Abstract
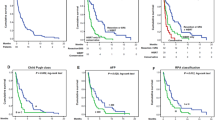
The incidence of brain metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is increasing because of the improved survival outcome of HCC patients, but the prognosis of these patients is extremely poor. HCC patients with brain metastasis were investigated to identify their prognostic factors for overall survival. Patients with brain metastasis from HCC who had been treated with whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) in five hospitals were enrolled in the study. The medical records of the patients were reviewed, and the clinical factors were analyzed to identify the prognostic factors for overall survival. Of the total of 97 patients who were enrolled in the study, 83 were male and the median age at the brain metastases was 56.6 years. Motor weakness (43.3 %) and headache (41.2 %) were common presenting symptoms. The median AFP level was 4180 ng/ml, and 81 patients were assessed as belonging to Child-Pugh classification A upon the diagnosis of brain metastasis. WBRT alone in 71 patients, surgery or radiosurgery combined with WBRT as the adjuvant setting in 18 patients, and WBRT as salvage treatment in 8 patients were performed. The median overall survival of the patients was 3.5 months. In the multivariate analysis, the ECOG performance status (PS), Child-Pugh classification, AFP, and treatment aim showed significant association with the overall survival of the patients. Based on these factors, a nomogram predicting the prognosis was developed. The concordance index of the nomogram was 0.74, and the prediction was well calibrated. In conclusion, the survival outcome of patients with brain metastasis from HCC can be predicted with the nomogram constructed from the ECOG PS, Child-Pugh classification, AFP, and treatment aim.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim M, Na DL, Park SH, Jeon BS, Roh JK (1998) Nervous system involvement by metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. J Neurooncol 36:85–90
Chang L, Chen YL, Kao MC (2004) Intracranial metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma: review of 45 cases. Surg Neurol 62:172–177. doi:10.1016/j.surneu.2003.10.002
Murakami K, Nawano S, Moriyama N, Sekiguchi R, Satake M, Fujimoto H, Ichikawa T (1996) Intracranial metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma: CT and MRI. Neuroradiology 38(Suppl 1):S31–S35
Choi HJ, Cho BC, Sohn JH, Shin SJ, Kim SH, Kim JH, Yoo NC (2009) Brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic factors and outcome: brain metastasis from HCC. J Neurooncol 91:307–313. doi:10.1007/s11060-008-9713-3
Shao YY, Lu LC, Cheng AL, Hsu CH (2011) Increasing incidence of brain metastasis in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of antiangiogenic targeted therapy. Oncologist 16:82–86. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2010-0272
Lorenzoni J, Devriendt D, Massager N, David P, Ruiz S, Vanderlinden B, Van Houtte P, Brotchi J, Levivier M (2004) Radiosurgery for treatment of brain metastases: estimation of patient eligibility using three stratification systems. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 60:218–224. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.02.017
Gaspar L, Scott C, Rotman M, Asbell S, Phillips T, Wasserman T, McKenna WG, Byhardt R (1997) Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 37:745–751
Weltman E, Salvajoli JV, Brandt RA, de Morais Hanriot R, Prisco FE, Cruz JC, de Oliveira Borges SR, Wajsbrot DB (2000) Radiosurgery for brain metastases: a score index for predicting prognosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 46:1155–1161
Sperduto PW, Berkey B, Gaspar LE, Mehta M, Curran W (2008) A new prognostic index and comparison to three other indices for patients with brain metastases: an analysis of 1960 patients in the RTOG database. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 70:510–514. doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.06.074
Patchell RA, Tibbs PA, Walsh JW, Dempsey RJ, Maruyama Y, Kryscio RJ, Markesbery WR, Macdonald JS, Young B (1990) A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N Engl J Med 322:494–500. doi:10.1056/NEJM199002223220802
Pollock BE, Brown PD, Foote RL, Stafford SL, Schomberg PJ (2003) Properly selected patients with multiple brain metastases may benefit from aggressive treatment of their intracranial disease. J Neurooncol 61:73–80
Andrews DW, Scott CB, Sperduto PW, Flanders AE, Gaspar LE, Schell MC, Werner-Wasik M, Demas W, Ryu J, Bahary JP, Souhami L, Rotman M, Mehta MP, Curran WJ Jr (2004) Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363:1665–1672. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16250-8
Park TY, Na YC, Lee WH, Kim JH, Chang WS, Jung HH, Chang JH, Chang JW, Park YG (2013) Treatment options of metastatic brain tumors from hepatocellular carcinoma: surgical resection vs. gamma knife radiosurgery vs. whole brain radiation therapy. Brain Tumor Res Treat 1:78–84. doi:10.14791/btrt.2013.1.2.78
Jiang XB, Ke C, Zhang GH, Zhang XH, Sai K, Chen ZP, Mou YG (2012) Brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma: clinical features and prognostic factors. BMC Cancer 12:49. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-12-49
Han MS, Moon KS, Lee KH, Cho SB, Lim SH, Jang WY, Jung TY, Kim IY, Jung S (2013) Brain metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma: the role of surgery as a prognostic factor. BMC Cancer 13:567. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-13-567
Lim S, Lee S, Lim JY, Park JS, Seong JS, Chang WS, Han KH, Choi HJ (2014) Hepatocellular carcinoma specific graded prognostic assessment can predict outcomes for patients with brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. J Neurooncol 120:199–207. doi:10.1007/s11060-014-1546-7
Kim KS, Kim K, Chie EK, Kim YJ, Yoon JH, Lee H-S, Ha SW (2014) Prognostic stratification of brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma. J Neurooncol 120:209–214
Barnholtz-Sloan JS, Yu C, Sloan AE, Vengoechea J, Wang M, Dignam JJ, Vogelbaum MA, Sperduto PW, Mehta MP, Machtay M, Kattan MW (2012) A nomogram for individualized estimation of survival among patients with brain metastasis. Neuro-oncology 14:910–918. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nos087
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Additional information
Younghee Park and Kyung Su Kim have equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, Y., Kim, K.S., Kim, K. et al. Nomogram prediction of survival in patients with brain metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma treated with whole-brain radiotherapy: a multicenter retrospective study. J Neurooncol 125, 377–383 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1926-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1926-7