Abstract
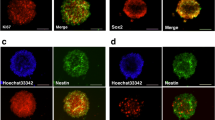
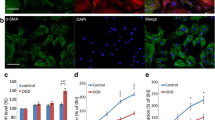
Cerebral ischemia increases neural progenitor cell proliferation and neurogenesis. However, the precise molecular mechanism is poorly understood. The present study was undertaken to determine roles of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt and their signaling pathways in neural progenitor cells exposed to hypoxia/reoxygenation (H/R), an in vitro model of ischemia/reperfusion. Neural progenitor cells were isolated from postnatal mouse brain. ERK and Akt were transiently activated during the early phase of reoxygenation following 4-h of hypoxia. The ERK activation was inhibited by U0126, a specific inhibitor of MEK, but not by LY294002, a specific inhibitor of PI3K, whereas the Akt activation was blocked by LY294002, but not by U0126. Reoxygenation following 4-h hypoxia stimulated cell proliferation, which was dependent on ERK and Akt activation. Inhibitors of growth factor receptor (AG1478) and Src (PP2) and the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine did not affect activation of ERK and Akt, while the Ras and Raf inhibitors inhibited activation of ERK, but not Akt. PKC inhibitors inhibited both ERK and Akt activation. Taken together, these results suggest that H/R induces activation of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt survival signaling pathways through a PKC-dependent mechanism. These pathways may be responsible for the repair process during ischemia/reperfusion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin K, Minami M, Lan JQ, Mao XO, Batteur S, Simon RP, Greenberg DA (2001) Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(8):4710–4715
Liu J, Solway K, Messing RO, Sharp FR (1998) Increased neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus after transient global ischemia in gerbils. J Neurosci 18(19):7768–7778
Nakatomi H, Kuriu T, Okabe S, Yamamoto S, Hatano O, Kawahara N, Tamura A, Kirino T, Nakafuku M (2002) Regeneration of hippocampal pyramidal neurons after ischemic brain injury by recruitment of endogenous neural progenitors. Cell 110(4):429–441
Sasaki T, Kitagawa K, Sugiura S, Omura-Matsuoka E, Tanaka S, Yagita Y, Okano H, Matsumoto M, Hori M (2003) Implication of cyclooxygenase-2 on enhanced proliferation of neural progenitor cells in the adult mouse hippocampus after ischemia. J Neurosci Res 72(4):461–471
Sharp FR, Liu J, Bernabeu R (2002) Neurogenesis following brain ischemia. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 134(1–2):23–30
Hayashi T, Iwai M, Ikeda T, Jin G, Deguchi K, Nagotani S, Zhang H, Sehara Y, Nagano I, Shoji M, Ikenoue T, Abe K (2005) Neural precursor cells division and migration in neonatal rat brain after ischemic/hypoxic injury. Brain Res 1038(1):41–49
Fisher M (2003) Stem cell transplantation for stroke: does it work, and if so, how? Stroke 34(8):2083
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM (2000) Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256(1):34–41
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu BE, Karandikar M, Berman K, Cobb MH (2001) Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways: regulation and physiological functions. Endocr Rev 22(2):153–183
Xia Z, Dickens M, Raingeaud J, Davis RJ, Greenberg ME (1995) Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 270(5240):1326–1331
Cobb MH (1999) MAP kinase pathways. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 71(3–4):479–500
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88(4):435–437
Kandel ES, Hay N (1999) The regulation and activities of the multifunctional serine/threonine kinase Akt/PKB. Exp Cell Res 253(1):210–229
Coffer PJ, Jin J, Woodgett JR (1998) Protein kinase B (c-Akt): a multifunctional mediator of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J 335(Pt 1):1–13
Yu JM, Kim JH, Song GS, Jung JS (2006) Increase in proliferation and differentiation of neural progenitor cells isolated from postnatal and adult mice brain by Wnt-3a and Wnt-5a. Mol Cell Biochem 288(1–2):17–28
Bjorklund A, Lindvall O (2000) Self-repair in the brain. Nature 405(6789):892–895
Temple S (2001) The development of neural stem cells. Nature 414(6859):112–117
Palmer TD, Markakis EA, Willhoite AR, Safar F, Gage FH (1999) Fibroblast growth factor-2 activates a latent neurogenic program in neural stem cells from diverse regions of the adult CNS. J Neurosci 19(19):8487–8497
Yamamoto S, Yamamoto N, Kitamura T, Nakamura K, Nakafuku M (2001) Proliferation of parenchymal neural progenitors in response to injury in the adult rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol 172(1):115–127
Kilic U, Kilic E, Reiter RJ, Bassetti CL, Hermann DM (2005) Signal transduction pathways involved in melatonin-induced neuroprotection after focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Pineal Res 38(1):67–71
