Abstract
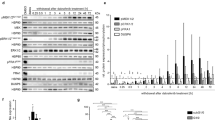
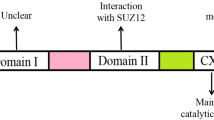
The mRNA cap-binding protein eukaryotic initiation factor 4E (eIF4E) plays an important role in mRNA translation; its activity is implicated in cell growth and proliferation. In experimental models, eIF4E over-expression induces cellular transformation, tumorigenesis, and lymphomagenesis. The activity of eIF4E is regulated by the Akt/mTOR and MAPK/MAP kinase-interacting kinase-1 (MNK1) pathways. While investigating the participation of the MNK1/eIF4E signaling pathway in primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL), we noted the over-expression of eIF4E and phosphorylated eIF4E (p-eIF4E) in specimens from PCNSL patients. Western blot analysis using B-cell lymphoma cell lines showed that eIF4E phosphorylation was serum-independent and was selectively inhibited by the MNK1 inhibitor. Furthermore, MNK1 inhibitor led to reduced cyclin D1 expression and caused inhibition of cell proliferation and cell death in human brain malignant lymphoma cell line (HKBML). Also, the growth of the subcutaneous HKBML xenografts in mice was inhibited by intraperitoneal administration of MNK1 inhibitor compared with mice treated with vehicle (P = 0.026). Our data suggest that in PCNSL cells eIF4E phosphorylation plays an important role in proliferation and our results identify inhibition of the MNK1/eIF4E pathway as a potential therapeutic target in patients with PCNSL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Makino K, Nakamura H, Kino T, Takeshima H, Kuratsu J (2006) Rising incidence of primary central nervous system lymphoma in Kumamoto, Japan. Surg Neurol 66:503–506
Richter JD, Sonenberg N (2005) Regulation of cap-dependent translation by eIF4E inhibitory proteins. Nature 433:477–480
Rousseau D, Gingras AC, Pause A, Sonenberg N (1996) The eIF4E-binding proteins 1 and 2 are negative regulators of cell growth. Oncogene 13:2415–2420
Zimmer SG, DeBenedetti A, Graff JR (2000) Translational control of malignancy: the mRNA cap-binding protein, eIF-4E, as a central regulator of tumor formation, growth, invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res 20:1343–1351
De Benedetti A, Graff JR (2004) eIF-4E expression and its role in malignancies and metastases. Oncogene 23:3189–3199
Byrnes K, White S, Chu Q et al (2006) High eIF4E, VEGF, and microvessel density in stage I to III breast cancer. Ann Surg 243:684–690 (discussion 691–692)
Khoury T, Alrawi S, Ramnath N et al (2009) Eukaryotic initiation factor-4E and cyclin D1 expression associated with patient survival in lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 10:58–66
Ruggero D, Montanaro L, Ma L et al (2004) The translation factor eIF-4E promotes tumor formation and cooperates with c-Myc in lymphomagenesis. Nat Med 10:484–486
Wendel HG, De Stanchina E, Fridman JS et al (2004) Survival signalling by Akt and eIF4E in oncogenesis and cancer therapy. Nature 428:332–337
Mamane Y, Petroulakis E, Rong L, Yoshida K, Ler LW, Sonenberg N (2004) eIF4E–from translation to transformation. Oncogene 23:3172–3179
Waskiewicz AJ, Flynn A, Proud CG, Cooper JA (1997) Mitogen-activated protein kinases activate the serine/threonine kinases Mnk1 and Mnk2. EMBO J 16:1909–1920
Pyronnet S (2000) Phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eIF4E by the MAPK-activated protein kinase Mnk1. Biochem Pharmacol 60:1237–1243
Scheper GC, Proud CG (2002) Does phosphorylation of the cap-binding protein eIF4E play a role in translation initiation? Eur J Biochem 269:5350–5359
Ueda T, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Fukuyama H, Nagata S, Fukunaga R (2004) Mnk2 and Mnk1 are essential for constitutive and inducible phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E but not for cell growth or development. Mol Cell Biol 24:6539–6549
Wendel HG, Silva RL, Malina A et al (2007) Dissecting eIF4E action in tumorigenesis. Genes Dev 21:3232–3237
Bianchini A, Loiarro M, Bielli P et al (2008) Phosphorylation of eIF4E by MNKs supports protein synthesis, cell cycle progression and proliferation in prostate cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 29:2279–2288
Koga K, Todaka T, Morioka M et al (2001) Expression of angiopoietin-2 in human glioma cells and its role for angiogenesis. Cancer Res 61:6248–6254
Shinojima N, Tada K, Shiraishi S et al (2003) Prognostic value of epidermal growth factor receptor in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Res 63:6962–6970
Wang S, Rosenwald IB, Hutzler MJ et al (1999) Expression of the eukaryotic translation initiation factors 4E and 2alpha in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Am J Pathol 155:247–255
Noske A, Lindenberg JL, Darb-Esfahani S et al (2008) Activation of mTOR in a subgroup of ovarian carcinomas: correlation with p-eIF-4E and prognosis. Oncol Rep 20:1409–1417
Rosenwald IB, Lazaris-Karatzas A, Sonenberg N, Schmidt EV (1993) Elevated levels of cyclin D1 protein in response to increased expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Mol Cell Biol 13:7358–7363
Topisirovic I, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Borden KL (2004) Phosphorylation of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E contributes to its transformation and mRNA transport activities. Cancer Res 64:8639–8642
Culjkovic B, Topisirovic I, Skrabanek L, Ruiz-Gutierrez M, Borden KL (2005) eIF4E promotes nuclear export of cyclin D1 mRNAs via an element in the 3’UTR. J Cell Biol 169:245–256
Soni A, Akcakanat A, Singh G et al (2008) eIF4E knockdown decreases breast cancer cell growth without activating Akt signaling. Mol Cancer Ther 7:1782–1788
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research 19591688 (K. Makino). We thank Dr Hermann Gram of Novartis Pharma for providing the CGP57380 inhibitor. We also thank Dr S. Hirata and Dr Y. Nishimura, Department of Immunogenetics, Graduate School of Medical Sciences, Kumamoto University, for technical assistance in cell proliferation and apoptosis assays, and Masayo Obata for technical assistance in the immunohistochemistry studies.
Conflict of interest disclosures
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muta, D., Makino, K., Nakamura, H. et al. Inhibition of eIF4E phosphorylation reduces cell growth and proliferation in primary central nervous system lymphoma cells. J Neurooncol 101, 33–39 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0233-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-010-0233-6