Abstract
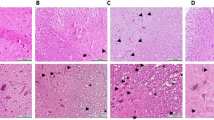
Spinal cord injury (SCI) results in rapid and significant oxidative stress. This study was aimed to investigate the possible beneficial effects of Ebselen in comparison with Methylprednisolone in experimental SCI. Thirty six Wistar albino rats (200–250 g) were divided in to six groups; A (control), B (only laminectomy), C (Trauma; laminectomy + spinal trauma), D (Placebo group; laminectomy + spinal trauma + serum physiologic), E (Methylprednisolone group; laminectomy + spinal trauma + Methylprednisolone treated), F (Ebselen group; laminectomy + spinal trauma + Ebselen treated), containing 6 rats each. Spinal cord injury (SCI) was performed by placement of an aneurysm clip, extradurally at the level of T11–12. After this application, group A, B and C were not treated with any drug. Group D received 1 ml serum physiologic. Group E received 30 mg/kg Methylprednisolone and, Group F received 10 mg/kg Ebselen intraperitoneally (i.p.). Rats were neurologically examined 24 h after trauma and spinal cord tissue samples had been harvested for both biochemical and histopathological evaluation. All rats were paraplegic after SCI except the ones in group A and B. Neurological scores were not different in traumatized rats than that of non-traumatized ones. SCI significantly increased spinal cord tissue malondialdehyde (MDA) and protein carbonyl (PC) levels and also decreased superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) enzyme activities compared to control. Methylprednisolone and Ebselen treatment decreased tissue MDA and PC levels and prevented inhibition of the enzymes SOD, GSH-Px and CAT in the tissues. However, the best results were obtained with Ebselen. In groups C and D, the neurons of the spinal cord tissue became extensively dark and degenerated with picnotic nuclei. The morphology of neurons in groups E and F were very well protected, but not as good as the control group. The number of neurons in the spinal cord tissues of the groups C and D were significantly less than the groups A, B, E and F. We concluded that the use of Ebselen treatment might have potential benefits in spinal cord tissue damage on clinical grounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. B. Bracken M. J. Shepard W. F. Collins T. R. Holford W. Young D. S. Baskin H. M Eisenberg E. Flamm L. Leo-Summers J. Maroon et al. (1990) ArticleTitleA randomized, controlled trial of methylprednisolone or naloxone in the treatment of acute spinal-cord injury. Results of the Second National Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study N. Engl. J. Med. 322 1405–1411 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BB3s7js1A%3D Occurrence Handle2278545
M. B. Bracken M. J. Shepard W. F. Collins T. R Holford D. S. Baskin H. M. Eisenberg E. Flamm L. Leo-Summers J. C. Maroon L. F. Marshall et al. (1992) ArticleTitleMethylprednisolone or naloxone treatment after acute spinal cord injury: one-year follow-up data. Results of the Second National Acute Spinal Cord Injury Study J. Neurosurg. 76 23–31 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By2D2sbgtlw%3D Occurrence Handle1727165
D. K. Anderson E. D. Hall (1993) ArticleTitlePathophysiology of spinal cord trauma Ann. Emerg. Med. 22 987–992 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB2snpvV0%3D Occurrence Handle8503537
C. H. Tator (1998) ArticleTitleBiology of neurological recovery and functional restoration after spinal cord injury Neurosurgery 42 696–708 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3jtlyhsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9574633
M. Maiorino A. Roveri M. Coassin F. Ursini (1988) ArticleTitleKinetic mechanism and substrate specificity of glutathione peroxidase activity of ebselen (PZ51) Biochem. Pharmacol. 37 2267–2271 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXksFSku7k%3D Occurrence Handle3377822
A. Muller E. Cadenas P. Graf H. Sies (1984) ArticleTitleA novel biologically active seleno-organic compound I. Glutathione peroxidase-like activity in vitro and antioxidant capacity of PZ 51 (Ebselen) Biochem. Pharmacol. 33 3235–3239 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqD383nsVw%3D Occurrence Handle6487370
A. Malecki R. Garrido M. P. Mattson B. Henning M. Toborek (2000) ArticleTitle4-hydroxynonenal induces oxidative stress and death of cultured spinal cord neurons J. Neurochem. 74 2278–2287 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsVKku7s%3D Occurrence Handle10820187
