antioxidant and prooxidant properties of caffeine, theobromine and xanthine. Med Sci Monit 9:325–330
Alptekin N, Seçkin S, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S et al (1996) Lipid peroxides, glutathione, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase and gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase activities in several tissues of rats following water-immersion stress. Pharmacol Res 34:167–169. doi:10.1006/phrs.1996.0084
Akpinar D, Yargiçoglu P, Derin N et al (2007) The effect of lipoic acid on antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in rats exposed to chronic restraint stress. Physiol Res 57:893–901
Derin N, Yargiçoğlu P, Aslan M et al (2006) The effect of sulfite and chronic restraint stress on brain lipid peroxidation and anti-oxidant enzyme activities. Toxicol Ind Health 22:233–240. doi:10.1191/0748233706th264oa
Torres IL, Gamaro GD, Silveira-Cucco SN et al (2001) Effect of acute and repeated restraint stress on glucose oxidation to CO2 in hippocampal and cerebral cortex slices. Braz J Med Biol Res 34:111–116
Halliwell B (2001) Role of free radicals in the neurodegenerative diseases: therapeutic implications for antioxidant treatment. Drugs Aging 18:685–716. doi:10.2165/00002512-200118090-00004
Haber F, Weiss J (1934) The catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide by iron salts. Proc R Soc Lond 147:332–351
de Oliveira MR, Silvestrin RB, Mello E, Souza T, Moreira JC (2007) Oxidative stress in the hippocampus, anxiety-like behavior and decreased locomotory and exploratory activity of adult rats: effects of sub acute vitamin A supplementation at therapeutic doses. Neurotoxicology 28:1191–1199. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2007.07.008
Warner BB, Stuart L, Gebb S et al (1996) Redox regulation of manganese superoxide dismutase. Am J Physiol 271:L150–L158
Yoo HY, Chang MS, Rho HM (1999) The activation of the rat copper/zinc superoxide dismutase gene by hydrogen peroxide through the hydrogen peroxide-responsive element and by paraquat and heat shock through the same heat shock element. J Biol Chem 274:23887–23892
Kim ST, Choi JH, Chang JW et al (2005) Immobilization stress causes increases in tetrahydrobiopterin, dopamine, and neuromelanin and oxidative damage in the nigrostriatal system. J Neurochem 95:89–98. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03342.x
Bhattacharya A, Ghosal S, Bhattacharya SK (2001) Anti-oxidant effect of Withania somnifera glycowithanolides in chronic footshock stress-induced perturbations of oxidative free radical scavenging enzymes and lipid peroxidation in rat frontal cortex and striatum. J Ethnopharmacol 74:1–6. doi:10.1016/S0378-8741(00)00309-3
Madrigal JL, Olivenza R, Moro MA et al (2001) Glutathione depletion, lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial dysfunction are induced by chronic stress in rat brain. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:420–429. doi:10.1016/S0893-133X(00)00208-6
Acknowledgments
Financial support: National Research Council of Brazil (CNPq), FAPERGS-PRONEX and FINEP/Rede IBN 01.06.0842-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-0107-5
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noschang, C.G., Krolow, R., Pettenuzzo, L.F. et al. Interactions Between Chronic Stress and Chronic Consumption of Caffeine on the Enzymatic Antioxidant System. Neurochem Res 34, 1568–1574 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9945-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9945-4