Abstract
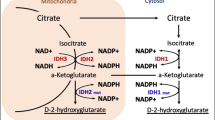
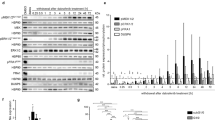
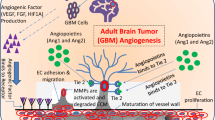
Increasing evidence suggests that an inflammatory microenvironment promotes invasion by glioblastoma (GBM) cells. Together with p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) activation being regarded as promoting inflammation, we hypothesized that elevated inflammatory cytokine secretion and p38 MAPK activity contribute to expansion of GBMs. Here we report that IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 levels and p38 MAPK activity are elevated in human glioblastoma specimens and that p38 MAPK inhibitors attenuate the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines by microglia and glioblastoma cells. RNAi knockdown and immunoprecipitation experiments suggest that the p38α MAPK isoform drives inflammation in GBM cells. Importantly, p38 MAPK inhibition strongly reduced invasion of U251 glioblastoma cells in an inflammatory microenvironment, providing evidence for a p38 MAPK-regulated link between inflammation and invasiveness in GBM pathophysiology.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR, Karin M (2010) Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 140:883–899
Bonavia R, Inda MM, Vandenberg S, Cheng SY, Nagane M, Hadwiger P, Tan P, Sah DW, Cavenee WK, Furnari FB (2011) EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NFκB, interleukin-8 pathway. Oncogene. doi:10.1038/onc.2011.563
Solinas G, Marchesi F, Garlanda C, Mantovani A, Allavena P (2010) Inflammation-mediated promotion of invasion and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29:243–248
Hussain SF, Yang D, Suki D, Aldape K, Grimm E et al (2006) The role of human glioma-infiltrating microglia/macrophages in mediating antitumor immune responses. Neuro Oncol 8:261–279
Yamaguchi S, Tanabe K, Takai S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Adachi S et al (2009) Involvement of Rho-kinase in tumor necrosis factor-α-induced interleukin-6 release from C6 glioma cells. Neurochem Int 55:438–445
Griffin BD, Moynagh PN (2006) Persistent interleukin-1β signaling causes long term activation of NFκB in a promoter-specific manner in human glial cells. J Biol Chem 281:10316–10326
Radeff-Huang J, Seasholtz TM, Chang JW, Smith JM, Walsh CT et al (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated cell proliferation is mediated through sphingosine kinase-dependent Akt activation and cyclin D expression. J Biol Chem 282:863–870
Brat DJ, Bellail AC, Van Meir EG (2005) The role of interleukin-8 and its receptors in gliomagenesis and tumoral angiogenesis. Neuro Oncol 7:122–133
de la Iglesia N, Konopka G, Lim KL, Nutt CL, Bromberg JF et al (2008) Deregulation of a STAT3-interleukin 8 signaling pathway promotes human glioblastoma cell proliferation and invasiveness. J Neurosci 28:5870–5878
Tchirkov A, Rolhion C, Bertrand S, Doré JF, Dubost JJ et al (2001) IL-6 gene amplification and expression in human glioblastomas. Br J Cancer 85:518–522
Tchirkov A, Khalil T, Chautard E, Mokhtari K, Véronèse L et al (2007) Interleukin-6 gene amplification and shortened survival in glioblastoma patients. Br J Cancer 96:474–476
Weissenberger J, Loeffler S, Kappeler A, Kopf M, Lukes A et al (2004) IL-6 is required for glioma development in a mouse model. Oncogene 23:3308–3316
Inda MM, Bonavia R, Mukasa A, Narita Y, Sah DW et al (2010) Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev 24:1731–1745
Sarkar S, Yong VW (2009) Inflammatory cytokine modulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression and invasiveness of glioma cells in a 3-dimensional collagen matrix. J Neurooncol 91:157–164
Schieven GL (2005) The biology of p38 kinase: a central role in inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem 5:921–928
Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC (2003) p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:717–726
Munoz L, Ramsay EE, Manetsch M, Ge Q, Peifer C et al (2010) Novel p38 MAPK inhibitor ML3403 has potent anti-inflammatory activity in airway smooth muscle. Eur J Pharmacol 635:212–218
Yoshino Y, Aoyagi M, Tamaki M, Duan L, Morimoto T et al (2006) Activation of p38 MAPK and/or JNK contributes to increased levels of VEGF secretion in human malignant glioma cells. Int J Oncol 29:981–987
Kim YJ, Hwang SY, Oh ES, Oh S, Han IO (2006) IL-1β, an immediate early protein secreted by activated microglia, induces iNOS/NO in C6 astrocytoma cells through p38 MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways. J Neurosci Res 84:1037–1046
Demuth T, Reavie LB, Rennert JL, Nakada M, Nakada S et al (2007) MAP-ing glioma invasion: mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 3 and p38 drive glioma invasion and progression and predict patient survival. Mol Cancer Ther 6:1212–1222
Munoz L, Ammit AJ (2010) Targeting p38 MAPK pathway for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuropharmacology 58:561–568
Dziembowska M, Danilkiewicz M, Wesolowska A, Zupanska A, Chouaib S et al (2007) Cross-talk between Smad and p38 MAPK signalling in transforming growth factor β signal transduction in human glioblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:1101–1106
Tanabe K, Matsushima-Nishiwaki R, Yamaguchi S, Iida H, Dohi S et al (2010) Mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced interleukin-6 synthesis in glioma cells. J Neuroinflammation 7:16
Markovic DS, Vinnakota K, Chirasani S, Synowitz M, Raguet H et al (2009) Gliomas induce and exploit microglial MT1-MMP expression for tumor expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12530–12535
Malchinkhuu E, Sato K, Horiuchi Y, Mogi C, Ohwada S et al (2005) Role of p38 mitogen-activated kinase and c-Jun terminal kinase in migration response to lysophosphatidic acid and sphingosine-1-phosphate in glioma cells. Oncogene 24:6676–6688
