Abstract
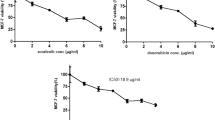
RLIP76, a GTPase-activating protein, is a central regulator in multiple pathways that respond to redox states and control cell growth, motility, division, and apoptosis in many malignant cancer cells. In this study, human glioblastoma cell lines U87 and U251 were stably transfected with a lentivirus vector expressing a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) targeting RLIP76. shRNA knockdown of RLIP76 induced cell cycle arrest in U87 and U251 cells and inhibited their invasiveness. Quantitative Western blot analysis revealed that cells stably underexpressing RLIP76 showed lower expression of cyclin D1 and decreased expression and activity of matrix metalloproteinase 2 compared to cells stably transfected with a control vector. Furthermore, RLIP76 expression levels were correlated with IC50 values for the antitumor drug temozolomide (TMZ). Compared with TMZ alone (17.19 ± 1.78 and 22.18 ± 1.99 μg/mL in U87 and U251 cells, respectively) or combined shGFP and TMZ (18.04 ± 1.07 and 23.040 ± 1.77 μg/mL in U87 and U251 cells, respectively), combined shRNA and TMZ therapy resulted in a significant decrease in IC50 value (7.61 ± 2.99 and 6.91 ± 2.59 μg/mL in U87 and U251 cells, respectively). Combined RLIP76 knockdown and TMZ treatment inhibited cell proliferation in vitro more effectively than either treatment alone. Furthermore, RLIP76 downregulation enhanced chemosensitivity to TMZ without affecting protein expression of MDR1 and MRP1. The results indicate that inhibition of RLIP76 expression may be an effective means for overcoming RLIP76-associated chemoresistance in human malignant glioma cells and may represent a potential gene-targeting approach for glioma treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wen PY, Kesari S (2008) Malignant gliomas in adults. N Engl J Med 359:492–507
Van Meir EG, Hadjipanayis CG, Norden AD, Shu HK, Wen PY (2010) Exciting new advances in neuro-oncology: the avenue to a cure for malignant glioma. CA Cancer J Clin 60:166–193
Singhal SS, Singhal J, Nair MP, Lacko AG, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2007) Doxorubicin transport by RALBP1 and ABCG2 in lung and breast cancer. Int J Oncol 30:717–725
Singhal SS, Sehrawat A, Sahu M, Singhal P, Vatsyayan R, Rao Lelsani PC, Yadav S, Awasthi S (2010) Rlip76 transports sunitinib and sorafenib and mediates drug resistance in kidney cancer. Int J Cancer 126:1327–1338
Singhal SS, Sehrawat A, Mehta A, Sahu M, Awasthi S (2009) Functional reconstitution of RLIP76 catalyzing ATP-dependent transport of glutathione-conjugates. Int J Oncol 34:191–199
Drake KJ, Singhal J, Yadav S, Nadkar A, Pungaliya C, Singhal SS, Awasthi S (2007) RALBP1/RLIP76 mediates multidrug resistance. Int J Oncol 30:139–144
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Singhal J, Yang Y, Zimniak P, Awasthi YC (2003) Role of RLIP76 in lung cancer doxorubicin resistance: III. Anti-RLIP76 antibodies trigger apoptosis in lung cancer cells and synergistically increase doxorubicin cytotoxicity. Int J Oncol 22:721–732
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Singhal J, Cheng J, Zimniak P, Awasthi YC (2003) Role of RLIP76 in lung cancer doxorubicin resistance: II. Doxorubicin transport in lung cancer by RLIP76. Int J Oncol 22:713–720
Awasthi S, Hallene KL, Fazio V, Singhal SS, Cucullo L, Awasthi YC, Dini G, Janigro D (2005) RLIP76, a non-ABC transporter, and drug resistance in epilepsy. BMC Neurosci 6:61
Awasthi S, Cheng J, Singhal SS, Saini MK, Pandya U, Pikula S, Bandorowicz-Pikula J, Singh SV, Zimniak P, Awasthi YC (2000) Novel function of human RLIP76: ATP-dependent transport of glutathione conjugates and doxorubicin. Biochemistry 39:9327–9334
Stuckler D, Singhal J, Singhal SS, Yadav S, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2005) RLIP76 transports vinorelbine and mediates drug resistance in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 65:991–998
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Srivastava SK, Zimniak P, Bajpai KK, Saxena M, Sharma R, Ziller SA III, Frenkel EP, Singh SV et al (1994) Adenosine triphosphate-dependent transport of doxorubicin, daunomycin, and vinblastine in human tissues by a mechanism distinct from the P-glycoprotein. J Clin Invest 93:958–965
Awasthi S, Singhal SS, Pandya U, Gopal S, Zimniak P, Singh SV, Awasthi YC (1999) ATP-dependent colchicine transport by human erythrocyte glutathione conjugate transporter. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 155:215–226