Gabryel B, Pudelko A, Malecki A (2004) Erk1/2 and Akt kinases are involved in the protective effect of aniracetam in astrocytes subjected to simulated ischemia in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 494(2–3):111–120
Lederer ED, Sohi SS, McLeish KR (2000) Parathyroid hormone stimulates extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activity through two independent signal transduction pathways: role of ERK in sodium-phosphate cotransport. J Am Soc Nephrol 11(2):222–231
Nosaka Y, Arai A, Kanda E, Akasaki T, Sumimoto H, Miyasaka N, Miura O (2001) Rac is activated by tumor necrosis factor alpha and is involved in activation of Erk. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 285(3):675–679
Agazie Y, Ischenko I, Hayman M (2002) Concomitant activation of the PI3K-Akt and the Ras-ERK signaling pathways is essential for transformation by the V-SEA tyrosine kinase oncogene. Oncogene 21(5):697–707
Gingery A, Bradley E, Shaw A, Oursler MJ (2003) Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase coordinately activates the MEK/ERK and AKT/NFkappaB pathways to maintain osteoclast survival. J Cell Biochem 89(1):165–179
Rommel C, Clarke BA, Zimmermann S, Nunez L, Rossman R, Reid K, Moelling K, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (1999) Differentiation stage-specific inhibition of the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway by Akt. Science 286(5445):1738–1741
Moelling K, Schad K, Bosse M, Zimmermann S, Schweneker M (2002) Regulation of Raf-Akt cross-talk. J Biol Chem 277(34):31099–31106
Lee JT Jr, McCubrey JA (2002) The Raf/MEK/ERK signal transduction cascade as a target for chemotherapeutic intervention in leukemia. Leukemia 16(4):486–507
Sato K, Sato A, Aoto M, Fukami Y (1995) c-Src phosphorylates epidermal growth factor receptor on tyrosine 845. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 215(3):1078–1087
Jin K, Mao XO, Del Rio Guerra G, Jin L, Greenberg DA (2005) Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor-like growth factor stimulates cell proliferation in cerebral cortical cultures through phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurosci Res 81(4):497–505
Muralikrishna Adibhatla R, Hatcher JF (2006) Phospholipase A2, reactive oxygen species, and lipid peroxidation in cerebral ischemia. Free Radic Biol Med 40(3):376–387
Droge W (2002) Free radicals in the physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev 82(1):47–95
Goldkorn T, Balaban N, Matsukuma K, Chea V, Gould R, Last J, Chan C, Chavez C (1998) EGF-receptor phosphorylation and signaling are targeted by H2O2 redox stress. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 19(5):786–798
Guyton KZ, Liu Y, Gorospe M, Xu Q, Holbrook NJ (1996) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase by H2O2. Role in cell survival following oxidant injury. J Biol Chem 271(8):4138–4142
Sugano T, Yanagita T, Yokoo H, Satoh S, Kobayashi H, Wada A (2006) Enhancement of insulin-induced PI3K/Akt/GSK-3beta and ERK signaling by neuronal nicotinic receptor/PKC-alpha/ERK pathway: up-regulation of IRS-1/-2 mRNA and protein in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem 98(1):20–33
Zhang P, Wang YZ, Kagan E, Bonner JC (2000) Peroxynitrite targets the epidermal growth factor receptor, Raf-1, and MEK independently to activate MAPK. J Biol Chem 275(29):22479–22486
Mochly-Rosen D (1995) Localization of protein kinases by anchoring proteins: a theme in signal transduction. Science 268(5208):247–251
Nishizuka Y (1995) Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses. Faseb J 9(7):484–496
Wang J, Bright R, Mochly-Rosen D, Giffard RG (2004) Cell-specific role for epsilon- and betaI-protein kinase C isozymes in protecting cortical neurons and astrocytes from ischemia-like injury. Neuropharmacology 47(1):136–145
Koponen S, Goldsteins G, Keinanen R, Koistinaho J (2000) Induction of protein kinase Cdelta subspecies in neurons and microglia after transient global brain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20(1):93–102
Harada K, Maekawa T, Abu Shama KM, Yamashima T, Yoshida K (1999) Translocation and down-regulation of protein kinase C-alpha, -beta, and -gamma isoforms during ischemia-reperfusion in rat brain. J Neurochem 72(6):2556–2564
Bright R, Mochly-Rosen D (2005) The role of protein kinase C in cerebral ischemic and reperfusion injury. Stroke 36(12):2781–2790
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the MRC program of MOST/KOSEF (R13-2005-009) and the 21st Century Frontier/Stem Cell Research Committee (SC3130) in South Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, S.M., Jung, D.S., Kwon, C.H. et al. Hypoxia/Reoxygenation Stimulates Proliferation Through PKC-Dependent Activation of ERK and Akt in Mouse Neural Progenitor Cells. Neurochem Res 32, 1932–1939 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9390-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9390-1