Munoz L, Ralay Ranaivo H, Roy SM, Hu W, Craft JM et al (2007) A novel p38 MAPK inhibitor suppresses brain proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation and attenuates synaptic dysfunction and behavioral deficits in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Neuroinflammation 4:21
Guillemin GJ, Smythe G, Takikawa O, Brew BJ (2005) Expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and production of quinolinic acid by human microglia, astrocytes, and neurons. Glia 49:15–23
Vila de Muga S, Timpson P, Cubells L, Evans R, Hayes TE et al (2009) Annexin A6 inhibits Ras signalling in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 28:363–377
Munoz L, Selig R, Yeung YT, Peifer C, Laufer S (2010) Fluorescence polarisation binding assay to develop inhibitors of inactive p38α mitogen-activated protein kinase. Anal Biochem 401:125–133
Hagel M, George EL, Kim A, Tamimi R, Opitz SL et al (2002) The adaptor protein paxillin is essential for normal development in the mouse and is a critical transducer of fibronectin signaling. Mol Cell Biol 22:901–915
Bryce NS, Clark ES, Leysath LJ, Currie JD, Webb DJ et al (2005) Cortactin promotes cell motility by enhancing lamellipodial persistence. Curr Biol 15:1276–1285
Peterson G (1977) A simplification of the protein assay method by Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem 83:346–356
Hu W, Ralay Ranaivo H, Roy SM, Behanna HA, Wing LK et al (2007) Development of a novel therapeutic suppressor of brain proinflammatory cytokine up-regulation that attenuates synaptic dysfunction and behavioral deficits. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:414–418
Gao HM, Zhou H, Zhang F, Wilson BC, Kam W, Hong JS (2011) HMGB1 acts on microglia Mac1 to mediate chronic neuroinflammation that drives progressive neurodegeneration. J Neurosci 31:1081–1092
Thuringer D, Hammann A, Benikhlef N, Fourmaux E, Bouchot A et al (2011) Transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor by heat shock protein 90 via Toll-like receptor 4 contributes to the migration of glioblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 286:3418–3428
Paugh BS, Bryan L, Paugh SW, Wilczynska KM, Alvarez SM et al (2009) Interleukin-1 regulates the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 in glioblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 284:3408–3417
Kesanakurti D, Chetty C, Bhoopathi P, Lakka SS, Gorantla B et al (2011) Suppression of MMP-2 attenuates TNF-α induced NF-κB activation and leads to JNK mediated cell death in glioma. PLoS One 6:e19341
Tanabe K, Kozawa O, Iida H (2011) Midazolam suppresses interleukin-1β-induced interleukin-6 release from rat glial cells. J Neuroinflammation 8:68
Junttila MR, Ala-aho R, Jokilehto T, Peltonen J, Kallajoki M et al (2007) p38α and p38δ mitogen-activated protein kinase isoforms regulate invasion and growth of head and neck squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene 26:5267–5279
Chen L, Mayer JA, Krisko TI, Speers CW, Wang T et al (2009) Inhibition of the p38 kinase suppresses the proliferation of human ER-negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 69:8853–8861
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2010) Cancer and Inflammation: implications for pharmacology and therapeutics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 87:401–406
Reynes G, Vila V, Martin M, Parada A, Fleitas T et al (2011) Circulating markers of angiogenesis, inflammation, and coagulation in patients with glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 102:35–41
Sharma V, Dixit D, Koul N, Mehta VS, Sen E (2011) Ras regulates interleukin-1β-induced HIF-1α transcriptional activity in glioblastoma. J Mol Med 89:123–136
Maruno M, Kovach J, Kelly PJ, Yanagihara T (1997) Distribution of endogeneous tumour necrosis factor α in gliomas. J Clin Pathol 50:559–562
Kostianovsky AM, Maier LM, Anderson RC, Bruce JN, Anderson DE (2008) Astrocytic regulation of human monocytic/microglial activation. J Immunol 181:5425–5432
Nabors LB, Suswam E, Huang Y, Yang X, Johnson MJ et al (2003) Tumor necrosis factor α induces angiogenic factor up-regulation in malignant glioma cells. Cancer Res 63:4181–4187
Hong TM, Teng LJ, Shun CT, Peng MC, Tsai JC (2009) Induced interleukin-8 expression in gliomas by tumor-associated macrohages. J Neurooncol 93:289–301
Rao JS (2003) Molecular mechanisms of glioma invasiveness: the role of proteases. Nat Rev Cancer 3:489–501
Park MJ, Park IC, Hur JH, Kim MS, Lee HC et al (2002) Modulation of phorbol ester-induced regulation of matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases by SB203580, a specific inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Neurosurg 97:112–118
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Cure for Life Foundation, Alzheimer’s Australia, and The JR and JO Wicking Foundations (managed by ANZ Trustees) to LM; the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (510293, 510294) and the University of Sydney (2010-02681) to TG; the Australian Research Council (DP1094232) to NB, and the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (1009914) to GG. The authors acknowledge scientific and technical input and support from the Australian Microscopy and Microanalysis Research Facility (AMMRF) at the University of Sydney.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeung, Y.T., Bryce, N.S., Adams, S. et al. p38 MAPK inhibitors attenuate pro-inflammatory cytokine production and the invasiveness of human U251 glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol 109, 35–44 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0875-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0875-7