Yadav S, Zajac E, Singhal SS, Singhal J, Drake K, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2005) POB1 over-expression inhibits RLIP76-mediated transport of glutathione-conjugates, drugs and promotes apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 328:1003–1009
Singhal SS, Yadav S, Vatsyayan R, Chaudhary P, Borvak J, Singhal J, Awasthi S (2009) Increased expression of cdc2 inhibits transport function of RLIP76 and promotes apoptosis. Cancer Lett 283:152–158
Hu Y, Mivechi NF (2003) HSF-1 interacts with Ral-binding protein 1 in a stress-responsive, multiprotein complex with HSP90 in vivo. J Biol Chem 278:17299–17306
Vatsyayan R, Lelsani PC, Awasthi S, Singhal SS (2010) RLIP76: a versatile transporter and an emerging target for cancer therapy. Biochem Pharmacol 79:1699–1705
Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M (2003) Cost of migration: invasion of malignant gliomas and implications for treatment. J Clin Oncol 21:1624–1636
Singhal SS, Singhal J, Yadav S, Sahu M, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2009) RLIP76: a target for kidney cancer therapy. Cancer Res 69:4244–4251
Singhal SS, Singhal J, Yadav S, Dwivedi S, Boor PJ, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2007) Regression of lung and colon cancer xenografts by depleting or inhibiting RLIP76 (Ral-binding protein 1). Cancer Res 67:4382–4389
Singhal SS, Roth C, Leake K, Singhal J, Yadav S, Awasthi S (2009) Regression of prostate cancer xenografts by RLIP76 depletion. Biochem Pharmacol 77:1074–1083
Singhal SS, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2006) Regression of melanoma in a murine model by RLIP76 depletion. Cancer Res 66:2354–2360
Singhal J, Yadav S, Nagaprashantha LD, Vatsyayan R, Singhal SS, Awasthi S (2011) Targeting p53-null neuroblastomas through RLIP76. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 4:879–889
Wang J, Wang Q, Cui Y, Liu ZY, Zhao W, Wang CL, Dong Y, Hou L, Hu G, Luo C, Chen J, Lu Y (2012) Knockdown of cyclin D1 inhibits proliferation, induces apoptosis, and attenuates the invasive capacity of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 106:473–484
Singhal SS, Yadav S, Singhal J, Zajac E, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S (2005) Depletion of RLIP76 sensitizes lung cancer cells to doxorubicin. Biochem Pharmacol 70:481–488
Vatsyayan R, Chaudhary P, Lelsani PC, Singhal P, Awasthi YC, Awasthi S, Singhal SS (2009) Role of RLIP76 in doxorubicin resistance in lung cancer. Int J Oncol 34:1505–1511
Herlyn M, Malkowicz SB (1991) Regulatory pathways in tumor growth and invasion. Lab Invest 65:262–271
Bouterfa H, Darlapp AR, Klein E, Pietsch T, Roosen K, Tonn JC (1999) Expression of different extracellular matrix components in human brain tumor and melanoma cells in respect to variant culture conditions. J Neurooncol 44:23–33
Nakada M, Okada Y, Yamashita J (2003) The role of matrix metalloproteinases in glioma invasion. Front Biosci 8:e261–e269
Wang M, Wang T, Liu S, Yoshida D, Teramoto A (2003) The expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas of different pathological grades. Brain Tumor Pathol 20:65–72
Komatsu K, Nakanishi Y, Nemoto N, Hori T, Sawada T, Kobayashi M (2004) Expression and quantitative analysis of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in human gliomas. Brain Tumor Pathol 21:105–112
Thorns V, Walter GF, Thorns C (2003) Expression of MMP-2, MMP-7, MMP-9, MMP-10 and MMP-11 in human astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. Anticancer Res 23:3937–3944
Grana X, Reddy EP (1995) Cell cycle control in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases (CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene 11:211–219
Mousseau M, Chauvin C, Nissou MF, Chaffanet M, Plantaz D, Pasquier B, Schaerer R, Benabid A (1993) A study of the expression of four chemoresistance-related genes in human primary and metastatic brain tumours. Eur J Cancer 29A:753–759
Sugawara I, Yamada H, Nakamura H, Sumizawa T, Akiyama S, Masunaga A, Itoyama S (1995) Preferential expression of the multidrug-resistance-associated protein (MRP) in adenocarcinoma of the lung. Int J Cancer 64:322–325
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Sciences Fund Project of China (NSFC Nos.30930094).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qi Wang and Jun Qian contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Qian, J., Wang, J. et al. Knockdown of RLIP76 expression by RNA interference inhibits invasion, induces cell cycle arrest, and increases chemosensitivity to the anticancer drug temozolomide in glioma cells. J Neurooncol 112, 73–82 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1045-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-013-1045-2