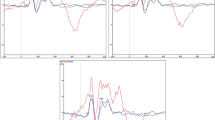
Emotional face recognition has been shown to be drastically impaired among patients with schizophrenia. Since the underlying processes of this deficit have not been widely addressed, we attempted to investigate the relationship between facial expression perception and clinical symptoms in patients with schizophrenia. We enrolled 28 patients with schizophrenia and 28 healthy adults matched by their sex and age. The amplitude and latency of component N170 in event-related EEG potentials (ERPs) induced by presentations of happy, fearful, and neutral face images were comparatively evaluated in these two groups. Furthermore, the relationship between the N170 measures and clinical symptoms of schizophrenia were assessed using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS). The N170 responses to facial expressions in patients with schizophrenia were significantly delayed, as compared to healthy control participants [F (1, 54) = 4.25, P = 0.044]. The N170 response to fearful faces (as compared to happy and neutral faces) was elicited with the minimum latency in the control group, while this component was most delayed among schizophrenics. Positive schizophrenia symptoms correlated with the amplitudes of the left-hemisphere N170 component in response to happy, fearful, and neutral faces. Our findings suggest that the facial expression deficit in schizophrenia is related to delayed responses in face perception and is influenced by the severity of positive symptoms. The evident delay in fearful face perception among patients with schizophrenia may partly explain their inappropriate reactions to threatening conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Martinez, S. A. Hillyard, E. C. Dias, et al., “Magnocellular pathway impairment in schizophrenia: evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging,” J. Neurosci., 28, 7492-7500 (2008).
V. M. Goghari, S. R. Sponheim, and A. W. MacDonald, “The functional neuroanatomy of symptom dimensions in schizophrenia: a qualitative and quantitative review of a persistent question,” Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev., 34, 468-486 (2010).
C. G. Kohler, J. B. Walker, E. A. Martin, et al., “Facial emotion perception in schizophrenia: a meta-analytic review,” Schizophr. Bull., 36, 1009-1019 (2010).
G. Sachs, D. Steger-Wuchse, I. Kryspin-Exner, et al., “Facial recognition deficits and cognition in schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 68, 27-35 (2004).
S. Caharel, C. Bernard, F. Thibaut, et al., “The effects of familiarity and emotional expression on face processing examined by ERPs in patients with schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 95, 186-196 (2007).
J. Huang, T. Xu, and R. C. Chan, “Do patients with schizophrenia have a general or specific deficit in the perception of social threat? A meta-analytic study,” Psychiat. Res., 185, 1-8 (2011).
C. G. Kohler, W. Bilker, M. Hagendoorn, et al., “Emotion recognition deficit in schizophrenia: association with symptomatology and cognition,” Biol. Psychiat., 48, 127-136 (2000).
Y. Chen, D. Norton, R. McBain, et al., “Visual and cognitive processing of face information in schizophrenia: detection, discrimination and working memory,” Schizophr. Res., 107, 92-98 (2009).
R. C. Chan, H. Li, E. F. Cheung, et al., “Impaired facial emotion perception in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis,” Psychiat. Res., 178, 381-390 (2010).
G. P. Strauss, S. S. Jetha, S. A. Ross, et al., “Impaired facial affect labeling and discrimination in patients with deficit syndrome schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 118, 146-153 (2010).
F. Schneider, R. C. Gur, K. Koch, et al., “Impairment in the specificity of emotion processing in schizophrenia,” Am. J. Psychiat., 163, 442-447 (2006).
M. Batty and M. J. Taylor, “Early processing of the six basic facial emotional expressions,” Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res., 17, 613-620 (2003).
H. Li, R. C. Chan, G. M. McAlonan, et al., “Facial emotion processing in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of functional neuroimaging data,” Schizophr. Bull., 36, 1029-1039 (2010).
D. J. Holt, L. Kunkel, A. P. Weiss, et al., “Increased medial temporal lobe activation during the passive viewing of emotional and neutral facial expressions in schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 82, 153-162 (2006).
Y. J. Pan, S. H. Chen, W. J. Chen, et al., “Affect recognition as an independent social function determinant in schizophrenia,” Comp. Psychiat., 50, 443-452 (2009).
B. Bediou, N. Franck, M. Saoud, et al., “Effects of emotion and identity on facial affect processing in schizophrenia,” Psychiat. Res., 133, 149-157 (2005).
А. А. Kovalenko and V. B. Pavlenko, “Emotional significance of the stimulus and features of the personality as factors reflected in the pattern of evoked EEG potentials,” Neurophysiology, 41, No. 4, 282-302 (2009).
T. Nakashima, K. Kaneko, Y. Goto, et al., “Early ERP components differentially extract facial features: evidence for spatial frequency-and-contrast detectors,” Neurosci. Res., 62, 225-235 (2008).
