Abstract
We aimed to establish age-related reference values for Erythropoietin (EPO) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and to evaluate concentrations in neurological diseases. CSF and serum EPO was measured in controls with tension-type headache (CTTH), in patients with ALS, dementia and depression using ELISA technique.
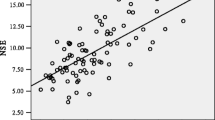
Stability experiments showed CSF EPO to be stable for two and a half months and over two thaw/freeze cycles. A positive correlation of CSF EPO with age was found (P < 0.01). We found a CSF/serum EPO concentration ratio of 0.126, pointing towards an intrathecal synthesis of EPO. The ALS group showed significantly lowered CSF EPO compared to age-matched CTTH (P < 0.012), whereas the dementia and depression group showed no significant differences compared to CTTH.
The establishment of age-related reference values in a large cohort of controls will improve the interpretation of future CSF EPO evaluations in neurological diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brines ML, Ghezzi P, Keenan S et al (2000) Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10526–10531
Juul SE, Anderson DK, Li Y et al (1998) Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor in the developing human central nervous system. Pediatr Res 43:40–49
Marti HH (2004) Erythropoietin and the hypoxic brain. J Exp Biol 207:3233–3242
Buemi M, Cavallaro E, Floccari F et al (2002) Erythropoietin and the brain: from neurodevelopment to neuroprotection. Clin Sci (Lond) 103:275–282
Knabe W, Knerlich F, Washausen S et al (2004) Expression patterns of erythropoietin and its receptor in the developing midbrain. Anat Embryol (Berl) 207:503–512
Sakanaka M, Wen TC, Matsuda S et al (1998) In vivo evidence that erythropoietin protects neurons from ischemic damage. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4635–4640
Agnello D, Bigini P, Villa P et al (2002) Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res 952:128–134
Eid TBrines M (2002) Recombinant human erythropoietin for neuroprotection: what is the evidence? Clin. Breast Cancer 3(Suppl 3):S109–115
Brooks BR, Miller RG, Swash M et al (2000) El Escorial revisited: revised criteria for the diagnosis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 1:293–299
Strong M, Rosenfeld J (2003) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a review of current concepts. Amyotroph Lateral Scler Other Motor Neuron Disord 4:136–143
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M et al (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Neary D, Snowden JS, Gustafson L et al (1998) Frontotemporal lobar degeneration: a consensus on clinical diagnostic criteria. Neurology 51:1546–1554
Roman GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T et al (1993) Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN international workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Petersen RC, Smith GE, Waring SC et al (1997) Aging, memory, and mild cognitive impairment. Int Psychogeriatr1:(Suppl 9) 65–69
Sussmuth SD, Tumani H, Ecker D et al (2003) Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: disease stage related changes of tau protein and S100 beta in cerebrospinal fluid and creatine kinase in serum. Neurosci Lett 353:57–60
Felgenhauer K (1974) Protein size and cerebrospinal fluid composition. Klin Wochenschr 52:1158–1164
Fisher JW (2003) Erythropoietin: physiology and pharmacology update. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 228:1–14
Xenocostas A, Cheung WK, Farrell F et al (2005) The pharmacokinetics of erythropoietin in the cerebrospinal fluid after intravenous administration of recombinant human erythropoietin. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 61:189–195
Nakamura T, Ebihara I, Shimada N et al (1998) Elevated levels of erythropoietin in cerebrospinal fluid of depressed patients. Am J Med Sci 315:199–201
Juul SE, Harcum J, Li Y et al (1997) Erythropoietin is present in the cerebrospinal fluid of neonates. J Pediatr 130:428–430
van Engelen BG, Lamers KJ, Gabreels FJ et al (1992) Age-related changes of neuron-specific enolase, S-100 protein, and myelin basic protein concentrations in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chem 38:813–816
May C, Kaye JA, Atack JR et al (1990) Cerebrospinal fluid production is reduced in healthy aging. Neurology 40:500–503
Eckardt KU, Kurtz A, Hirth P et al (1988) Evaluation of the stability of human erythropoietin in samples for radioimmunoassay. Klin Wochenschr 66:241–245
Springborg JB, Sonne B, Frederiksen HJ et al (2003) Erythropoietin in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage originates from the brain. Brain Res 984:143–148
Sussmuth SD, Reiber H, Tumani H (2001) Tau protein in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): a blood-CSF barrier related evaluation in patients with various neurological diseases. Neurosci Lett 300:95–98
Ehrenreich H, Hasselblatt M, Dembowski C et al (2002) Erythropoietin therapy for acute stroke is both safe and beneficial. Mol Med 8:495–505
Ehrenreich H, Aust C, Krampe H et al (2004) Erythropoietin: novel approaches to neuroprotection in human brain disease. Metab Brain Dis 19:195–206
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors have not reported any conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Widl, K., Brettschneider, J., Schattauer, D. et al. Erythropoietin in Cerebrospinal Fluid: Age-related Reference Values and Relevance in Neurological Disease. Neurochem Res 32, 1163–1168 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9286-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-007-9286-0