T. Takasago E. E. Peters D. I. Graham H. Masayasu I. M. Macrae (1997) ArticleTitleNeuroprotective efficacy of ebselen an antioxidant with anti-inflammatory actions, in a rodent model of permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion Br. J. Pharmacol. 122 1251–1256 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXnsFWltbk%3D Occurrence Handle9401794
T. Yamaguchi K. Sano K. Takakura I. Saito Y. Shinohara T. Asano H. Yasuhara (1998) ArticleTitleEbselen in acute ischemic stroke: a placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial Stroke 29 12–17 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXntVKqsg%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9445321
I. Saito T. Asano K. Sano K. Takakura H. Abe T. Yoshimoto H. Kikuchi T. Ohta S. Ishibashi (1998) ArticleTitleNeuroprotective effect of an antioxidant, ebselen, in patients with delayed neurological deficits after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage Neurosurgery 42 269–278 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c7ktFarsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle9482177
A. S. Rivlin C. H. Tator (1978) ArticleTitleEffect of duration of acute spinal cord compression in a new acute cord injury model in the rat Surg. Neurol. 10 39–43
A. S. Rivlin C. H. Tator (1977) ArticleTitleObjective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat J. Neurosurg. 47 577–581 Occurrence Handle903810
O. H. Lowry N. J. Rosebrough R. J. Randall (1951) ArticleTitleProtein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent J. Biol. Chem. 193 265–275 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaG38XhsVyrsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle14907713
H. H. Draper M. Hadley (1990) ArticleTitleMalondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation Methods Enzymol. 186 421–431 Occurrence Handle2233309
R. L. Levine D. Garland C. N. Oliver A. Amici I. Climent A. G. Lenz B. W. Ahn S. Shaltiel E. R. Stadtman (1990) ArticleTitleDetermination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins Methods Enzymol. 186 464–478 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXksVGhtLY%3D Occurrence Handle1978225
Y. Sun L. W. Oberley Y. Li (1988) ArticleTitleA simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase Clin. Chem. 34 497–500 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXhvVamt7Y%3D Occurrence Handle3349599
H. Aebi (1974) Catalase H. U. Bergmeyer (Eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis Academic Press New York 673–677
D. E. Paglia W. N. Valentine (1967) ArticleTitleStudies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70 158–169 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF2sXks1Wjur8%3D Occurrence Handle6066618
A. I. Faden P. H. Chan S. Longar (1987) ArticleTitleAlterations in lipid metabolism, Na+,K+-ATPase activity, and tissue water content of spinal cord following experimental traumatic injury J. Neurochem. 48 1809–1816 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXksFKrtbg%3D Occurrence Handle3033150
K. Iwasa T. Ikata K. Fukuzawa (1989) ArticleTitleProtective effect of vitamin E on spinal cord injury by compression and concurrent lipid peroxidation Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 6 599–606 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaA38nitlE%3D Occurrence Handle2753391
D. Liu R. Yang X. Yan D. J. McAdoo (1994) ArticleTitleHydroxyl radicals generated in vivo kill neurons in the rat spinal cord: Electrophysiological, histological, and neurochemical results J. Neurochem. 62 37–44 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXnsVOmtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8263539
S. K. Agrawal M. G. Fehlings (1997) ArticleTitleRole of NMDA and non-NMDA ionotropic glutamate receptors in traumatic spinal cord axonal injury J. Neurosci. 17 1055–1063 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXos1yrsA%3D%3D Occurrence Handle8994060
Y. Taoka K. Okajima (1998) ArticleTitleSpinal cord injury in the rat Prog. Neurobiol. 55 1–18 Occurrence Handle9602498
E. D. Means D. K. Anderson (1983) ArticleTitleNeuronophagia by leukocytes in experimental spinal cord injury J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 42 707–719 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiuD3srit1E%3D Occurrence Handle6631457
R. J. Reiter D. X. Tan M. Allegra (2002) ArticleTitleMelatonin: Reducing molecular pathology and dysfunction due to free radicals and associated reactants Neuro. Endocrinol. Lett. Suppl. 1 3–8
G. W. Konat R. C. Wiggins (1985) ArticleTitleEffect of reactive oxygen species on myelin membrane proteins J. Neurochem. 45 1113–1118 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlsFGntL8%3D Occurrence Handle4031880