M. J. Herrmann, H. Ellgring, A. J. Fallgatter, et al., “Early-stage face processing dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia,” Am. J. Psychiat., 161, 915-917 (2004).
P. J. Johnston, W. Stojanov, H. Devir, et al., “Functional MRI of facial emotion recognition deficits in schizophrenia and their electrophysiological correlates,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 22, 1221-1232 (2005).
B. I. Turetsky, C. G. Kohler, T. Indersmitten, et al., “Facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia: when and why does it go awry?” Schizophr. Res., 94, 253-263 (2007).
S. Campanella, C. Montedoro, E. Streel, et al., “Early visual components (P100, N170) are disrupted in chronic schizophrenic patients: an event-related potentials study,” Neurophysiol. Clin., 36, 71-78 ( 2006).
B. Bediou, M. A. Henaff, O. Bertrand, et al., “Impaired fronto-temporal processing of emotion in schizophrenia,” Neurophysiol. Clin., 37, 77-87 (2007).
G. D. Pearlson, “Neurobiology of schizophrenia,” Ann. Neurol., 48, 556-566 (2000).
P. Rocca, F. Castagna, T. Mongini, et al., “Exploring the role of face processing in facial emotion recognition in schizophrenia,” Acta Neuropsychiat., 21, 292-300 (2009).
M. van ‘t Wout, A. Aleman, R. P. C. Kessels, et al., “Exploring the nature of facial affect processing deficits in schizophrenia,” Psychiat. Res., 150, 227-235 (2007).
S. H. Lee, E. Y. Kim, S. Kim, et al., “Event-related potential patterns and gender effects underlying facial affect processing in schizophrenia patients,” Neurosci. Res., 67, 172-180 (2010).
M. J. Herrmann, A. Reif, B. E. Jabs, et al., “Facial affect decoding in schizophrenic disorders: a study using event-related potentials,” Psychiat. Res., 141, 247-252 (2006).
M. Streit, A. Ioannides, T. Sinneman, et al., “Disturbed facial affect recognition in patients with schizophrenia associated with hypoactivity in distributed brain regions: a magnetoencephalographic study,” Am. J. Psychiat., 158, 1429-1436 (2001).
R. C. Oldfield, “The assessment and analysis of handedness: the Edinburgh inventory,” Neuropsychologia, 9, 97-113 (1971).
J. Endicott and R. L. Spitzer, “A diagnostic interview: the schedule for affective disorders and schizophrenia,” Arch. Gen. Psychiat., 35, 837-844 (1978).
S. R. Kay, L. A. Opler, and J. P. Lindenmayer, “The positive and negative syndrome scale (PANSS): rationale and standardization,” Br. J. Psychiat., Suppl., 59-67 (1989).
F. Ghassemi, M. H. Moradi, M. Tehrani-Doost, et al., “Effects of correct and wrong answers on ERPs recorded under conditions of the continuous performance test in ADHD/normal participants,” Neurophysiology, 42, No. 3, 213-220 (2010).
M. Eimer, “The face-specific N170 component reflects late stages in the structural encoding of faces,” Cogn. Neurosci., 11, 2319-2324 (2000).
J. K. Wynn, J. Lee, W. P Horan, et al., “Using event related potentials to explore stages of facial affect recognition deficits in schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Bull., 34, 679-687 (2008).
K. Kirihara, K. Kasai, M. Tada, et al., “Neurophysiological impairment in emotional face processing is associated with low extraversion in schizophrenia,” Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiat., 37, 270-275 (2012).
S. K. An, S. J. Lee, C. H. Lee, et al., “Reduced P3 amplitudes by negative facial emotional photographs in schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 64, 125-135 (2003).
R. E. Gur, C. G. Kohler, J. D. Ragland, et al., “Flat affect in schizophrenia: relation to emotion processing and neurocognitive measures,” Schizophr. Bull., 32, 279-287 (2006).
R. J. Thoma, F. M. Hanlon, S. N. Moses, et al., “M50 sensory gating predicts negative symptoms in schizophrenia,” Schizophr. Res., 73, 311-318 (2005).
M. Higashima, T. Nagasawa, Y. Kawasaki, et al., “Auditory P300 amplitude as a state marker for positive symptoms in schizophrenia: cross-sectional and retrospective longitudinal studies,” Schizophr. Res., 59, 147-157 (2003).
J. Hall, J. M. Harris, R. Sprengelmeyer, et al., “Social cognition and face processing in schizophrenia,” Br. J. Psychiat., 185, 169-170 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akbarfahimi, M., Tehrani-Doost, M. & Ghassemi, F. Emotional Face Perception in Patients with Schizophrenia: an Event-Related Potential Study. Neurophysiology 45, 249–257 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9363-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-013-9363-8