E. Kaptanoglu M. Tuncel S. Palaoglu A. Konan E. Demirpence K. Kilinc (2000) ArticleTitleComparison of the effects of melatonin and methylprednisolone in experimental spinal cord injury J. Neurosurg. Spine 93 77–84 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltFShsbc%3D
E. D. Hall (1993) ArticleTitleLipid antioxidants in acute central nervous system injury Ann. Emerg. Med. 22 1022–1027 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByyB2snpslU%3D Occurrence Handle8503522
R. D. Saunders L. L. Dugan P. Demediuk E. D. Means L. A. Horrocks D. K. Anderson (1987) ArticleTitleEffects of methylprednisolone and the combination of alpha-tocopherol and selenium on arachidonic acid metabolism and lipid peroxidation in traumatized spinal cord tissue J. Neurochem. 49 24–31 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXktlOntrg%3D Occurrence Handle3108455
H. B. Demopoulos E. S. Flamm D. D. Pietonigro M. L. Seligman (1980) ArticleTitleThe free radical pathology and the microcirculation in the major central nervous system disorders Acta. Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 492 91–119 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXhvV2ltb0%3D Occurrence Handle6939309
E. C. Benzel (1990) ArticleTitleA new rat spinal cord injury model. A ventral compression technique J Spinal Disorders 4 334–338
E. D. Means D. K. Anderson T. R. Waters L. Kalaf (1981) ArticleTitleEffect of methylprednisolone in compression trauma to the feline spinal cord J. Neurosurg. 55 200–208 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xlt1SksLs%3D Occurrence Handle7252543
A. Wendel M. Fausel H. Safayhi G. Tiegs R. Otter (1984) ArticleTitleA novel biologically active seleno-organic compound, II: activity of PZ51 in relation to glutathione peroxidase Biochem. Pharmacol. 33 3241–3245 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXjvFKitw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle6487371
C. W. Nogueira L. N. Rotta G. Zeni D. O. Souza J. B. Rocha (2002) ArticleTitleExposure to ebselen changes glutamate uptake and release by rat brain synaptosomes Neurochem. Res. 27 283–288 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsFCr Occurrence Handle11958529
A. Muller H. Gabriel H. Sies (1985) ArticleTitleA novel biologically active selenoorganic compound, IV: Protective glutathione-dependent effect of PZ 51 (ebselen) against ADP-Fe induced lipid peroxidation in isoleted hepatocytes Biochem. Pharmacol. 34 1185–1189 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiqC1MbhvFY%3D Occurrence Handle3994741
H. Safayhi G. Tiegs A. Wendel (1985) ArticleTitleA novel biologically active selenoorganic compound, V: inhibition by ebselen (PZ 51) on rat peritoneal neutrophil lipoxygenase Biochem. Pharmacol. 34 2691–2694 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXkvFyntrY%3D Occurrence Handle2990494
V. Ullrich P. Weber F. Meisch F. Appen (1996) ArticleTitleEbselen-binding equilibria between plasma and target proteins Biochem. Pharmacol. 52 15–19 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjvVGntLo%3D Occurrence Handle8678900
S. Ichikawa K. Omura T. Katayama N. Okamura T. Ohtsuka S. Ishibashi H. Masayasu (1987) ArticleTitleInhibition of superoxide anion production in guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes by a seleno-organic compound, ebselen J. Pharmacobio. Dyn. 10 595–597 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXjtFGntQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle2831335
R. Hattori R. Inoue K. Sase H. Eizawa K. Kosuga T. Aoyama H. Masayasu C. Kawai S. Sasayama Y. Yui (1994) ArticleTitlePreferential inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase by ebselen Eur. J. Pharmacol. 267 R1–R2 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXivFSjtL8%3D
H. Masumoto H. Sies (1996) ArticleTitleThe reaction of ebselen with peroxynitrite Chem. Res. Toxicol. 9 262–267 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXhtVSjs7bP Occurrence Handle8924601
S. Moussaoui M. C. Obinu N. Daniel M. Reibaud V. Blandchard A. Imperato S. Moussaoui M. C. Obinu N. Daniel M. Reibaud V. Blandchard A. Imperato (2000) ArticleTitleThe antioxidant ebselen prevents neurotoxicity and clinical symptoms in a primate model of Parkinson’s disease Exp. Neurol. 166 235–245 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXotFCrsLY%3D Occurrence Handle11085889
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalayci, M., Coskun, O., Cagavi, F. et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Ebselen on Experimental Spinal Cord Injury in Rats. Neurochem Res 30, 403–410 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-2615-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-005-2615-2